Abstract
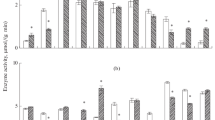
The quantitative release of enterokinase from isolated rat enterocytes following treatment with taurocholate-taurodeoxycholate, papain, chymotrypsin, elastase, carbamylcholine, and cholecystokinin-octapeptide was examined. Alkaline phosphatase and lactate dehydrogenase activities were evaluated simultaneously to check for specificity. Bile salts promoted a concentration-dependent release of all enzymes. Concomitantly, bile salts also led to cell destruction in proportion to the amount of enzymes released. Proteases caused the release of enterokinase and alkaline phosphatase with no concomitant increase of lactate dehydrogenase or cell lysis. At equal concentrations, papain released more enzymes than chymotrypsin and elastase. Chymotrypsin and elastase, however, led to higher ratios of enterokinase to alkaline phosphatase found in the media and suggested a selective release of enterokinase (EK) over that of alkaline phosphatase. Bile salts and pancreatic proteases together seem to have an additive effect of the release of EK. Carbamylcholine and cholecystokinin-octapeptide had no effect on enzyme release. These results suggested that pancreatic proteases are involved in the release of enterokinase by a selective action. Bile salts may also play a role through a nonselective detergent effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kunitz M: Formation of trypsin from crystalline trypsinogen by means of enterokinase. J Gen Physiol 22:429–496, 1939
Nordström C, Dahlqvist A: Rat enterokinase: The effect of ions and the localization in the intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta 242:209–225, 1971
Hadorn B, Steiner N, Sumida C, Peters TJ Intestinal enterokinase. Mechanisms of its “secretion” into the lumen of the small intestine. Lancet 1:165–166, 1971
Nordström C, Dahlqvist A: Localization of human enterokinase. Lancet 2:933–934, 1972
Nordström C: Enzyme release of enteropeptidase from isolated rat duodenal brush borders. Biochim Biophys Acta 268:711–718, 1972
Louvard S, Maroux J, Barratti J, Desnuelle P: On the distribution of enterokinase in porcine intestine and on its subcellular localization. Biochim Biophys Acta 309:127–137, 1973
Götze H, Götze J, Adelson JW: Studies on intestinal enzyme secretion: The action of cholecystokinin-pancreozymin, pentagastrin and bile. Res Exp Med 173:17–25, 1978
Hadorn B, Tarlow MJ, Lloyd JK, Wolff OH: Intestinal enterokinase deficiency. Lancet 1:812–813, 1969
Eggermont E, Molla AM, Tytgat G, Rutgeerts L: Distribution of enterokinase activity in the human intestine. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 34:655–662, 1971
Lebenthal E, Antonowitz I, Schwachman H: The interrelationship of enterokinase and trypsin activity in intractable diarrhea of infancy, celiac disease, and intravenous alimentation. Pediatrics 56:585–591, 1975
Lebenthal E, Lee PC: Effect of pancreozymin and secretin on intraluminal enterokinase, trypsin, and chymotrypsin activities of cystic fibrosis and control children. Digestion 23:39–47, 1982
Nordström C: Release of enteropeptidase and other brush border enzymes from the small intestine wall in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta 289:367–377, 1972
Alpers DH, Tedesco FJ: The possible role of pancreatic proteases in the turnover of intestinal brush border proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 401:28–40, 1975
Rinderknecht H, Nagaraja MR, Adham NF: Effect of bile acids and pH on the release of enteropeptidase in man. Am J Dig Dis 23:332–336, 1978
Goldman RB, Kim YS, Jones RS, Sleisenger MH: The effect of glucagon on enterokinase secretion from Brunner's gland pouches in dog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 138:562–565, 1971
Götze H, Adelson JW, Hadorn HB, Protmann R, Troesch V: Hormone-elicited enzyme release by the small intestinal wall. Gut 13:471–476, 1972
Eloy R, Vaultier JP, Raul F, Mirhom R, Clendinnen G, Grenier JF: Hormonal stimulation of intestinal brush border enzyme release. Res Exp Med 172:109–121, 1978
Moss S, Birch GR, Lobley RW, Holmes R: The release of enterokinase following secretin and cholecystokininpancreozymin in man. Scand J Gastroenterol 14:1001–1007, 1979
Lebenthal E, Morrissey GW: Subcellular localization of enterokinase (enteropeptidase, EC 3.4.21.9) in rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta 497:558–566, 1977
Berger L, Rudolph GC: Alkaline and acid phosphatase.In Standard Methods of Clinical Chemistry, Vol 5. S Meitex (ed). New York, Academic Press, 1965, pp 211–221.
Bernstein LH, Everse J: Determination of the isoenzyme levels of lactate dehydrogenase. Methods Enzymol 41:47–52, 1961
McKay RH, Kaplau NO: The effect of proteolysis and urea treatment of coenzyme binding to beef-heart lactic dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta 52:156–169, 1961
Christophe J, Svoboda M, Calderon-Attas P, Lambert M, Vandermeers-Piret MC, Vandermeers A, Deschodt-Lanckman M, Robberecht P: Gastrointestinal hormone-receptor interactions in the pancreas.In Comprehensive Endocrinology: Gastrointestinal Hormones. L Martini, GBJ Glass (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1980, pp 451–476.
Mutt V: Cholecystokinin: Isolation, structure, and functions.In Comprehensive Endocrinology: Gastrointestinal Hormones. L Martini, GBJ Glass (eds). New York, Raven Press 1980, pp 169–221.
Louvard D, Maroux S, Vannier C, Desnuelle P: Topological studies on the hydrolases bound to the intestinal brush border membrane. 1. Solubilization by papain and Triton X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta 375:236–248, 1975
Maroux S, Louvard D: On the hydrophobic part of aminopeptidase and maltases which bind the enzyme to the intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 419:189–195, 1976
Ugolev AM, DeLaey P, Iezuitova NN, Rakhimov KR, Timofeeva NM, Stepanova AT: Membrane digestion and nutrient assimilation in early development. Ciba Found Symp 70:221–246, 1961
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toyoda, S., Lee, PC. & Lebenthal, E. Physiological factors controlling release of enterokinase from rat enterocytes. Digest Dis Sci 30, 1174–1180 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314053
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314053