Abstract
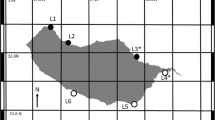
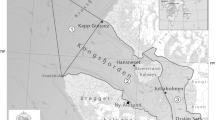
Relationships between community structure and environmental factors were sought through multivariate analysis (quantification analysis and correspondence analysis) of data obtained in a benthic macrofauna survey of a rocky low-tide platform located at Usujiri, southern Hokkaido, Japan. A total of 21 species were found. However, their annual mean abundance was dominated by only a few species. Three dominant species of the platform (Chthamalus challengeri, Littorina brevicula andSeptifer virgatus) accounted for an average of 92% of total abundance. Three environmental factors with associated species groups were examined. Among them, micro-topographic characteristics and wave action defined the main correspondence variables.L. brevicula was a characteristic member of the boulder and sheltered field.S. virgatus was the dominant species of sloped surfaces.C. challengeri, S. virgatus, andMytilus edulis were characteristic of ledge or bench environments. Finally,C. challengeri was characteristic of nip and high wave-exposure environments, given its exclusive appearences in these locations. However, as the degree of exposure depends on the scale of wash through the platform, it is directly limited by the microtopographic properties of low-tide platforms. Specific environmental influences such as exposure and height above the datum-plane were rather disapparent. Any overall effects on the community structure were synthesized by those of microtopography. After complete consideration, it was concluded that the community structure of the macrobenthos in this low-tide platform was found to be primarily under the influence of microtopographic characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Barnes, H., Powell, H. T. (1950). Some observations on the effect of fibrous glass surfaces upon the settlement of certain sedentary marine organisms. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 29: 299–302
Dekker, R. (1989). The macrozoobenthos of the subtidal western Dutch Wadden Sea. 1. Biomass and species richness. Neth. J. Sea Res. 23: 57–68
Hayashi, C. (1950). On the quantification of qualitative data from the mathematico-statistical point of view. Ann. Inst. Statist. Math. 2: 35–47
Jones, W. E., Demetropoulos, A. (1968). Exposure to wave action: measurements of an important ecological parameter on rocky shores on Anglesey. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 2: 46–63
Kohn, A. J. (1983). Microhabitat factors affecting abundance and diversity ofConus on coral reefs. Oecologia 60: 293–301
Lubchenco, J., Menge, B. A., Garrity, S. D., Lubchenco, P. J., Ashkenas, L. R., Gaines, S. D., Emlet, R., Lucas, J., Strauss, S. (1984). Structure, persistence, and role of consumers in a tropical rocky intertidal community (Taboguilla island, Bay of Panama). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 78: 23–73
Ludwing, J. A., Reynolds, J. F. (1988). Statistical ecology. A primer on methods and computing. Wiley, New York
Margalef, R. (1958). Information theory in ecology. General Systematics 3: 36–71
McQuaid, C. D., Branch, G. M. (1984). Influence of sea temperature, substratum and wave exposure on rocky intertidal communities: an analysis of faunal and floral biomass. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 19: 145–151
McQuaid, C.D., Branch, G. M. (1985). Trophic structure of rocky intertidal communities: response to wave action and implications for energy flow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 22: 153–161
Mori, K., Nishihira, S., Tanaka, M. (1985). Community structure of a rocky shore in Tsuji-sima Island, Amakusa. III. The analysis of relationships between distribution of organisms and microtopographical conditions using small quadrat. Publs Amakusa mar. biol. Lab. 8: 43–63
Pielou, E. C. (1969). An introduction to mathematical ecology. Wiley, New York
Pielou, E. C. (1984). The interpretation of ecological data. A primer on classification and ordination. Wiley, New York
Raffaelli, D. G., Hughes, R. N. (1978). The effects of crevice size and availability on populations ofLittorina rudis andLittorina neritoides. J. Anim. Ecol. 47: 71–83
Reichelt, R. E. (1982). Space: a non-limiting resource in the niches of some abundant coral reef gastropods. Coral Reefs 1: 3–11
Snedecor, G. W., Cochran, W. G. (1973). Statistical methods. Iowa State Univ. Press, Iowa
Spight, T. M. (1976). Censuses of rocky shore presobranchs from Washington and Costa Rica. Veliger 18: 309–317
Stephenson, T. A., Stephenson, A. (1949). The universal features of zonation between tidal-marks on rocky coasts. J. Ecol. 37: 289–305
Tanaka, M., Mori, K., Nojima, S., Kikuchi, T., Shibata, T., Nishino, T., Omori, K. (1985). Community structure of a rocky shore in Tsuji-sima Island, Amakusa. I. Horizontal and vertical distribution pattern of common animals. Publs Amakusa mar. biol. Lab. 8: 1–26
Tanaka, Y., Wakimoto, K. (1983). Methods of multivariate statistical analysis. Gendai Suugaku sha, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Tsuchiya, M. (1979). Quantitative survey of intertidal organisms on rocky shores in Mutsu Bay, with special reference to the influence of wave action. Bull. mar. biol. St Asamushi 16: 69–86
Underwood, A. J. (1981). Structure of a rocky intertidal community in New South Wales: patterns of vertical distribution and seasonal change. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 51: 57–85
Vermeij, G. J. (1971). Substratum relationships of some tropical Pacific intertidal gastropods. Mar. Biol. 10: 315–320
Witman, J. D. (1985). Refuges, biological disturbance, and rocky subtidal community structure in New England. Ecol. Monogr. 55: 421–445
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Tokyo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuji, A., Nomura, H. Community structure of the rocky shore macrobenthos in southern Hokkaido, Japan. Mar. Biol. 107, 471–477 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01313431
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01313431