Summary
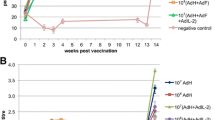
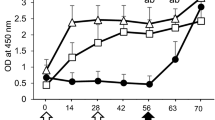
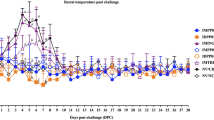
Pigs vaccinated twice intramuscularly with a highly attenuated strain of vaccinia virus (NYVAC) containing gene inserts for pseudorabies virus (PRV) glycoproteins gp50, gII, and gIII produced neutralizing antibodies for PRV and were less clinically affected than were nonvaccinated pigs following oronasal exposure to virulent PRV. Also, following oronasal exposure to virulent PRV the duration of virulent virus shedding by pigs that had been vaccinated intramuscularly with the recombinant virus was statistically less (p<0.05) than that of nonvaccinated pigs and like that of pigs vaccinated twice intramuscularly with inactivated PR vaccine. Intramuscular vaccination with the recombinant virus was compatible with the most commonly used differential diagnostic tests, namely those based on PRV glycoproteins gX and gI. Serum antibodies for these glycoproteins were absent from the sera of all pigs before and after vaccination with recombinant virus; whereas, they were present in the sera of all of the same pigs after they were exposed to virulent PRV. In contrast to the effectiveness of the recombinant virus administered intramuscularly, neither serum antibody nor clinical protection against PRV was detected when aliquots of the same recombinant virus preparation were administered either orally or intranasally. The latter finding suggests that recombinant virus replicates poorly, if at all, at these sites. If so, the dissemination of recombinant virus from vaccinated pigs to nonvaccinated pigs or other animals in contact seems unlikely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mettenleiter TC (1991) Molecular biology of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 14: 151–163
Wittmann G, Rziha HJ (1989) Aujeszky's disease (pseudorabies) in pigs. In: Wittmann G (ed) Herpesvirus diseases of cattle, horses, and pigs. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 230–325
Pensaert MB, Kluge JP (1989) Pseudorabies virus (Aujeszky's disease). In: Pensaert MB (ed) Virus infections of porcines. Elsevier Scientific Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 39–64
Kluge JP, Beran GW, Hill HT, Platt KB (1992) Pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease). In: Leman AD, Straw B, Mengeling WL, D'Allaire S, Taylor DJ (eds) Diseases of swine, 7th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 312–323
Wittmann G (1991) Spread and control of Aujeszky's disease (AD). Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 14: 165–173
Vandeputte J, Chappuis G, Fargeaud D, Precausta P, Guillemin F, Brun A, Desmettre Ph, Stellmann C (1990) Vaccination against pseudorabies with glycoprotein gI+ or glycoprotein gI− vaccine. Am J Vet Res 51: 1100–1106
Van Oirschot JT, De Waal CAH (1987) An ELISA to distinguish between Aujeszky's disease vaccinated and infected pigs. Vet Rec 121: 305–306
Wardley RC, Post LE (1989) The use of gX deleted vaccine PRV TK gX-1 in the control of Aujeszky's disease. In: Van Oirschot JT (ed) Vaccination and control of Aujeszky's disease. Kluwer, Dordrecht Brussel, pp 13–25
Mengeling WL, Lager KM, Brockmeier SL (1992) Effect of various vaccination procedures on shedding, latency, and reactivation of attenuated and virulent pseudorabies virus in swine. Am J Vet Res 53: 2164–2173
Tartaglia J, Perkus ME, Taylor J, Norton EK, Audonnet JC, Cox WI, Davis SW, van der Hoeven J, Meignier B, Riviere M, Languet B, Paoletti E (1992) NYVAC: A highly attenuated strain of vaccinia virus. Virology 188: 217–232
Brockmeier SL, Lager KM, J Tartaglia J, Riviere M, Paoletti E, Mengeling WL (1993) Vaccination of pigs against pseudorabies with highly attenuated vaccinia (NYVAC) recombinant viruses. Vet Microbiol 38: 41–58
Mengeling WL (1991) Virus reactivation in pigs latently infected with a thymidine kinase-negative vaccine strain of pseudorabies virus. Arch Virol 120: 57–70
Mengeling WL, Van Der Maeten MJ (1988) Preparation of bovine Embryonic spleen cell cultures. J Tissue Cult Methods 11: 135–138
Marchioli CC, Yancy Jr RV, Wardley RC, Thomsen DR, Post LE (1987) A vaccine strain of pseudorabies virus with deletions in the thymidine kinase and glycoprotein X genes. Am J Vet Res 48: 1577–1583
Riviere M, Tartaglia J, Perkus ME, Norton EK, Bongermino CM, Lacoste F, Duret C, Desmettre P, Paoletti (1992) Protection of mice and swine from pseudorabies virus conferred by vaccinia virus-based recombinants. J Virol 66: 3424–3434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mengeling, W.L., Brockmeier, S.L. & Lager, K.M. Evaluation of a recombinant vaccinia virus containing pseudorabies (PR) virus glycoprotein genes gp50, gII, and gIII as a PR vaccine for pigs. Archives of Virology 134, 259–269 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01310565
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01310565