Summary
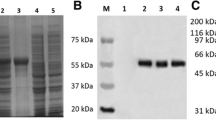
Adult diarrhea rotavirus (ADRV) has caused epidemics of diarrhea in China since 1982 and remains the only group B rotavirus associated with widespread disease in humans. We recently characterized the proteins of ADRV and have now proceeded to identify the gene segments encoding each protein. Viral RNA transcripts were synthesized in vitro with the endogenous viral RNA polymerase and separated by electrophoresis in agarose. The individual transcripts were translated in a cell-free system using nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates. The translation products were compared with polypeptides found in purified virus and were characterized by SDS-PAGE, immunoprecipitation, and Western blot analysis using antisera to double- and single-shelled virions, virus cores, and monoclonal antibodies. Furthermore, individual RNA transcripts were hybridized to total dsRNA to determine their genomic origin. Based on this analysis, the core polypeptides VP1, VP2 and VP3 are encoded by segments 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The main polypeptides in the inner capsid, VP6, and the outer capsid, VP4 and VP7, are encoded by segments 6, 4, and 8 respectively. Segments 5, 7, and 9 code for 60, 45, and 30 kDa nonstructural polypeptides. Two other nonstructural polypeptides (24 and 25 kDa) are derived from gene segment 11. Gene segment 10 codes for a 26 kDa polypeptide that is precipitated with serum to ADRV and may be a structural protein VP9. With this exception, gene coding assignments of ADRV are comparable to those of the group A rotaviruses. Our results have clear implications for further work in cloning, sequencing, and expression genes of ADRV and can provide direction towards understanding the origin and the evolution of this virus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pedley S, Bridger JC, Brown JF, McCrae MA (1983) Molecular characterization of rotavirus with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol 64: 2093–2101
Pedley S, Bridger JC, Chasey D, McCrae MA (1986) Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol 67: 131–137
Bridger JC (1987) Novel rotaviruses in animals and man. Ciba Found Symp 128: 5–23
Chasey D, Banks J (1984) The commonest rotaviruses from neonatal lamb diarrhoea in England and Wales have atypical electropherotypes. Vet Rec 115: 326–327
Snodgrass DR, Herring AJ, Campbell I, Inglis JM, Hargreaves FD (1984) Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs, and man. J Virol 65: 909–914
Vonderfecht SL, Huber AC, Eiden JJ, Mader LC, Yolken RH (1984) Infectious diarrhea of infant rats produced by a rotavirus-like agent. J Virol 52: 94–98
Vonderfecht SL, Eiden JJ, Torres A, Miskuff R, Mebuys CA, Yolken RH (1986) Identification of a bovine enteric syncytial virus as a non-group A rotavirus. Am J Vet Res 47: 1913–1918
Hung T, Chen G, Wang C (1984) Waterbourne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet i: 1139–1142
Hung T (1988) Rotavirus and adult diarrhea. Adv Virus Res 35: 193–218
Fang ZY, Ye Y, Ho M-S, Dong H, Qing S, Penaranda M, Hung T, Wen L, Glass RI (1989) Investigation of an outbreak of adult diarrhea rotavirus in China. J Infect Dis 160: 948–953
Penaranda ME, Ho M-S, Fang ZY, Dong H, Bai XS, Duan SC, Ye WW, Estes MK, Echeverria P, Hung T, Glass RI (1989) Seroepidemiology of adult diarrhea rotavirus in China. J Clin Microbiol 27: 2180–2183
Fang ZY, Glass RI, Penaranda ME, Dong H, Monroe SS, Wen L, Estes MK, Eiden J, Yolken RH, Saif L, Gouvea V, Hung T (1989) Purification and characterization of adult diarrhea rotavirus: identification of viral structural proteins. J Virol 63: 2191–2197
Chen G-M, Hung T, Mackow ER (1990) cDNA cloning of each genomic segment of the Group B rotavirus ADRV: molecular characterization of the 11th RNA segment. Virology 175: 605–609
Chen G-M, Hung T, Mackow ER (1990) Identification of the gene encoding and group B rotavirus VP7 equivalent: primary characterization of the ADRV segment 9 RNA. Virology 178: 311–315
Chen G-M, Werner-Eckert R, Tao H, Mackow ER (1991) Expression of the major inner capsid protein of the group B rotavirus ADRV: primary characterization of genome segment 5. Virology 182: 620–629
Eiden JJ, Allen JR (1992) Identification of cognate genes among heterologous strains of group B rotavirus. J Virol 66: 1232–1235
Mason BB, Graham DY, Estes MK (1980) In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol 33: 1111–1112
Fraenkel-Conrat H, Singer HB, Tsugita A (1961) Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology 14: 54–58
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Smith ML, Lazdins I, Holmes IH (1980) Coding assignments of double-stranded RNA segments of SA11 rotavirus established by in vitro translation. J Virol 33: 976–982
Tanaka TN, Conner ME, Graham DY, Estes MK (1988) Molecular characterization of three rabbit rotavirus strains. Arch Virol 98: 253–265
Coffin JM, Billeter MA (1976) A physical map of the Rous Sarcoma virus genome. J Mol Biol 100: 293–318
Flores J, Green KY, Garcia D, Sears J, Perez-Schael I, Avendano LF, Rodriguez WB, Taniguchi K, Urasawa S, Kapikian AZ (1989) Dot hybridization assay for detection of rotavirus serotypes. J Clin Microbiol 27: 29–34
Mason BB, Graham DY, Estes MK (1983) Biochemical mapping of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome. J Virol 46: 413–423
McCrae MA, McCorquodale JG (1982) Molecular biology of rotavirus. II. Identification of the protein-coding assignments of calf rotavirus genome RNA species. Virology 117: 435–443
Shatkin AJ, Kozak M (1983) Biochemical aspects of reovirus transcription and translation. In: Joklik WK (ed) The Reoviridae. Plenum, New York, pp 79–106
Both GW, Lavi S, Shatkin AJ (1975) Synthesis of all gene products of the reovirus genome in vivo and in vitro. Cell 4: 173–180
Dyall-Smith ML, Holmes IH (1981) Gene-coding assignments of rotavirus double-stranded RNA segments 10 and 11. J Virol 38: 1099–1103
Liu M, Offit PA, Estes MK (1988) Identification of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome segment 3 product. Virology 163: 26–32
Welch S-KW, Crawford SE, Estes MK (1989) The rotavirus SA11 genome segment 11 protein is a nonstructural phosphoprotein. J Virol 63: 3874–3982
Estes MK, Cohen J (1989) Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev 53: 410–419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Z.Y., Monroe, S.S., Dong, H. et al. Coding assignments of the genome of adult diarrhea rotavirus. Archives of Virology 125, 53–69 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01309628
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01309628