Abstract
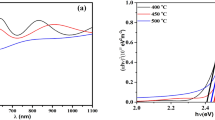
Thermally induced optical bistability of thin CdS platelets is shown to be a highly suitable model case for the study of interactions between absorptive and dispersive switching mechanisms. Beyond previous studies concerning this type of bistability, systematic investigations were necessary to obtain a set of optimization criteria concerning a desired hysteresis feature. Despite the fact that thermally induced bistability of CdS may exhibit too long switching times for application in optoelectronics, it is a valuable system for the investigation of general features of bistable processes in a very detailed manner and for the development of reliable quantitative models. The appearance of different forms of thermally induced optical bistability in CdS is discussed in dependence of switching power, temperature, shallow-impurity concentration, and of system as well as of sample configuration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klingshirn, C., Wegener, M., Dörnfeld, C., Lambsdorff, M., Bigot, J.Y., Fidorra, F.: Optical bistability III. Proceedings of the Topical Meeting on Optical Bistability. Tucson (Arizona, USA) 1985. In: Springer Proceedings in Physics. Gibbs, H.M., Mandel, P., Peyghambarian, N., Smith, S.D. (eds.), Vol. 8, p. 129. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1986
Lambsdorff, M., Dörnfeld, C., Klingshirn, C.: Z. Phys. B — Condensed Matter64, 409 (1986)
Haddad, I., Kretzschmar, M., Rossmann, H., Henneberger, F.: Phys. Status Solidi B138, 235 (1986)
Henneberger, F., Puls, J., Rossmann, H., Spiegelberg, Ch., Kretzschmar, M., Haddad, I.: Phys. Scri. T13, 195 (1986)
Wegener, M., Klingshirn, C.: Phys. Rev. A35, 1740 (1987)
Wegener, M., Klingshirn, C.: Phys. Rev. A35, 4247 (1987)
Bigot, J.-Y., Daunois, A., Cherkaoui Eddeqaqi, N., Oberle, J., Wegener, M., Klingshirn, C.: International Conference on ‘Optical Bistabillity’ IV, Aussois (France) 1988, J. Phys. (Paris)49 Colloq. C2, 153 (1988)
Wegener, M., Witt, A., Klingshirn, C., Gnass, D., Iyechika, Y., Jäger, D.: International Conference on ‘Optical Bistability’ IV, Aussois (France) 1988, J. Phys. (Paris)49 Colloq. C2, 109 (1988)
Dneprovskii, V.S., Furtichev, A.I., Klimov, V.I., Nazvanova, E.V., Okorokov, D.K., Vandihev, U.V.: Phys. Status Solidi B146, 341 (1988)
Gutowski, J., Hönig, T., Hollandt, J., Broser, I.: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on the Physics of Semiconductors, Warsaw (Poland) 1988. Zawadzki, W. (ed.), p. 1311. Inst. of Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences (1988)
Miller, D.A.B.: J. Opt. Soc. Am. B1, 857 (1984)
Hajto, J., Janossy, I.: Philos. Mag. B47, 347 (1983)
Eichler, H.J.: Laser Optoelektron.1, 59 (1988)
Witt, A., Wegener, M., Lyssenko, V.G., Klingshirn, C., Wingen, G., Iyechika, Y., Jäger, D., Müller-Vogt, G., Sitter, H., Heinrich, H., Mackenzie, H.A.: IEEE J. Quant. Electron.24, 2500 (1988)
Wegener, M.: PhD thesis, Frankfurt (FRG) 1987
Hoang Xuan Nguyen, Zimmermann, R.: Phys. Status Solidi B124, 191 (1984)
Henneberger, F.: Phys. Status Solidi B137, 371 (1986)
Fidorra, F., Wegener, M., Bigot, J.Y., Hönerlage, B., Klingshirn, C.: J. Luminescence35, 43 (1986)
Urbach, F.: Phys. Rev.92, 1324 (1953)
Martienssen, W.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids2, 257 (1958)
Dutton, D.: Phys. Rev.112, 785 (1958)
Kurik, M.: Phys. Status Solidi A8, 9 (1971)
Spiegelberg, S., Gutsche, E., Voigt, J.: Phys. Status Solidi B77, 233 (1976)
Gobrecht, H., Bartschat, A.: z. Phys.156, 131 (1959)
Langer, D.W.: J. Appl. Phys.37, 3530 (1966)
Unger, K., Schneider, H.G.: Verbindungshalbleiter. Leipzig: p. 144. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft Geest und Portig K.-G.
Kretzschmar, M., Henneberger, F., Rossmann, H., Haddad, I.: Phys. Status Solidi B143, K71 (1987)
Broser, I., Broser, R., Beckmann, E., Birkicht, E.: Solid State Commun.39, 1209 (1981)
Brodin, M.S., Vitrikhovskii, N.I., Kurik, M.V.: Phys. Status Solidi B10, 525 (1965)
Vitrikhovskii, N.I., Gnatenko, Yu.P., Kurik, M.V.: Ukr. Fiz. Zh.15, 842 (1970)
Lisitsa, M.P., Valakh, M.Ya., Terekhova, S.F.: Fiz. Tverd. Tela8, 305 (1966) (Sov. Phys.-Solid State8, 251 (1966))
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutowski, J., Hollandt, J. & Broser, I. Thin CdS platelets — a model case for the study and optimization of thermally induced absorptive and dispersive optical bistability. Z. Physik B - Condensed Matter 76, 547–557 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307906
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307906