Summary
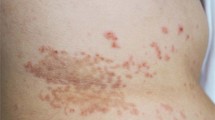
A patient who developed lichen planus while receiving chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for gallstones is described. Skin biopsy was performed and histological examination suggested a drug etiology. An association between lichen planus and liver disease is recognized, but this patient exhibited no clinical or biochemical evidence of liver disease and the rash disappeared after cessation of the bile acid therapy. Bile acids may cause lichen planus. The mechanism is unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeyda J, Levantine A: Lichenoid drug eruptions. Br J Dermatol 85:604–607, 1971
Black MM: Lichen planus and lichenoid eruptions.In Textbook of Dermatology. A Rook, DS Wilkinson, DJG Felding (eds). London, Blackwell, 1986, pp 1678–1679
Penneys NS, Ackerman B, Gottlieb NL: Gold dermatitis: A clinical and histopathological study. Arch Dermatol 109:372–376, 1974
Dowling RH: Chenodeoxycholic acid therapy of gallstones, Progress Report. A Hoffman and G Paumgartner (eds). Progress Report 1975. Stuttgart, Surataner Verlaj, 1975, pp 64–65
Herndon JH: Pathophysiology of pruritus associated with elevated bile acids in serum. Arch Intern Med 130:632–637, 1972
Sobotka H: Physiological Chemistry of the Bile. Bailliere Tindall and Cox, London, 1937, p 137
Bartholomew TC, Summerfield JA, Billing BH, Lawson AM, Setchell UDR: Bile acid profiles of human serum and serum interstitial fluid and their relationship to pruritus studied by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Clin Sci 63:65–73, 1982
Carey JB Jr, Williams G: Lowering of serum bile acid concentrations and relief of pruritus in jaundiced patients fed bile acid sequestering resin. J Lab Clin Med. 56:797–798, 1960
Cerio R, Murphy GM, Sladen GE, and Macdonald DM: A combination of phototherapy and cholestyramine for the relief of pruritus in primary biliary cirrhosis. Br J Dermatol 116:265–267, 1987
Wolf R, Kahane E: Atopic dermatitis-like eruption with elevated IgE levels possibly due to chenodeoxycholic acid. Cutis 40:373–374, 1987
Epstein D: Lichen planus and liver disease. Br J Dermatol 111:473–475, 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellul, J.P.M., Groves, R., Walters, J.R.F. et al. Lichen planus associated with chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid for gallstone dissolution. Digest Dis Sci 37, 628–630 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307592
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307592