Abstract
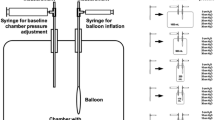
The effects of nifedipine (20 mg orally) on esophageal body resting tone and perception of esophageal distension were compared with those of placebo in 10 healthy volunteers, using a double-blind crossover design. A 3-cm silicon balloon positioned 10 cm above the lower esophageal sphincter was inflated with 2–20 ml of air, in 2-ml increments. The subjects scored their chest sensations, while pressure in the balloon was continuously recorded. In each experiment three series of measurements were made, at baseline and 15 and 30 min after administration of nifedipine or placebo. Bench tests were run to determine pressure-to-volume relationships for each of the balloons used in the study. Thirty minutes after nifedipine ingestion, a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure (from 112.6±2.3 to 99.0±2.0 mm Hg) was observed. Amplitude and duration of esophageal peristaltic contractions were significantly decreased by nifedipine (from 128.1±16.7 to 98.7±10.6 mm Hg and from 3.9±0.3 to 3.3±0.2 sec, respectively). With balloon volumes of 8 ml and higher, balloon pressures were higher with the balloon in the esophagus than on the bench, the difference being determined by the compliance of the esophagus. This difference rose from 18.5±6.8 to 40.2±7.2 mm Hg (8–20 ml) with placebo and from 23.1±3.7 to 35.9±5.8 mm Hg with nifedipine. No significant differences between nifedipine and placebo were found. The esophageal sensation scores increased linearly with increasing balloon volume from 6 ml onwards. Nifedipine had no significant effect on the perception of esophageal balloon distension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richter JE, Dalton CB, Buice RG, Castell DO: Nifedipine: A potent inhibitor of contractions in the body of the human esophagus. Gastroenterology 89:549–554, 1985
Richter JE, Spurling TJ, Cordova CM, Castell DO: Effects of oral calcium blocker, diltiazem, on esophageal contractions. Studies in volunteers and patients with nutcracker esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 29:649–656, 1984
Richter JE, Dalton CB, Bradley LA, Castell DO: Oral nifedipine in the treatment of noncardiac chest pain in patients with the nutcracker esophagus. Gastroenterology 93:21–28, 1987
Anderson KE: Calcium channel blockers and motility disorders of the esophagus. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 58 (suppl 2): 201–204, 1986
Hongo M, Traube M, McAllister RG, McCallum RW: Effects of nifedipine on esophageal motor function in humans: Correlation with plasma nifedipine concentration. Gastroenterology 86:8–12, 1984
Traube M, Dubovik S, Lange RS, McCallum RW: The role of nifedipine therapy in achalasia: results of a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol 84:1259–1262, 1989
Blackwell JN, Holt S, Heading RC: Effect of nifedipine on esophageal motility and gastric emptying. Digestion 21:50–56, 1981
Weiser FF, Lepsein G, Golenhofen K, Siewert R: Clinical and experimental studies on the effect of nifedipine on smooth muscle of the esophagus and LES.In Gastrointestinal Motility in Health and Disease. HL Duthie (ed). Lancaster, MTP Press, 1978, pp 565–572
Grbovic L, Radmonovic BZ: Effect of nifedipine on the contractile responses of the longitudinal and circular muscles of the guinea pig ileum to various agonists. Arch Int Pharmacodynam Ther 289:165–176, 1987
Richter JE, Barish CF, Castell DO: Abnormal sensory perception in patients with esophageal chest pain. Gastroenterology 91:845–852, 1986
Barish CF, Castell DO,Richter JE: Graded esophageal balloon distension. A new provocative test for noncardiac chest pain. Dig Dis Sci 31:1292–1298, 1986
Mitra R, Chura C, Rajendra GR, Schuster MM: Effect of progressive rectal distension in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 66:770–779, 1974
Golenhofen K: Differentiation of calcium activation processes in smooth muscle using selective agonists.In Smooth Muscle: An Assessment of Current Knowledge. E Bulbring, AW Jones, T Tomita (eds) London, Edward Arnold, 1981, pp 157–170
Karaki H, Weiss GE: Calcium channels in smooth muscle. Gastroenterology 87:960–970, 1984
Goyal RK, Rattan S: Effects of sodium nitroprusside and verapamil on lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol 238:G40-G44, 1980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smout, A.J.P.M., Devore, M.S., Dalton, C.B. et al. Effects of nifedipine on esophageal tone and perception of esophageal distension. Digest Dis Sci 37, 598–602 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307586
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01307586