Summary
In this paper theory and analysis of shells undergoing finite elastic and finite plastic strains and rotations are presented. The shell kinematics are based on a relaxed normality hypothesis allowing transverse normal material fibers to be stretched and bended, whereas shear deformations are neglected. Lagrangean logarithmic membrane and logarithmic bending strain measures are introduced, and it is shown that they can be additively decomposed into purely elastic and purely plastic parts for superposed moderately large strains and unrestricted rotations. The logarithmic strain measures are used to formulate thermodynamic-based constitutive equations for isotropic elastic and plastic material behavior with isotropic and kinematic hardening induced by continuous plastic flow. To analyse path-dependent elastic-plastic shell deformations by iterative procedures the application of logarithmic strain measures allows to realize load steps with corresponding moderate strains and unrestricted rotations. The moderate strain restriction for superposed deformations can be assured by an appropriate update procedure. Formulae are given to determine exactly the rotational change of the reference configuration during the update. Finally, the principle of virtual work with corresponding elastic-plastic material tensor is formulated and it is shown that the weak form of the virtual work leads to the Lagrangean equilibrium equations and boundary conditions well-known from the nonlinear theory of elastic shells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F :
-
deformation gradient
- U :
-
right Cauchy-Green stretch tensor
- R :
-
rotation tensor
- E :
-
Green strain tensor
- e :
-
Almansi strain tensor
- H :
-
Lagrangean logarithmic strain tensor
- τ:
-
Kirchhoff stress tensor in the 3-D continuum
- σ:
-
Cauchy stress tensor
- ()e :
-
reference to an elastic deformation
- ()p :
-
reference to a plastic deformation
- (−), (+):
-
reference to a first and a second superposed deformation, respectively
- (*):
-
reference to an alternative decomposition of the superposed deformation
- AB :
-
composition of the two tensorsA andB
- A T :
-
transposed ofA
- A 2 :
-
square ofA
- A −1 :
-
inverse ofA
- u :
-
displacement field of the shell space
- v :
-
displacement field of the middle surface
- h,\(\bar h\) :
-
shell thickness in the initial and the current state
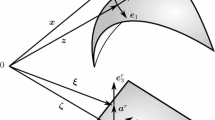
- ξ:
-
thickness coordinate,\( - \frac{h}{2} \leqq \zeta \leqq \frac{h}{2}\)
- g i ,g i :
-
base vectors in the undeformed shell space,i∈{1, 2, 3}
- \(\bar g_i ,\bar g^i \) :
-
base vectors in the deformed shell space
- a α,a α :
-
surface base vectors on the undeformed middle surface ξ=0, α∈{1, 2}
- āα, āα :
-
surface base vectors on the deformed reference surface ξ=0
- n,\(\bar n\) :
-
unit normal vector on the surface ξ=0 in the initial and the deformed configuration, respectively
- b,\(\bar b\) :
-
curvature tensor of the surface ξ=0 in the initial and current state
- γ:
-
Green membrane strain tensor
- χ:
-
Green bending strain tensor
- π:
-
Green second order strain tensor
- g :
-
logarithmic membrane strain tensor
- k :
-
logarithmic bending strain tensor
- p :
-
logarithmic second order strain tensor
- T :
-
plane Kirchhoff stress tensor
- N :
-
stress resultant tensor
- ℓ:
-
stress couple tensor
- ℒ:
-
second order stress resultant tensor
References
Naghdi, P. M.: The theory of shells and plates. In: Handbuch der Physik, vol. VIa/2 (Flügge, S., ed.), pp. 425–640. Wien New York: Springer 1972.
Pietraszkiewicz, W., Szwabowicz, M. L.: Entirely Lagrangean nonlinear theory of thin shells. Arch. Mech.33, 273–288 (1981).
Nolte, L.-P.: Beitrag zur Herleitung und vergleichende Untersuchung geometrisch nichtlinearer Schalentheorien unter Berücksichtigung großer Rotationen. Mitt. Inst. f. Mech.39, Ruhr-Universität Bochum 1983.
Schmidt, R., Stumpf, H.: On the stability and post-buckling of thin elastic shells with unrestricted rotations. Mech. Res. Comm.11, 105–114 (1984).
Pietraszkiewicz, W.: Lagrangean description and incremental formulation in the non-linear theory of thin shells. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech.19, 115–140 (1984).
Pietraszkiewicz, W.: Geometrically nonlinear theories of thin elastic shells. Adv. Mech.12, 51–130 (1989).
Stumpf, H.: General concept of the analysis of thin elastic shells. ZAMM64, 337–350 (1986).
Nolte, L.-P., Makowski, J., Stumpf, H.: On the derivation and comparative analysis of large rotation shell theories. Ing.-Arch.56, 145–160 (1986).
Valid, R.: Finite rotations, variational principles and buckling in shell theory. In: Finite rotations in structural mechanics (Pietraszkiewicz, W., ed.), pp. 317–332. Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo: Springer 1986.
Başar, Y., Krätzig, W.: A consistent shell theory for finite deformation. Acta Mech.76, 73–87 (1986).
Stumpf, H., Makowski, J.: On large strain deformation of shells. Acta Mech.45, 153–168 (1986).
Gruttmann, F., Stein, E., Wriggers, P.: Theory and numerics of thin elastic shells with finite rotations. Ing. Arch.59, 54–67 (1989).
Başar, Y., Ding, Y.: Finite rotation elements for the non-linear analysis of thin shell structures. Int. J. Solids Struct.26, 83–87 (1990).
Simo, J. C., Rifai, M. S., Fox, D. D.: On a stress resultant geometrically exact shell model. Part IV: Variable thickness shells with through-the-thickness stretching. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.81, 91–126 (1990).
Schieck, B., Pietraszkiewicz, W., Stumpf, H.: Theory and numerical analysis of shells undergoing large elastic strains. Int. J. Solids Struct.29, 689–709 (1992).
Taber, L. A.: Large elastic deformation of shear deformable shells of revolution: theory and analysis. ASME J. Appl. Mech.54, 578–584 (1987).
Makowski, J., Stumpf, H.: Finite axisymmetric deformation of shells of revolution with application to flexural buckling of circular plates. Ing.-Arch.39, 456–472 (1989).
Makowski, J., Stumpf, H.: Buckling equations of elastic shells with rotational degrees of freedom undergoing finite strain deformation. Int. J. Solids Struct.26, 353–368 (1990).
Chroscielewski, J., Makowski, J., Stumpf, H.: Genuinely resultant shell finite elements accounting for geometric and material non-linearity. Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng.35, 63–94 (1992).
Green, A. E., Naghdi, P. M.: Theory of an elastic-plastic Cosserat surface. Int. J. Solids Struct.4, 907–927 (1968).
Simo, J. C., Kennedy, J. G.: On a stress resultant geometrically exact shell model. Part V. Nonlinear plasticity: formulation and integration algorithms. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.96, 133–171 (1992).
Stumpf, H.: Shakedown of structures undergoing large elastic-plastic deformation. In: Anisotropy and localization of plastic deformation. Proc. Plasticity '91, Third Int. Symp. Plasticity and its Current Applications. (Boehler, J.-P., Khan, A., eds.), pp. 668–671 Amsterdam: Elsevier 1991.
Stumpf, H.: Theoretical and computational aspects in the shakedown analysis of finite elastoplasticity. Int. J. Plasticity9, 583–602 (1993).
Schmidt, R., Weichert, D.: A refined theory of elastic-plastic shells at moderate rotations. ZAMM69, 11–21 (1989).
Başar, Y., Weichert, D.: A finite-rotation theory for elastic-plastic shells under consideration of shear deformations. ZAMM71, 379–389 (1991).
Eckart, C.: The thermodynamics of irreversible processes. 4. The theory of elasticity and inelasticity. Phys. Rev.73, 373–382 (1948).
Sedov, L. I.: Foundations of the non-linear mechanics of continua. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1966.
Lee, E. H., Liu, D. T.: Finite strain elastic-plastic theory with application to plane-wave analysis. J. Appl. Phys.38, 19–27 (1967).
Lee, E. H.: Elasto-plastic deformation at finite strains. J. Appl. Mech.36, 1–6 (1969).
Simo, J. C.: A framework for finite strain elastoplasticity based on maximum plastic dissipation and the multiplicative decomposition: Part I. Continuum formulation. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.66, 199–219 (1988).
Le, K. Ch., Stumpf, H.: Constitutive equations for elastoplastic bodies at finite strain: Thermodynamic implementation. Acta Mech.100, 155–170 (1993).
Stumpf, H., Badur, J.: On missing links of rate-independent elasto-plasticity at finite strains. Mech. Res. Comm.17, 353–364 (1990).
Weber, G., Anand, L.: Finite deformation constitutive equations and a time integration procedure for isotropic, hyperelastic-viscoplastic solids. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng.79, 173–202 (1990).
Etorovic, A. L., Bathe, K. J.: A hyperelastic-based large strain elasto-plastic constitutive formulation with combined isotropic-kinematic hardening using the logarithmic stress and strain measures. Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng.30, 1099–1114 (1990).
Schieck, B., Stumpf, H.: Deformation analysis for finite elastic-plastic strains in a Lagrangean type description. Int. J. Solids Struct.30, 2639–2660 (1993).
Nemat-Nasser, S.: Phenomenological theories of elastoplasticity and strain localization at high strain rates. Appl. Mech. Rev.45/3, 19–45 (1992).
Ogden, R. W.: On Eulerian and Lagrangean objectivity in continuum mechanics. Arch. Mech.36, 207–218 (1984).
Anand, L.: On Hencky's approximate strain-energy function for moderate deformations. ASME J. Appl. Mech.46, 78–82 (1979).
Anand, L.: Moderate deformations in extension-torsion of incompressible isotropic elastic materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids34, 293–304 (1986).
Schieck, B.: Große elastische Dehnungen in Schalen aus hyperelastischen, inkompressiblen Materialien. Mitt. Inst. f. Mech.69, Ruhr-Universität Bochum 1989.
Schieck, B., Stumpf, H.: The appropriate corotational rate, the exact formula of the plastic spin and constitutive model for finite elastoplasticity (submitted).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stumpf, H., Schieck, B. Theory and analysis of shells undergoing finite elastic-plastic strains and rotations. Acta Mechanica 106, 1–21 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300941
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300941