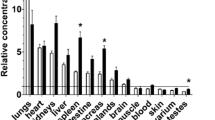
Abstract
Glutamine synthetase is responsible for the ATP-dependent amidation of glutamate to glutamine. In liver the enzyme is highly localized in perivenous hepatocytes; in brain the enzyme is localized in astrocytes. Portacaval anastomosis resulted in liver atrophy, hyperammonemia, and up to 90% loss of glutamine synthetase activity in liver homogenates. This effect, which appears to be irreversible, probably reflects the selective loss of perivenous hepatocytes following portacaval anastomosis. Glutamine synthetase activities in brain were unaffected by portacaval anastomosis of up to 12 weeks' duration. Enzyme activities in homogenates of skeletal muscle, on the other hand, were significantly increased at one and four weeks after shunt surgery. These effects were not the result of decreased food intake in shunted animals. These findings suggest fundamentally different regulatory mechanisms for glutamine synthetase in these tissues. Skeletal muscle may thus provide an important alternative site for ammonia detoxification after portal-systemic shunting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haussinger D, Gerok W: Hepatocyte heterogeneity in ammonia metabolism: impairment of glutamine synthesis in CCl4-induced liver cell necrosis with no effect on urea synthesis. Chem Biol Interact 48:191–194, 1984
Butterworth RF, Giguère JF, Michaud J, Lavoie J, Pomier Layrargues G: Ammonia: Key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Pathol 6:1–12, 1987
Lockwood AH, McDonald JM, Reiman RE, Gelbard AS, Laughlin JS, Duffy TE, Plum F: The dynamics of ammonia metabolism in man. Effects of liver disease and hyperammonemia. J Clin Invest 63:449–460, 1979
Hourani BT, Hamlin EM, Reynolds TB: Cerebrospinal fluid glutamine as a measure of hepatic encephalopathy. Arch Intern Med 127:1033–1036, 1971
Oei LT, Kuys J, Lombarts AJP: Cerebrospinal fluid glutamine levels and EEG findings in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 81:59–63, 1979
Ganda OP, Ruderman NB: Muscle nitrogen metabolism in chronic hepatic insufficiency. Metabolism 25:427–435, 1976
Butterworth RF, Girard G, Giguère JF: Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portacaval anastomosis. J Neurochem 51:486–490, 1988
Lee SH, Fisher B: Portacaval shunt in the rat. Surgery 50:668–672, 1961
Kun E, Kearney EB: Ammonia.In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. HV Berkmeyer (ed). New York, Academic Press, 1974, pp 1802–1806
Hindfelt B, Plum F, Duffy TE: Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J Clin Invest 59:386–396, 1977
Patel AJ, Hunt A, Tahourdin CSM: Regional development of glutamine synthetase activity in the rat brain and its association with the differentiation of astrocytes. Dev Brain Res 8:31–37, 1983
Lavoie J, Giguère JF, Pomier Layrargues G, Butterworth RF: Activities of neuronal and astrocytic marker enzymes in autopsied brain tissue from patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2:283–290, 1987
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275, 1951
Dubuisson L, Bioulac P, Saric J, Balabaud C: Hepatocyte ultrastructure in rats with portacaval shunt. A morphometric study of acinar zones. Dig Dis Sci 27:1003–1010, 1982
Meyers OL, Hickman R, Keraan M, Engelbrecht GHC, Webber BL, Terblanche J: Acute biochemical and histological effect of portacaval shunt in the normal rat. S Afr Med J 49:1048–1050, 1975
Gerbhardt R, Mecke D: Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J 2:567–570, 1983
Kaiser S, Gerok W, Haussinger D: Ammonia and glutamine metabolism in human liver slices: new aspects on the pathogenesis of hyperammonemia in chronic liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest 18:535–542, 1988
Cooper AJL, Mora SN, Cruz NF, Gelbard AS: Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats. J Neurochem 44:1716–1723, 1985
Colombo JP, Bachmann C, Peheim E, Beruter J: Enzymes of ammonia detoxication after portacaval shunt in the rat II. Enzymes of glutamate metabolism. Enzyme 22:399–406, 1977
Subbalakshmi GYCV, Murthy CRK: Differential response of enzymes of glutamate metabolism in neuronal perikarya and synaptosomes in acute hyperammonemia in rat. Neurosci Lett 59:121–126, 1985
Cremer JE, Heath DF, Teal HM, Woods MS, Cavanagh JB: Some dynamic aspects of brain metabolism in rats given a portacaval anastomosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 3:293–311, 1975
Ukida M, Morishita H, Morimoto Y, Usui H, Nagashima H: Limited glutamine synthesis in brains of dogs with a portacaval anastomosis after15N-ammonium chloride loading.In Advances in Ammonia Metabolism and Hepatic Encephalopathy. PB Soeters, JHP Wilson, AJ Meijer, E Holm (eds). Amsterdam, Excerpta Medica, 1988, pp 433–438
Raabe WA: Neurophysiology of ammonia intoxication.In Hepatic Encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatment. RF Butterworth, G Pomier Layrargues (eds). Clifton, New Jersey, 1989, Humana Press, pp 49–78
Coy D, Gottstein J, Blei AT: The postoperative course of rats after portacaval anastomosis (PCA) is determined by the portacaval pressure gradient. Hepatology 14:90A, 1991 (abstract)
Arola LI, Palou A, Remesar X, Alemany M: Glutamine synthetase activity in the organs of fed and 24 hours fasted rats. Horm Metab Res 13:199–202, 1981
King PA, Goldstein L, Newsholme EA: Glutamine synthetase activity of muscle in acidosis. Biochem J 216:523–525, 1983
Chang TW, Goldberg AL: The origin of alanine produced in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 253:3677–3684, 1978
Hod G, Chaouat M, Haskel Y, Lernau OZ, Nissan S, Mayer M: Ammonia uptake by skeletal muscle in the hyperammonemic rat. Eur J Clin Invest 12:445–450, 1982
Norenberg MD: The use of cultured astrocytes in the study of hepatic encephalopathy.In Hepatic Encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatment. RF Butterworth, G Pomier Layrargues (eds). Clifton, New Jersey, Humana Press, 1989, pp 215–229
Naylor CD, O'Rourke K, Detsky AS, Baker JP: Parenteral nutrition with branched-chain amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 97:1033–1042, 1989
Conn HO, Eriksson LS: Nutritional therapy of portalsystemic encephalopathy: The branched chain amino acid story.In Hepatic Encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatment. RF Butterworth, G Pomier Layrargues (eds). Clifton, New Jersey, Humana Press, 1989, pp 509–528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girard, G., Butterworth, R.F. Effect of portacaval anastomosis on glutamine synthetase activities in liver, brain, and skeletal muscle. Digest Dis Sci 37, 1121–1126 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300297
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01300297