Summary
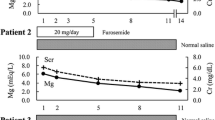
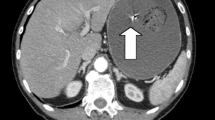
A case of small bowel ulceration and perforation possibly due to therapy with Klotrix in a patient with Crohn's disease is presented. Following emergent surgery with creation of a diverting loop jejunostomy, subsequent reestablishment of intestinal continuity was carried out with excellent clinical results. Gastrointestinal mucosal lesions possibly due to wax-matrix potassium chloride preparations are reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CA, Boley SJ, Schultz L, Schwartz S: Potassiuminduced lesions of the small bowel. II. Pathology and Pathogenesis. JAMA 193:1001–1006, 1965
Maggio-Cavaliere MB, Dirkstein WG, Arnold JD, Berger AE: Absence of gastrointestinal bleeding with controlled-release potassium chloride tablets. Clin Pharmacol Ther 16:685–690, 1974
Boley SF, Allen AC, Schultz L, Schwartz S Potassium-induced lesions of the small bowel. I. Clinical Aspects. JAMA 193:997–1000, 1965
Heffernan SJ, Murphy JJ: Ulceration of the small intestine and slow-release potassium tablets. Br Med J 2:746, 1975
Farquharson-Roberts MA, Giddings AEB, Nunn AJ: Perforation of small bowel due to slow-release potassium chloride (Slow-K). Br Med J 2:206, 1975
Weiss SM, Rutenberg HL, Paskin DL, Zaren HA: Gut lesions due to slow-release KCl tablets. N Engl J Med 296:111–112, 1977
Lofgren RP, Rothe PR, Carlson GJ: Jejunal perforation associated with slow-release potassium chloride therapy. South Med J 75:1154–1155, 1982
McAvoy BR: Mouth ulceration and slow-release potassium tablets. Br Med J 2:164–165, 1974
Lambert JR, Newman A: Ulceration and stricture of the esophagus due to oral potassium chloride (slow-release tablet) therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 73:508–511, 1980
McMahon FG, Akdamar K: Gastric ulceration after “Slow-K.”. N Engl J Med 295:733–734, 1976
McMahon FG, Akdamar K, Ryan JR, Ertan A: Upper gastrointestinal lesions after potassium chloride supplements: A controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2:1059–1061, 1982
Glenn F, Grafe WR: Surgical complications of adrenal steroid therapy. Ann Surg 165:1023–1034, 1967
Markowitz AM: The less common perforations of the small bowel. Ann Surg 152:240–257, 1963
Watson MR: Primary nonspecific ulceration of the small bowel. Arch Surg 87:600–603, 1963
Clark PA, Hsai YE, Huntsman RG: Toxic complications of treatment with 6-mercaptopurine. Br Med J 1:393–395, 1960
Waye JD, Lithgrow C: Small-bowel perforations in regional enteritis. Gastroenterology 53:625–629, 1967
Abascal J, Diaz-Rojas F, Jorge J, Sanchez-Vegazo I, Escartin P, Abreu L, Chantar C: Free perforation of the small bowel in Crohn's disease. World J Surg 6:216–220, 1982
Menguy R: Surgical management of free perforation of the small intestine complicating regional enteritis. Ann Surg 175:178–189, 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The opinions or assertions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Department of the Navy or the naval service at large.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brower, R.A. Jejunal perforation possibly induced by slow-release potassium in a patient with Crohn's disease. Digest Dis Sci 31, 1387–1390 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01299819
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01299819