Abstract
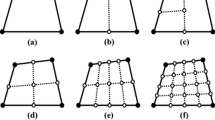
Use of quadrilateral elements for finite element mesh refinement can lead either to so-called ‘irregular’ meshes or the necessity of adjustments between finer and coarser parts of the mesh necessary. In the case of ‘irregular’ meshes, constraints have to be introduced in order to maintain continuity of the displacements. Introduction of finite elements based on blending function interpolation shape functions using piecewise boundary interpolation avoids these problems. This paper introduces an adaptive refinement procedure for these types of elements. The refinement is anh-method. Error estimation is performed using the Zienkiewicz-Zhu method. The refinement is controlled by a switching function representation. The method is applied to the plane stress problem. Numerical examples are given to show the efficiency of the methodology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuška, I.; Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Gago, J.; de A. Oliveira, E.R. (editors) (1986) Accuracy Estimates and Adaptive Refinements in Finite Element Computations, New York, Wiley & Sons
Oden, J.T.; Demkowicz, L. (1989) Advances in adaptive improvements—A survey of adaptive finite element methods in computational mechanics. In State-of-the-Art Surveys on Computational Mechanics, Noor, A.K.; Oden, J.T. (Editors), New York, ASME
Mackerle, J. (1993) Mesh generation and refinement for FEM and BEM—A bibliography (1990–1993), Finite Elements in Analysis and Design 15, 177–188
Mackerle, J. (1994) Error analysis, adaptive techniques and finite and boundary elements—A bibliography (1992–1993), Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 17, 231–246
Kikuchi, N.; Torigaki, T. (1993) Adaptive finite element methods in computer aided engineering. In Advanced Techniques in the Optimum Design of Structures, Hernández, S. (Editor). Southampton, UK, Computational Mechanics Pubheations
Szabo, B.A.; Babuška, I. (1991) Finite Element Analysis, New York, Wiley & Sons
Kato, K.; Lee, N.-S.; Bathe, K.-J. (1993) Adaptive finite element analysis of large strain elastic response, Computers and Structures 47, 829–855
Lee, N.-S.; Bathe, K.-J. (1994) Error indicators and adaptive remeshing in large deformation finite element analysis, Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 16, 99–140
Gordon, W.J. (1971) Blending-function methods of bivariate and multivariate interpolation and approximation, SIAM Numer. Anal., 8, 158–177
Gordon, W.J.; Hall, C.A. (1973) Transfinite element methods: blending-function interpolation over arbitrary curved element domains, Numer. Math., 21, 109–129
Birkhoff, G.; Cavendish, J.C.; Gordon, W.J. (1974) Multivariate approximation by locally blended univariate interpolants, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 71, 3423–3425
Cavendish, J.C.; Gordon, W.J.; Hall, C.A. (1976) Ritz-Galerkin approximations in blending function spaces, Number. Math., 26, 155–178
Cavendish, J.C.; Gordon, W.J.; Hall, C.A. (1977) Substructured marco elements based on locally blended interpolation, Int. J. Num. Meth. Engn., 11, 1405–1421
Röhr, U. (1985) Lokale finite Elementnetzverfeinerungen bei Platten und Scheibenaufgaben mittels gemischter Interpolation, Schiffbauforschung, 24, 39–50
Röhr, U. (1986) Elastostatische Strukturanalyse des Schiffs-körpers mittels FE-FS-Kombination, Teil 1: Theoretische Grundlagen, Schiffbauforschung, 25, 220–233
Röhr, U. (1987) Elastostatische Strukturanalyse des Schiffs-körpers mittels FE-FS-Kombination, Teil 2, Schiffbauforschung, 26, 48–53
Röhr, U.; Silge, F.; Phillipp, R. (1987) Zur Torsionsanalyse eines Mehrzweckfrachschiffes mit extrem offenem Deck mittels einer Finiten-Elemente-Kombination, Schiffbauforschung, 26, 173–184
Röhr, U. (1990) Versteifte räumliche Flächenelemente für ein kombiniertes FE-Modell des Schiffskörpers, Schiffbauforschung, 29, 95–111
Reißmann, C.; Röhr, U.; Gabriel, G.; Chmielewski, R.; Schulz, T. (1991) Nonconventional FEM-application in ship structure analysis, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Marine Structures, ISMS '91, Shanghai
Bathe, K. J. (1982) Finite Element Procedures in Engineering Analysis, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice Hall
Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. (1987) A simple error estimation and adaptive procedure for practical engineering analysis, Int. J. Num. Meth. Engn., 24, 337–357
Ainsworth, M., Zhu, J.Z.; Craig, A.W.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. (1989) Analysis of the Zienkiewicz-Zhua-posteriori error estimator in finite element method, Int. J. Num. Meth. Engn., 28, 2161–2174
Schramm, U. (1992) Adaptive mesh refinement using elements with blended interpolation, Proceedings of the International Conference on Education, Practice and Promotion of Computational Methods in Engineering using Small Computers, EPMESC IV, Dalian, Peoples Republic of China
Shpitalnij, M.; Bar-Yoseph, P.; Kimberg, Y. (1989) Finite element mesh generation via switching function representation, Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 5 119–130
Möller, P.; Tischer, A. (1993) Einführung effektiver Vernetzungstechniken für Finite-Elemente-Analysen im Schiffbau, FDS-Report Nr. 246/1993, Forschungszentrum des Deutschen Schiffbaus, Hamburg
Timoshenko, S.P. (1934) Theory of Elasticity, New York, McGraw-Hill
Reißmann, C.; Hopp, C.; Fröhling, W. (1977) Berechnung von Kerbspannungen in tordierten Wellen, Maschinenbautechnik, 26, 160–163
Zhu, J.Z.; Zienkiewicz, O.C. (1990) Superconvergence patch recovery anda-posteriori Error Estimates. Part 1: The Recovery Technique, Int. J. Num. Meth. Engn., 30, 1321–1339
Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. (1992) The superconvergence recovery technique anda-posteriori error estimators, Int. J. Num. Meth. Engn., 33, 1331–1364
Strang, G.; Fix, G.J. (1973) An Analysis of the Finite Element Metyod, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, Prentice Hall
Reißmann, C.; Möller, P.; Tischer, A. (1993) Globale Schiffsfestigkeitsanalyse mit adaptiver FE-Netzverfeinerung in lokalen Bereichen, Jahrbuch der Schiffbautechnischen Gesellschaft, 87, 436–444
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schramm, U., Möller, P., Tischer, A. et al. Adaptive mesh refinement using piecewise-linear shape functions based on the blending function method. Engineering with Computers 12, 84–93 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01299394
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01299394