Abstract
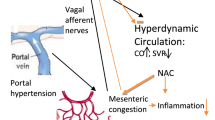
The present experiments investigated the possible relationship between portal hypertension and norepinephrine metabolism in the central nervous system (hypothalamus and medulla oblongata) and the portal vein in the rat. Group I (72), portal hypertensive, and group II (70) sham-operated animals, were sacrificed day 14, and endogenous norepinephrine content, uptake and release from hypothalamus, medulla oblongata, and portal vein were investigated. In group I our results showed increases in norepinephrine storage (69%; 8.3%) and release (19.7%; 43.8%) and a diminished uptake (42.3%; 27.5%) in the hypothalamus and medulla oblongata, respectively. Portal veins showed a decreased content and uptake (62.5% and 43.5%, respectively) and increased release (25%) compared to group II rats. These results suggest a close relationship between the central nervous system and rat portal hypertension, perhaps related to modifications of central sympathetic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bichet DG, Van Putten VJ, Schrier RW: Potential role of increased sympathetic activity in impaired sodium and water excretion in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 307:1552–1557, 1982
Gaudin C, Braillon A, Poo JL, Kleber G, Moreau R, Lebrec D: Plasma catecholamines in patients with presinusoidal portal hypertension: Comparison with cirrhotic patients and nonportal hypertensive subjects. Hepatology 13(5):913–916, 1991
Willett IR, Jennings G, Esler M, Dudley FJ: Sympathetic tone modulates portal venous pressure in alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet 2:939, 942, 1986
Bernardi M, Trevisani F, Santini C, Zoli G, Baraldini M, Ligabue A, Gasparrini G: Plasma norepinephrine, weak neurotransmitters, and renin activity during active tilting in liver cirrhosis: relationship with cardiovascular homeostasis and renal function. Hepatology 5:56–64, 1983
Henriksen JC, Ring-Larsen H, Christensen NJ: Circulating noradrenaline and central haemodynamics in patients with cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol 20:1185–1190, 1985
Vidal NA, Fernandez BE, dominquez AE, Taquini AMKC: Catecholamines in various areas of the central nervous system in normal and hypertensive rats. Arch Int Physiol Biochem 80:661–667, 1972
Chojkier M, Groszmann RJ: Measurement of portal systemic shunting in the rat by using gamma-labeled microspheres. Am J Physiol 240:G371-G375, 1981
von Euler US, Lishajko F: The estimation of catecholamines in urine. Acta Physiol Scand 45:122–132, 1959
Cohen G, Goldenberg M: The simultaneous fluorometric characteristics of adrenaline and noradrenaline in plasma. I. The fluorescence characteristics of adrenolutine and noradrenolutine and their simultaneous in mixtures. Neurochemistry 2:58–70, 1957
Fernandez BE, Dominguez AE, Vatta MS, Mendez MA, Bianciotti LG, Martinez Seeber A: Atrial natriuretic peptide and angiotensin II interaction on norandrenaline uptake in the central nervous system. Arch Int Physiol Biochim 307:11–17, 1990
Dominguez AE, Fernandez AE, Vidal NA, Martinez Seeber A: Angiotensin II—norepinephrine relationship in the central nervous system. Arch Int Physiol Biochim 90:269–275, 1982
Fernández B, Vatta MS, Bianciotti L, Feldstein C: Comparative effects of bradikinin and atrial natriuretic factor in neuronal and nonneuronal norepinephrine uptake. Am J Hypertension 5 (part II):64, 1992 (abstract)
Kostreva DR, Castaner A, Kampine JP: Reflex effects of hepatic baroreceptors on renal and cardiac sympathetic nerves. Am J Physiol 238:R390-R394, 1980
Niijima A: Afferent discharges from venous pressorreceptors in liver. Am J Physiol 232:C76-C81, 1977
Andrews CJH, Andrews WHHX: A sympathetic reflex elicited by distension of the mesenteric venous bed. J Physiol (London) 226:119–131, 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by Consejo de Investigaciones Técnicas y Cientificas of Argentina (CONICET) by grants PIA 2042/90 and 0738/91-010 and by the University of Buenos Aires grant FA 031.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemberg, A., Eizayaga, F.X., Vatta, M. et al. Prehepatic portal hypertension in rats modifies norepinephrine metabolism in hypothalamus medulla oblongata and portal vein. Digest Dis Sci 38, 1259–1262 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296075
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296075