Summary
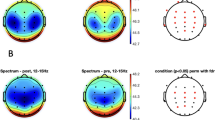
15 normal volunteers were treated over three weeks with haloperidol (HAL) and in the third week additionally with biperidene (BIP). The order of the EEG spectra at different topographical locations and in different frequency bands during a movement task was analyzed using uncertainty analysis (UA), a multivariate analysis technique based on informationtheoretical methods. Different patterns of drug-induced changes were found. HAL decreases the theta and alpha band order at the fronto-central lateral areas but increases it at the fronto-central midline in the theta band and at the parietal areas in the alpha band. With the exception of the fronto-central midline locations, BIP more or less counterbalances the effect of HAL. Volunteers felt unwell and had motor disturbances during HAL and felt well again during HAL + BIP. Reaction time values were increased during HAL and normalized during HAL + BIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bente D (1984) Elektroenzephalographische Vigilanzbestimmungen: Methoden und Beispiele. Z EEG-EMG 15: 173–179
Borenstein J, Dabbah M, Bles G (1962) Etude électroencéphalographic de l'halopéridol. Ann Medico Psychol 1: 133
Buchsbaum MS, Haier RJ (1987) Functional and anatomical brain imaging impact in schizophrenia research. Schizophr Bull 13: 115–132
Campbell A, Baldessarini RJ (1985) Prolonged pharmacologic activity of neuroleptics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42: 637
Diekmann V, Grözinger B, Westphal KP, Reinke W, Kornhuber HH (1990) The order of EEG activity of schizophrenic patients and the influence of haloperidol and biperidene on the EEG order of healthy subjects. In: Deecke L, Eccels JC, Mountcastle VB (eds) From neuron to action. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 495–500
Galderisi S, Mucci A, Mignone ML, Maj M, Kemali D (1992) CEEG mapping in drugfree schizophrenics. Differences from healthy subjects and changes induced by haloperidol treatment. Schizophr Res 6: 15–24
Grözinger B, Neher KD, Westphal KP, Diekmann V, Kornhuber HH (1984) The EEG in schizophrenia. Changes in relation to voluntary movement in the theta and delta band. Naturwissenschaften 71: 320–321
Haag C (1986) Untersuchung zur Wirkung von Biperiden auf EEG und Bereitschaftspotential vor und während einer Willkürbewegung, sowie Aufmerksamkeit, Reaktionszeit und motorische Leistungen bei gesunden Normalpersonen. Thesis, University of Ulm
Itil TM (1977) Quantitative and qualitative EEG findings in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 3: 61–79
Jenkins GM, Watts DG (1968) Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden Day, San Francisco
Lang W, Lang M, Kornhuber A, Diekmann V, Kornhuber HH (1988) Event related EEG-spectra in a concept formation task. Hum Neurobiol 6: 295–301
Morihisa JM (1986) Computerized mapping of electrophysiologic data in schizophrenia research: two possible organizing strategies. In: Nasrallah HA, Weinberger DK (eds) The neurology of schizophrenia. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 267–276 (Handbook of schizophrenia, vol 1)
Pfeiffer CC, Goldstein L, Murphree HB (1968) Effects of parenteral administration of haloperidol and chlorpromazine in man. I. Normal subjects: quantitative EEG and subjective responses. J Clin Pharmacol 8: 79–88
Reinke W, Diekmann V (1987) Uncertainty analysis of human EEG spectra: a multivariate information theoretical method for the analysis of brain activity. Biol Cybern 57: 379–387
Reinke W, Westphal KP, Diekmann V, Grözinger B, Kornhuber HH (1994) Changes in functionally determined order processes of the EEG in a motor task due to various dosages of biperidene. Neuropsychobiology 29: 194–201
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. The University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Saletu B, Küfferle B, Grünberger J, Anderer P (1986) Quantitative EEG, SPEM, and psychometric studies in schizophrenics before and during different neuroleptic therapy. Pharmacopsychiatry 19: 434–437
Shakow D (1963) Psychological deficit in schizophrenia. Behav Sci 8: 275–303
Westphal KP, Grözinger B, Foit A, Diekmann V, Schwab B, Kornhuber HH (1986) The influence of concentration and relaxation on the EEG power spectra during a CNV paradigm. Arch Ital Biol 124: 221–228
Westphal KP, Grözinger B, Haag C, Scherb W, Diekmann V, Kornhuber HH (1987) The influence of biperidene on the EEG power spectra during the Bereitschaftspotential paradigm. In: Johnson R, Rohrbough JW, Parasuraman R (eds) Current trends in event-related potential research. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 556–561 (EEG Suppl 40)
Westphal KP, Grözinger B, Diekmann V, Scherb W, Reeß J, Leibing U, Kornhuber HH (1989) Comparison of untreated and treated schizophrenic patients, normals and neuroleptic treated normals: “hypofrontality” and different EEG spectra before and during voluntary movement. Psychiatr Res 9: 395–398
Westphal KP, Grözinger B, Reeß J, Leibing U, Kornhuber AW, Diekmann V, Kornhuber HH (1992) Anticholinergoc influences of biperidene on the EEG effects of haloperidol. Clin Physiol Biochem 9: 26–34
Wienecke GH, Verhoeven WMA, Westenberg HGM, de Wilde H, Lopes da Siva FH, van Praag HM, Storm van Leeuwen W (1981) The effects of haloperidol on the EEG spectrum. Psychopharmacology 74: 33–34
von Zerssen D (1976a) Die Befindlichkeits-Skala. Manual. Beltz Test, Weinheim
von Zerssen D (1976b) Die Beschwerden-Liste. Manual. Beltz Test, Weinheim
von Zerssen D (1986) Clinical self-rating scales (CSRS) of the Munich Psychiatric Information System (Psychis München). In: Sartorius N, Ben TA (eds) Assessment of depression. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 270–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diekmann, V., Grözinger, B., Westphal, K.P. et al. Changes in EEG order in neuroleptically treated normal volunteers during a voluntary movement task. J. Neural Transmission 103, 1127–1139 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291797
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291797