Summary
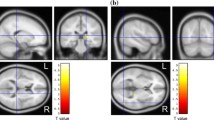
To visualise and quantify dopamine D2 receptor binding in the corpus striatum of patients with neurological Wilson's disease (WD) 123I-Iodobenzamide (IBZM) binding was measured using single photon emission computer tomography (SPECT). Ratios of striatal to frontal countrates were calculated in 8 patients and in 21 healthy control subjects. We found reduced IBZM binding ratios in all patients with WD in comparison to those in controls (1.48 +- 0.13 vs. 1.73 +- 0.09). The reduction in IBZM binding was correlated with the overall severity of neurological deficits and the severity of dysarthria (correlation coefficients −0.86 [p < 0.01] and −0.79 [p s< 0.01], respectively). When patients of three different subgroups of neurological WD were compared no differences in IBZM binding were found. We conclude that assessing basal ganglia function in vivo using IBZM-SPECT is a valuable diagnostic tool in WD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen AM, Martel W, Gabrielson TO, Glazer GM, Brewer G, Young AB, Hill G (1985) Wilson's disease of the brain: MR imaging. Radiology 157: 137–141
Brücke T, Podreka I, Angelberger P, Wenger S, Topitz A, Küfferle B, Müller C, Deecke L (1991a) Dopamine D2 receptor imaging with SPECT: studies in different neuropsychiatrie disorders. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11: 220–228
Brücke T, Wenger S, Podreka I, Asenbaum S (1991b) Dopamine receptor classification, neuroanatomical distribution, and in vivo imaging. Wien Klin Wochenschr 103: 639–646
Dawson TM, Gehlert DR, Wamsley JK (1986) Quantitative autoradiographic localization of central dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol 204: 93–118
De Haan J, Grossmann RI, Civitello L, Hackney DB, Goldberg HI, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmermann RA (1987) High-field magnetic resonance imaging of Wilson's disease. J Comput Tomogr 11: 132–135
De Voider A, Sindic CJM, Goffinet AM (1988) Effect of D-penicillamine treatment on brain metabolism in Wilson's disease: a case study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51: 947–949
Grimm G, Prayer L, Oder W, Ferenci P, Madl Ch, Knoflach P, Schneider B, Imhof H, Gangl A (1991) Comparison of functional and structural brain disturbances in Wilson's disease. Neurology 41: 272–276
Hartard C, Weisner B, Dieu C, Kunze K (1994) Wilson's disease with cerebral manifestation: monitoring therapy by CSF copper concentration. J Neurol 24: 101–107
Hawkins RA, Mazziotta JC, Phelps ME (1987) Wilson's disease studied with FDG and positron emission tomography, Neurology 37: 1707–1711
Hefter H, Arendt G, Stremmel W, Freund H-J (1993) Motor impairment in Wilson's disease. I. Slowness of voluntary limb movements. Acta Neurol Scand 87: 133–147
Kluin K, Starosta-Rubinstein S, Young AB, Hill GM, Brewer GJ (1985) Dysarthria in Wilson's disease: neurological correlations. Neurology 35 [Suppl 1]: 176–177
Kuwert T, Hefter H, Scholz D (1992) Regional cerebral gluose consumption measured by positron emission tomography in patients with Wilson's disease. Eur J Nucl Med 19: 96–101
Lawler GA, Pennock JM, Steiner RE, Jenkins WJ, Sherlock S, Young IR (1983) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging in Wilson's disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 1–8
Magalhaes ACA, Caramelli P, Menezes JR, Bacheschi LA, Rosemberg LA, Magalhaes A (1994) Wilson's disease: MRI with clinical correlation. Neuroradiology 36: 97–100
Metzer WS, Angtuaco E (1986) Long-term follow-up computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings in hepatolenticular degeneration: case report and summary of the literature. Mov Disord 1: 145–149
Oder W, Grimm G, Kollegger H, Ferenci P, Schneider B, Deecke L (1991) Neurological and neuropsychiatrie spectrum of Wilson's disease: a propsective study in 45 cases. J Neurol 238: 281–287
Oder W, Prayer L, Grimm G, Spatt J, Ferenci P, Kollegger H, Schneider B, Gangl A, Deecke L (1993) Wilson's disease: evidence of subgroups derived from clinical findings and brain lesions. Neurology 43: 120–124
Oder W, Prayer L, Grimm G, Deecke L (1994) Wilson's disease: clinical and MRI findings in 47 patients. J Neurol 241: 281
Oertel WH, Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Kraft E, Trenkwalder C, Scherer J, Weinzierl M, Vogl T, Kirsch CM (1992) Decrease of D2 receptors indicated by 1231-iodobenzamide single-photon emission computed tomography relates to neurological deficit in treated Wilson's disease. Ann Neurol 32: 743–748
Palacios J, Pazos A (1987) Vizualisation of dopamine receptors: a progress reviews. In: Creese I, Fraser CM (eds) Receptor biochemistry and methodology. Dopamine receptors. Alan Liss, New York, pp 175–197
Prayer L, Wimberger D, Kramer J, Grimm G, Oder W, Imhof H (1990) Cranial MRI in Wilson's disease. Neuroradiology 32: 211–214
Roh JK, Lee TG, Wie BA, Park SH, Chang KH (1994) Initial and follow-up brain MRI findings and correlation with the clinical course in Wilson's disease. Neurology 44: 1064–1068
Schwarz J, Antonini A, Kraft E, Tatsch K, Vogl T, Kirsch CM, Leenders KL, Oertel WH (1994) Treatment with D-penicillamine improves dopamine D2 receptor binding and T2 signal intensity in de novo Wilson's disease. Neurology 44: 1079–1082
Scheinberg IH, Sternlieb I (1984) Wilson's disease. Saunders, Philadelphia
Smith WT (1976) Intoxications, poisons, and related metabolic disorders. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis JAN (eds) Greefield's neuropathology. Edward Arnold, London, pp 172–177
Starosta-Rubinstein S, Young AB, Kluin K, Hill G, Aisen AM, Gabrielsen T, Brewer GJ (1987) Clinical assessment of 31 patients with Wilson's disease. Correlations with structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol 44: 365–370
Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Oertel WH, Kirsch CM (1991) Spect imaging of dopamine D2 receptors with 123I-IBZM: initial experience in controls and patients with Parkinson's syndrome and Wilson's disease. Nucl Med Comm 12: 699–707
Walshe JM (1986) Wilson's disease. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn, Klawans HI (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 5. Extrapyramidal disorders. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 223–238
Webster DD (1968) Critical analysis of the disability in Parkinson's disease. Med Treat 5: 257–282
Williams FJB, Walshe JM (1981) Wilson's disease. An analysis of the cranial computerized tomographic appearances found in 60 patients and the changes in response to treatment with chelating agents. Brain 104: 735–752
Young AB, Shoulson I, Penney JB, Starosta-Rubinstein S, Gomez F, Travers H, Ramos-Arroyo MA, Snodgrass SR, Bonilla E, Monero H, Wexler NS (1986) Huntington's disease in Venezuela: neurologic features and functional decline. Neurology 36: 244–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oder, W., Brücke, T., Kollegger, H. et al. Dopamine D2 receptor binding is reduced in Wilson's disease: Correlation of neurological deficits with striatal123I-Iodobenzamide binding. J. Neural Transmission 103, 1093–1103 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291794