Conclusions
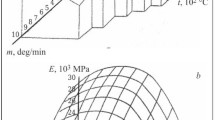
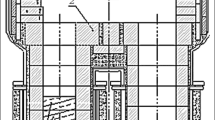
Using the instrument described, which has been improved in design for testing refractory materials for slag and hot slag resistance, we investigated the properties of magnesite, magnesite-chromite, and chrome-magnesite specimens. It was established that their life is determined by the resistance of the refractory bond. The best resistance is possessed by periclase-spinel specimens. An increase in the content of calcium oxide in the slags reduces the slag resistance of all periclase-spinel refractories that were tested. Impregnating the magnesite products with a saturated solution of chromium acetate and firing them after impregnation at 400–500°C markedly increases their slag resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. N. Bluvshtein et al., Information TsIIN, ChM, No. 5, Series 8 (1962).
P. S. Mamykin and N. U. Uskumbaev, Ogneupory, No. 3, 36 (1965).
P. S. Mamykin et al., Ogneupory, No. 1, 37 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Ogneupory, No. 7, pp. 47–52, July, 1968.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mamykin, P.S., Kashcheev, I.D. Slag and hot-slag resistance of basic refractories. Refractories 9, 444–448 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01284501
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01284501