Summary
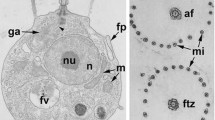
The protostelidPlanoprotostelium aurantium Olive andStoianovitch has trophic cells which are either amoebae or flagellates. The general morphology and ultrastructure are consistent with what has been reported for otherEumycetozoa (protostelids, myxomycetes, and dictyostelids). The flagellar apparatus structure has the same basic pattern as that of other flagellate eumycetozoans. It shares with all these an anteriorly directed flagellum and centriole and microtubule arrays (MTA) 2–4. Unlike more primitive species which have two centrioles per flagellar apparatus,P. aurantium has only one. Also, the flagellar apparatus is independent of the nucleus inP. aurantium, not linked to it as in the primitive species. These features are useful in explaining the differences in swimming behavior betweenP. aurantium and biflagellate species. Evidence is presented to show thatP. aurantium is closely related to the non-flagellateProtostelium mycophaga Olive andStoianovitch.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich, H. C., 1968: The development of flagella in swarm cells of the myxomycetePhysarum flavicomum. J. gen. Microbiol.50, 217–222.
Barr, D. J. S., Hadland-Hartmann, V. E., 1978: The flagellar apparatus of the Chytridiales. Can. J. Bot.56, 887–900.
Bray, D. F., Wagenaar, E. B., 1978: A double staining technique for improved contrast of thin sections from Spurr-embedded tissue. Can. J. Bot.56, 129–132.
Collins, O. R., 1979: Myxomycete biosystematics; some recent developments and future research opportunities. Bot. Rev.45, 145–201.
Dykstra, M. J., 1977: The possible phylogenetic significance of mitochondrial configurations in the acrasid cellular slime molds with reference to members of theEumycetozoa and the fungi. Mycologia69, 579–591.
Furtado, J. S., Olive, L. S., 1970: Ultrastructural studies of the protostelids: the amoebo-flagellate stage. Cytobiologie2, 200–219.
— —, 1971: Ultrastructure of the protostelidCeratiomyxella tahitiensis including scale formation. Nova Hedwigia21, 537–576.
George, R. P., 1968: Cell Organization and Ultrastructure During Culmination of the Cellular Slime Molds. Ph.D. Dissertation: University of Hawaii.
Gray, W. D., Alexopoulos, C. J., 1968: Biology of the Myxomycetes. New York: The Ronald Press.
Gustafson, R. A., Thurston, E. L., 1974: Calcium deposition in the myxomyceteDidymium squamulosum. Mycologia66, 397–412.
Haskins, E. F., 1978: A study of the amoebo-flagellate transformation in the slime moldEchinostelium minutum de Bary. Protoplasma94, 193–206.
Hibberd, D. J., 1979: The structure and phylogenetic significance of the transition region in the chlorophyll c-containing algae. BioSystems11, 243–261.
Hoffman, L. R., 1976: Fine structure ofCylindrocapsa zoospores. Protoplasma87, 191–219.
Hohl, H. R., Hamamoto, S. T., Hemmes, D. E., 1968: Ultrastructural aspects of cell elongation, cellulose synthesis, and spore differentiation inAcytostelium leptosomum, a cellular slime mold. Amer. J. Bot.55, 783–796.
Ishigami, M., 1977: A light and electron microscopy study of the flagellate to ameba conversion in the myxomyceteStemonitis pallida. Protoplasma91, 31–54.
Nelson, R. K., Scheetz, R. W., 1975: Swarm cell ultrastructure inCeratiomyxa fruticulosa. Mycologia67, 733–740.
Olive, L. S., 1964: A new member of theMycetozoa. Mycologia67, 885–896.
—, 1975: The Mycetozoans. New York: Academic Press.
—,Stoianovitch, C., 1971:Planoprotostelium, a new genus of protostelids. J. Elisha Mitchell Sci. Soc.87, 115–119.
— —, 1977:Clastostelium, a new ballistosporous protostelid (Mycetozoa) with flagellate cells. Trans. Brit. Mycol. Soc.69, 83–88.
— —, 1979: Observations of the mycetozoan genusCeratiomyxa: description of a new species. Mycologia71, 546–555.
Patterson, D. J., 1980: Contractile vacuoles and associated structures: their organization and function. Biol. Rev.55, 1–46.
Pickett-Heaps, J. D., 1969: The evolution of the mitotic apparatus: an attempt at comparative ultrastructural cytology in dividing cells. Cytobios1, 257–280.
—, 1975: Green Algae. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates.
Roos, U. P., 1975: Fine structure of an organelle associated with the nucleus and cytoplasmic microtubules in the cellular slime moldPolysphondylium yiolaceum. J. Cell Sci.18, 315–316.
Schuster, F. L., 1965: Ultrastructure and morphogenesis of solitary stages of the true slime molds. Protistologica1, 49–62.
Spiegel, F. W., 1981: Phylogenetic significance of the flagellar apparatus in protostelids (Eumycetozoa). BioSystems14, 491–499.
Spiegel, F. W., Olive, L. S., Brown, R. M., Jr., 1979: Roles of actin during sporocarp culmination in the simple mycetozoanPlanoprotostelium aurantium. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.76, 2335–2339.
Stewart, K. D., Mattox, K. R., 1980: Phylogeny of phytoflagellates. In: Phytoflagellates (Cox, E. R., ed.), pp. 433–462. New York: Elsevier/North Holland.
Veneble, J. H., Coggeshall, R., 1965: A simplified lead citrate stain for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.25, 407–408.
Wright, M. A., Moisand, A., Mir, L., 1979: The structure of the flagellar apparatus of the swarm cells ofPhysarum polycephalum. Protoplasma100, 231–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research represents part of a Ph.D. dissertation presented to the University of North Carolina.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiegel, F.W. The ultrastructure of the trophic cells of the protostelidPlanoprotθstelium aurantium . Protoplasma 113, 165–177 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01280904
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01280904