Summary
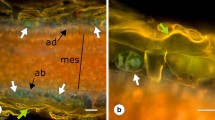
The cytological changes which accompany wounding and wound recovery in the coenocytic algaCaulerpa simpliciuscula have been studied using both light and electron microscopy. Within one minute of wounding, there are three responses.
-
1.
The formation of a gelatinous plug on the surface of the wound. The material contributing to this external plug appears to be formed from vacuolar contents which undergo sol to gel transformation following extrusion under turgor pressure.
-
2.
The formation of an internal wound plug of different composition to the external plug. Deposition of the internal wound plug continues for up to 11 hours following wounding. On the basis of staining reactions this material appears to be either a sulphated glycoprotein, or a mixture of protein and sulphated polysaccharide.
-
3.
The retraction of cytoplasm away from the wound site, and the formation of a large number of vesicles between the cytoplasm and the surface of the internal wound plug. The formation of these vesicles appears to result from the re-organization of membrane components present in the unwounded cytoplasm into the surface membranes of the vesicle.
During the interval of 11 to 24 hours following wounding, there is a gradual extension of the retracted cytoplasm to the inner surface of the internal wound plug with a corresponding resorbtion of some of the vesiculate material. The synthesis of a new cell wall has begun by 11 hours, and is complete after 6 days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burr, F. A., Evert, R. F., 1972: A cytochemical study of the wound-healing protein inBryopsis hypnoides. Cytobios.6, 199–215.
—,West, J. A., 1970: Light and electron microscope observations on the vegetative and reproductive structures ofBryopsis hypnoides. Phycologia9, 17–37.
— —, 1971: Protein bodies inBryopsis hypnoides: Their relationship to wound-healing and branch septum development. J. Ultrastruct. Res.35, 476–498.
Calvert, H. E., Dawes, C. J., Borowitzka, M. A., 1976: Phylogenetic relationships ofCaulerpa (Chlorophyta) based on comparative chloroplast ultrastructure. J. Phycol.12, 149–162.
Dawes, C. J., Barilotti, D. C., 1969: Cytoplasmic organization and rhythmic streaming in growing blades ofCaulerpa prolifera. Amer. J. Bot.56, 8–15.
—,Rhamstine, E. L., 1967: An ultrastructural study of the giant green algal coenocyte,Caulerpa prolifera. J. Phycol.3, 117–126.
Dean, R. T., 1977: Lysosomes and membrane recycling—a hypothesis. Biochem. J.168, 603–605.
Frei, E., Preston, R. D., 1964: Non-cellulosic structural polysaccharides in algal cell walls. I. Xylan in siphonaceous green algae. Proc. Roy. Soc. Ser. B160, 293–313.
Fritsch, F. E., 1935: Structure and reproduction of the algae, Vol. I. Cambridge, University Press.
Gibor, A., 1965: Surviving chloroplastsin vivo. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (U.S.)54, 1527–1531.
Hauser, H., Levine, B. A., Williams, R. J. P., 1976: Interactions of ions with membranes. T.I.B.S.1, 278–281.
Howard, R. J., Gayler, K. R., Grant, B. R., 1975: The products of photosynthesis inCaulerpa simpliciuscula (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol.11, 463–471.
—,Wright, S. W., Grant, B. R., 1976: Structure and some properties of the soluble 1,3 β glucan isolated from the green algaCaulerpa simpliciuscula. Plant Physiol.58, 459–463.
—,Grant, B. R., Fock, H., 1977: Storage and structural products formed during photosynthesis in the siphonous algaCaulerpa simpliciuscula (Chlorophyceae). J. Phycol.131, 340–345.
Iwasaki, H., 1961: The life cycle ofPorphyra tenera in vitro. Biol. Bull.121, 173–187.
Jacobs, W. P., 1970: Development and regeneration of the algal giant coenocyteCaulerpa. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.175, 732–748.
Janse, J. M., 1906: Polarität und Organbildung beiCaulerpa prolifera. Jb. wiss. Bot.42, 394–461.
Koreeda, A., Harada, T., Ogawa, K., Sato, S., Kasai, N., 1974: Study of the ultrastructure of gel-forming (1–3) β D-glucan (curdlan-type polysaccharide) by electronmicroscopy. Carbohydrate Res.33, 396–399.
Lohr, C. A., 1975: Cytological and chemical aspects of the wound response inCaulerpa prolifera. Ph. D. Thesis, University S. Forida.
—,Dawes, C. J., 1974: Some aspects of the wound response inCaulerpa prolifera. J. Phycol.10 (supplement), 17.
Markowitz, A. S., 1976: Protoplasmic and plasma membrane relationships. T.I.B.S.1, 161–163.
Mishra, A. K., 1969: Fine structure of the growing point of the coenocytic algaC. sertu-larioides. Canad. J. Bot.47, 1599–1603.
Parker, B. C., Diboll, A. G., 1966: Alcian stains for histochemical localization of acid and sulphated polysaccharides in algae. Phycologia6, 37–46.
Pasternak, C. A., 1976: Surface membranes during the cell cycle. T.I.B.S.1, 148–151.
Sabnis, D. D., 1969: Observations on the ultrastructure of the coenocytic marine algaCaulerpa prolifera, with particular reference to some unusual cytoplasmic components. Phycologia7, 24–41.
—,Jacobs, W. P., 1967: Cytoplasmic streaming and microtubules in the coenocytic marine algaCaulerpa prolifera. J. Cell Sci.2, 465–472.
Saier, M. H., Stiles, C. D., 1975: Molecular dynamics in biological membranes. New York: Springer.
Smith, M. M., McCully, M. E., 1977: Mild temperature stress and callose synthesis. Planta136, 65–70.
Spurr, A. R., 1969: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31–43.
Tippit, D. H., Pickett-Heaps, J. D., 1977: Mitosis in the pennate diatomSurirella ovalis. J. Cell Biol.73, 705–727.
Turner, J. B., Friedmann, E. I., 1974: Fine structure of capitular filaments in the coenocytic green algaPenicillus. J. Phycol.10, 125–134.
van den Driessche, T., Hars, R., Hellin, J., Bouloukhére, M., 1973: The substructure of cytoplasts obtained fromAcetabularia mediterranea. J. Ultrastruct. Res.42, 479–490.
Walker, T. S., 1972: The purification and some properties of a protein causing gelling in phloem sieve tube exudate fromCucurbita pepo. B.B.A.257, 433–444.
—,Thaine, R., 1971: Proteins and fine structural components in exudate from sieve tubes inCucurbita pepo stems. Ann. Bot.35, 773–790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreher, T.W., Grant, B.R. & Wetherbee, R. The wound response in the siphonous algaCaulerpa simpliciuscula C. Ag.: Fine structure and cytology. Protoplasma 96, 189–203 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279585
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279585