Summary
Neurotensin, an endogenous peptide and putative neurotransmitter, exhibits a wide range of interactions with dopaminergic neurons and displays some actions akin to neuroleptics. Moreover, neurotensin receptors are abundant in specific layers of the entorhinal cortex where cytoarchitectural abnormalites have been reported in schizophrenia. We therefore examined the entorhinal cortex from postmortem specimens of five control patients and six schizophrenic patients for alterations in neurotensin receptor quantitation and distribution using receptor autoradiography.
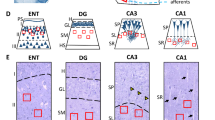
Specific125I-neurotensin binding was concentrated in layer II cell clusters, with a 40% reduction in binding in the schizophrenic group (p<0.05). Moderate binding was observed in both cohorts in deep layers V/VI, with negligible binding in the hippocampus. There was no statistical difference in quantitative neurotensin binding in other lamina of the entorhinal cortex of schizophrenics compared with controls. The characteristic laminar pattern of binding did not differ between cohorts. The reduction in neurotensin binding in schizophrenics is consistent with an increasing number of reports of structural abnormalities in the medial temporal lobe of schizophrenics in general and the entorhinal cortex in particular. Further studies are required to examine the evidence for neuroanatomic and neurochemical pathology in the entorhinal cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuler LL, Casanova MF, Goldberg TE, Kleinman JE (1990) The hippocampus and parahippocampus in schizophrenia, suicide, and control brains. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47: 1029–1034
Amaral DG, Insausti R (1990) The hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G (ed) The human nervous system. Academic Press, New York, pp 711–755
Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR (1991a) Some cytoarchitectural abnormalities of the entorhinal cortex in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48: 625–632
Arnold SE, Lee VM, Raquel RE, Trojanowski JQ (1991b) Abnormal expression of two microtubule-associate proteins (MAP2 and MAP5) in specific subfields of the hippocampal formation in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 10850–10854
Benzing WC, Mufson EJ, Jennes L, Stopa EG, Armstrong DM (1992) Distribution of neurotensin immunoreactivity within the human amygdaloid complex: a comparison with acetylcholinesterase and Nissl-stained tissue sections. J Comp Neurol 317: 283–297
Braak H, Braak E (1992) The human entorhinal cortex: normal morphology and lamina-specific pathology in various diseases. Neurosci Res 15: 6–31
Chinaglia G, Probst A, Palacios JM (1990) Neurotensin receptors in Parkinson's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: an autoradiographic study in basal ganglia. Neuroscience 39: 351–360
Clapacs JT, Cain ST, Knight DL, Smith WE, Nemeroff CB (1991) Changes in neurotensin receptor density in rats treated chronically with haloperidol and sigma antagonist BMY 14802. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17(1): 806
Falkai P, Bogerts B, Rozumek M (1988a) Limbic pathology in schizophrenia: the entorhinal region — a morphometric study. Biol Psychiatry 24: 515–521
Falkai P, Bogerts B, Roberts GW, Crow TJ (1988b) Measurement of the alpha-cell-migration in the entorhinal region: a marker for the developmental disturbances in schizophrenia? Schizophr Res 1: 157–158
Herve D, Tassin JP, Studlen JM, Pana D, Kitagbi P, Vincent JP, Glowinski J, Rostene W (1986) Dopaminergic control of125I-labeled neurotensin binding site density in corticolimbic structures of the rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 6203–6207
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Kromer LJ, Damasio AR (1986) Perforant pathway changes and the memory impairment of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 20: 472–481
Jakob H, Beckmann H (1986) Prenatal developmental disturbances in the limbic allocortex in schizophrenics. J Neural Transm 65: 303–326
Jakob H, Beckmann H (1989) Gross and histological criteria for developmental disorders in brains of schizophrenics. J Roy Soc Med 89: 466–469
Jansen KLR, Faull RLM, Dragunow M (1989) Excitatory amino acid receptors in the human cerebral cortex: a quantitative autoradiographic study comparing the distributions of [3H]TCP, [3H]glycine, L-[3H] glutamate, [3H]AMPA and [3H]kainic acid binding sites. Neuroscience 32: 587–607
Jansen KLR, Faull RLM, Dragunow M, Synek BL (1990) Alzheimer's disease: changes in hippocampal n-methyl-d-aspartate, quisqualate, neurotensin, adenosine, benzodiazepine, serotonin and opioid receptors — an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 39: 613–627
Joyce JN, Janowsky A, Neve KA (1991) Characterization and distribution of [125I]epidepride binding to dopamine D2 receptors in basal ganglia and cortex of human brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257: 1253–1263
Joyce JN, Lexow N, Kim SJ, Artymyshyn R, Senzon S, Lawrence D, Casanova MF, Kleinman JE, Bird ED, Winokur A (1992) Distribution of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes in human post-mortem brain: alterations in limbic regions of schizophrenics. Synapse 10: 228–246
Joyce JN, Murray A, Ryoo H, Goldsmith S (1993) Expression of D2 and D3 receptors in limbic system of normals, schizophrenics and Alzheimer's cases. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19: 1370
Kanba KS, Kanba S, Okazaki H, Richelson E (1986) Binding of [3H]neurotensin in human brain: properties and distribution. J Neurochem 46: 946–952
Kasckow J, Nemeroff CB (1991) The neurobiology of neurotensin: focus on neurotensindopamine interactions. Regul Pept 36: 153–164
Kerwin R, Robinson P, Stephenson J (1992) Distribution of CCK binding sites in the human hippocampal formation and their alteration in schizophrenia: a postmortem autoradiographic study. Psychol Med 22: 37–43
Kohler C, Radesater A-C, Chan-Palay V (1987) Distribution of neurotensin receptors in the primate hippocampal region: a quantitative autoradiographic study in the monkey and the postmortem human brain. Neurosci Lett 76: 145–150
Mai JK, Triepel J, Metz J (1987) Neurotensin in the human brain. Neuroscience 22: 499–524
Meunier M, Bachevalier J, Mishkin M, Murray EA (1993) Effects on visual recognition of combined and separate ablations of the entorhinal and perirhinal cortex in rhesus monkeys. J Neurosci 13: 5418–5432
Merchant KM, Dorsa DM (1993) Differential induction of neurotensin and c-fos gene expression by typical versus atypical antipsychotics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90: 3447–3451
Moyse E, Rostene W, Vial M, Leonard K, Mazella J, Kitabgi P, Vincent J-P, Beaudet A (1987) Distribution of neurotensin binding sites in rat brain: a light microscopic radioautographic study using monoiodo [125I]Tyr3-neurotensin. Neuroscience 22: 525–536
Palacios JM, Chinablia G, Rigo M, Ulrich J, Probst A (1991) Neurotensin receptor binding levels in basal ganglia are not altered in Huntington's chorea or schizophrenia. Synapse 7: 114–122
Pazos A, Probst A, Palacios JM (1987) Serotonin receptors in the human brain. III. Autoradiographic mapping of serotonin-1 receptors. Neuroscience 21: 97–122
Quirion R, Welner S, Gauthier S, Bedard P (1987) Neurotensin receptor binding sites in monkey and human brain: autoradiographic distribution and effects of 1-methyl 4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine treatment. Synapse 1: 559–566
Reubi JC, Cortes R, Maurer R, Probst A, Palacios JM (1986) Distribution of somatostatin receptors in the human brain: an autoradiographic study. Neuroscience 18: 329–346
Royston MC, Slater P, Simpson MDC, Deakin JFW (1991) Analysis of laminar distribution of kappa opiate receptor in human cortex: comparison between schizophrenia and normal. J Neurosci Meth 36: 145–153
Sadoul JL, Checler F, Kitabgi P, Rostene W, Javoy-Agid F, Vincent JP (1984) Loss of high affinity neurotensin receptors in substantia nigra from parkinsonian subjects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 125: 395–404
Sarrieau A, Javoy-Agid F, Kitabgi P, Dussaillant M, Vial M, Vincent JP, Agid Y, Rostene WH (1985) Characterization and autoradiographic distribution of neurotensin binding sites in the human brain. Brain Res 348: 375–380
Saunders RC, Rosene DL (1988) A comparison of the efferents of the amygdala and the hippocampal formation in the rhesus monkey I. Convergence in the entorhinal, prohinal and perirhinal cortices. J Comp Neurol 271: 153–184
Saunders RC, Rosene DL (1995) Non-hippocampal entorhinal efferents in the rhesus monkey I. Subcortical projections (submitted)
Saunders RC, Krimer LS, Hyde TM (1995) The entorhinal cortex in the human: cytoarchitectonic organization and comparison with rhesus monkey (submitted)
Schotte A, Leysen JE, Laduron PM (1986) Evidence for a displaceable non-specific [3H]neurotensin binding site in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 333: 400–405
Steward O, Scoville SA (1976) Cells of origin of entorhinal cortical afferents to the hippocampus and fascia dentata of the rat. J Comp Neurol 169: 347–370
Szigethy E, Quirion R, Beaudet A (1990) Distribution of125I-neurotensin binding sites in human forebrain: comparison with the localization of acetylcholinesterase. J Comp Neurol 297: 487–498
Uhl GR, Kuhar MJ (1984) Chronic neuroleptic treatment enhances neurotensin receptor binding in human and rat substantia nigra. Nature 309: 350–352
Van Hoesen GW, Pandya DN (1975) Some connections of the entorhinal (area 28) and perirhinal (area 35) cortices of the rhesus monkey. III. Efferent connections. Brain Res 95: 39–59
Von Bonin G, Bailey P (1947) The neocortex of the macaca mulatta. Univ Illinois Press, Urbana IL
Witter MP, Van Hoesen GW, Amaral DG (1989) Topographical organization of the entorhinal projection to the dentate gyrus of the monkey. J Neurosci 9: 216–228
Wolf SS, Hyde TM, Moody TW, Saunders RC, Weinberger DR, Kleinman JE (1994) Autoradiographic characterization of125I-neurotensin binding sites in human entorhinal cortex. Brain Res Bull 35: 353–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, S.S., Hyde, T.M., Saunders, R.C. et al. Autoradiographic characterization of neurotensin receptors in the entorhinal cortex of schizophrenic patients and control subjects. J. Neural Transmission 102, 55–65 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276565
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276565