Summary
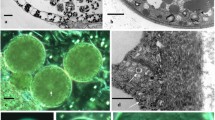
Time-lapse light micrographs of conidium development in the hyphomycete fungusPleiochaeta setosa (Kirchn.) Hughes, illustrate what appears to be normal holoblastic conidiogenesis followed by sympodial proliferation of the conidiogenous cell. Transmission and scanning electron micrographs, however, show that the wall of the conidium initial arisesde novo and endogenously from a conidiogenous mother cell. Maturation of conidia and setulae, nuclear behaviour and changes in cytoplasmic organelles are described. Sympodial proliferation of conidiophores is also shown to involve a new wall laid down under the septum delimiting the conidium from the conidiogenous cell. This layer extends down the sides of the conidiophore apex and erupts through the original conidiophore wall to produce the next conidium initial. The significance of these wall layers is discussed in relation to other types of conidiogenesis which have been characterized ultrastructurally, especially the phialidic and annellidic conidiogenous modes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arx, J. A. von, 1970: The genera of fungi sporulating in pure culture. Lehre: Verlag von J. Cramer.
Beckett, A., I. B. Heath, andD. J. McLaughlin, 1974: An atlas of fungal ultrastructure. London: Longmans. (In press).
Brenner, D. M., andG. C. Carrol, 1968: Fine-structure correlates of growth in hyphae ofAscodesmis sphaerospora. J. Bact.92 (2), 658–671.
Campbell, R., 1972: Ultrastructure of conidium ontogeny in the Deuteromycete fungusStachybotrys atra Corda. New Phytologist71, 1143–1149.
Cole, G. T., 1973: Ultrastructure of conidiogenesis inDrechslera sorokiniana. Can. J. Bot.51, 629–638.
Cook, Beryl E., 1974: The development of conidiophores and conidia in the imperfect fungusOedocephalum roseum. New Phytologist73, 115–130.
Ellis, M. B., 1971: Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Kew: Commonwealth Mycological Institute.
Ghiorse, W. C., andM. R. Edwards, 1973: Ultrastructure ofAspergillus fumigatus conidia. Development and Maturation. Protoplasma76, 49–59.
Goos, R. D., 1969: Conidium ontogeny inCacumisporium capitulatum. Mycologia61 (1), 52–56.
Griffiths, D. A., 1973: The fine structure of conidial development inEpicoccum nigrum. J. Microscopie17, 55–64.
Hammill, T. M., 1971: Fine structure of annellophores. I.Scopulariopsis brevicaulis andS. koningii. Amer. J. Bot.58 (1), 88–97.
—, 1972 a: Electron microscopy of phialoconidiogenesis inMetarrhizium anisopliae. Amer. J. Bot.59 (3), 317–326.
—, 1972 b: Fine structure of annellophores. II.Doratomyces nanus. Transactions of the British Mycological Society59 (2), 249–253.
—, 1972 c: Electron microscopy of conidiogenesis inChloridium chlamydosporis. Mycologia64, 1054–1065.
—, 1973: Fine structure of conidiogenesis in the holoblastic, sympodialTritirachium roseum. Can. J. Bot.51, 2033–2036.
Harvey, I. C., 1974: Striated fibres in the cytoplasm of the imperfect fungusPleiochaeta setosa (Kirchn.) Hughes. Protoplasma80, 371–380.
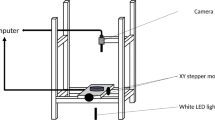
—, andH. T. Wenham, 1971: An apparatus for continuous microscopic examination of conidium ontogeny. New Zealand J. Bot.9 (1), 32–38.
Henderson, S. A., andB. C. Lu, 1968: The use of haematoxylin for squash preparations of chromosomes. Stain Technology43, 233–236.
Hughes, S. J., 1953: Conidiophores, conidia and classification. Can. J. Bot.31, 577–659.
Kendrick, B. (Editor), 1971: Taxonomy of fungi imperfecti. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Kiffer, E., F. Mangenot etO. Reisinger, 1971: Morphologie ultrastructurale et critères taxinomiques chez lesDeutéromycetes. IV.Doratomyces purpureofuscus (Fres.) Morton et Smith. Révie d'écologie et de Biologie du Sol8, 397–407.
Lowry, R. J., T. L. Durkee, andA. S. Sussman, 1967: Ultrastructural studies of microconidium formation inNeurospora crassa. J. Bact.94, 1757–1763.
Lu, B. C., andN. B. Raju, 1970: Meiosis inCoprinus. II. Chromosome pairing and the lampbrush diplotene stage of meiotic prophase. Chromosoma (Berl.)29, 305–316.
McKeen, W. E., 1971: Woronin bodies inErysiphe graminis D.C. Canad. J. Microbiol.17, 1557–1560.
Matile, P., andJ. Moor, 1968: Vacuolation: Origin and development of the lysosomal apparatus in root-tip cells. Planta (Berl.)80, 159–175.
Morgan-Jones, G., T. R. Nag Raj, andB. Kendrick, 1972: Conidium ontogeny inCoelomycetes. IV. Percurrently proliferating phialides. Can. J. Bot.50, 2009–2014.
Robards, A. W., 1970: Electron microscopy and plant ultrastructure. London: McGrawHill.
Reichle, R. E., andJ. V. Alexander, 1965: Multiperforate septation. Woronin bodies and septal plugs inFusarium. J. Cell Biol.24, 489–496.
Shearer, C. A., andJ. J. Motta, 1973: Ultrastructure and conidiogenesis inConioscypha (Hyphomycetes). Can. J. Bot.51, 1747–1751.
Spurr, A. R., 1969: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31–43.
Subramanian, C. V., 1971: Hyphomycetes, an account of Indian species, exceptCercosporae. New Dehli: Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
Trinci, A. P. J., A. Peat, andG. H. Banbury, 1968: Fine structure of phialide and conidiospore development inAspergillus giganteus Wehmer. Ann. Bot.32, 241–249.
Wergin, W. P., 1973: Development of Woronin bodies from microbodies inFusarium oxysporum f. sp.lycoperski. Protoplasma76, 249–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harvey, I.C. Light and electron microscope observations of conidiogenesis inPleiochaeta setosa (Kirchn.) Hughes. Protoplasma 82, 203–221 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276308
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276308