Summary
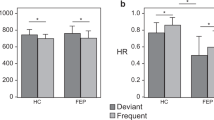
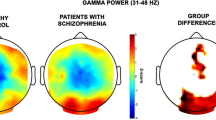
Our approaches to the use of EEG studies for the understanding of the pathogenesis of schizophrenic symptoms are presented. The basic assumptions of a heuristic and multifactorial model of the psychobiological brain mechainsms underlying the organization of normal behavior is described and used in order to formulate and test hypotheses about the pathogenesis of schizophrenic behavior using EEG measures. Results from our studies on EEG activity and EEG reactivity (= EEG components of a memory-driven, adaptive, non-unitary orienting response) as analyzed with spectral parameters and “chaotic” dimensionality (correlation dimension) are summarized. Both analysis procedures showed a deviant brain functional organization in never-treated first-episode schizophrenia which, within the framework of the model, suggests as common denominator for the pathogenesis of the symptoms a deviation of working memory, the nature of which is functional and not structural.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babloyantz A, Nicolis C, Salazar JM (1985) Evidence of chaotic dynamics of brain activity during the sleep sycle. Phys Lett A 111: 152–156
Dvorak I, Siska J, Wackermann J, Hrudova L, Dostalek C (1986) Evidence for interpretation of the EEG as a deterministic chaotic process with a low dimension. Activ Nerv Sup [Prague] 28: 228–230
Galderisi S, Mucci A, Mignone ML, Maj M, Kemali D (1992) CEEG mapping in drugfree schizophrenics. Differences from healthy subjects and changes induced by haloperidol treatment. Schizophr Res 6: 15–24
Grassberger P, Procaccia I (1983) On the characterization of strage attractors. Phys Rev Lett 50: 346–349
Günther W, Davous P, Godet JL, Guillibert E, Breitling D, Rondot P (1988) Bilateral brain dysfunction during motor activation in type II schizophrenia measured by EEG mapping. Biol Psychiatry 21: 295–311
Itil TM (1977) Qualitative and quantitative findings in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 3: 61–79
John ER, Prichep LS, Fridman J, Easton P (1988) Neurometrics: computerassisted differential diagnosis of brain dysfunction. Science 239: 162–169
Karlson CN, Coppola R, Morihisa JM, Weinberger DR (1987) Computed electroencephalographic activity mapping in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44: 514–517
Koukkou M (1980) EEG reactivity in acute schizophrenics reflects deviant (ectropic) state changes during information processing. In: Koukkou M, Lehmann D, Angst J (eds) Functional states of the brain: their determinants. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 265–290
Koukkou M (1982) EEG states of the brain, information processing, and schizophrenics primary symptoms. Psychiatry Res 6: 235–244
Koukkou-Lehmann M (1987) Hirnmechanismen normalen und schizophrenen Denkens. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Koukkou M, Lehmann D (1983) Dreaming: the functional state-shift hypothesis. A neuropsychophysiological model. Br J Psychiatry 142: 221–231
Koukkou M, Manske W (1986) Functional states of the brain and schizophrenics states of behavior. In: Shagass C, Josiassen RC, Roemer RA (eds) Brain electrical potentials and psychopathology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 91–114
Koukkou M, Lehmann D (1987 a) An information-processing perspective of psychophysiological measurements. J Psychophysiol 1: 109–112
Koukkou M, Lehmann D (1987 b) A reply to R.C. Howard's commentary on our paper: an information processing perspective on psychophysiological measurements. J Psychophysiol 1: 219–220
Koukkou M, Lehmann D (1993) A model of dreaming and its functional significance: the state-shift hypothesis. In: Moffitt A, Kramer M, Hoffmann R (eds) The functions of dreaming. State University of New York Press, Albany, NY, pp 51–115
Koukkou M, Bigler M, Lehmann D (1982) Central components of the orienting response (EEG reactivity) in acute and former schizophrenics, neurotics and normals. Adv Biol Psychiatry 9: 20–27
Koukkou M, Tremel E, Manske W (1991) A psychobiological model of the pathogenesis of schizophrenics symptoms. Int J Psychophysiol 10: 203–212
Koukkou M, Lehmann D, Wackermann J, Dvorak I, Henngeler B (1992) The dimensional complexity of the EEG in untreated acute schizophrenics, in persons in remission after a first schizophrenics episode, and in controls. Schizophr Res 6: 129
Koukkou M, Lehmann D, Wackermann J, Dvorak I, Henggeler B (1993) Dimensional complexity of EEG brain mechanisms in untreated schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 33: 397–407
Lehmann D, Koukkou M (1990) Brain states of visual imagery and dream generation. In: Kunzendorf RG, Sheikh AA (eds) The psychophysiology of mental imagery: theory, research and applications. Baywood, Amityville NY, pp 109–131
Mayer-Kress G, Layne SP (1987) Dimensionality of the human electroencephalogram. Ann NY Acad Sci 504: 62–87
Michel CM, Koukkou M, Lehmann D (1993) EEG reactivity in high and low symptomatic schizophrenics, using source modelling in the frequency domain. Brain Topogr 5: 389–394
Miyauchi T, Tanaka K, Hagimoto H, Miura T, Kishimoto H, Matsushita M (1990) Computerized EEG in schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 28: 488–494
Morstyn R, Duffy FH, McCarley RW (1983) Altered topography of EEG spectral content in schizophrenia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 56: 263–271
Rapp PE, Bashore TR, Martinerie JM, Albano AM, Zimmermann ID, Mees AI (1989) Dynamics of brain eletrical activity. Brain Topogr 2: 99–118
Röschke J, Basar E (1989) Correlation dimensions in various parts of cat and human brain in different states. In: Basar E, Bullock TH (eds) Brain dynamics — progress and perspectives. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 131–148
Shagass C (1987) Deviant cerebral functional topography as revealed by electrophysiology. In: Helmchen H, Henn FA (eds) Biological perspectives of schizophrenia. John Wiley, Chichester, pp 237–253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koukkou, M., Lehmann, D., Federspiel, A. et al. EEG reactivity and EEG activity in never-treated acute schizophrenics, measured with spectral parameters and dimensional complexity. J. Neural Transmission 99, 89–102 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271472
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271472