Abstract
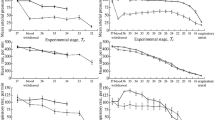
The effect of local cerebral hyperthermia on responses of pial microvessels of the mouse was investigated. A set protocol was followed, involving the performance of a craniotomy on anaesthetized animals and using intravital microscope-television closed circuitry. Controlled hyperthermic exposure was applied regionally by heating the brain surface with irrigating artificial cerebrospinal fluid. Microvascular responses such as changes in diameter, thrombosis and embolism were monitored and video-taped observations were further viewed and analysed. When both brain surface and core body temperatures were kept at 37° C, no changes in pial microvessels were noted. With core body temperature kept at 37° C and at a brain surface temperature of 43.1° C, passing emboli and arteriolar constriction were observed. A few minutes later, visible thrombosis was prevalent. Further spontaneous thrombo-embolic activity continued and at the end of a 50-min hyperthermic exposure, arterioles attained a constriction of 37%. Thrombus formation was sometimes massive enough to occlude fully the microvessel. The protocol followed in this study can be adopted to other small animal species and for a variety of experimental procedures involving hyperthermia and the pial microcirculation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Physiological Society (1993) Sourcebook for the use of animals in physiological research and teaching. American Physiological Society, USA
Bull JMC (1984) A review of systemic hyperthermia. Front Radiat Therap Oncol 18:171–176
Chao TC (1987) Post-mortem findings of heat stroke. In: Hales JRS, Richards DAB (eds) Heat stress: physical exertion and environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 297–302
Cheng KH, Hernandez M (1992) Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging detects structural damage in biological tissues upon hyperthermia. Cancer Res 52:6066–6073
Hales JRS (1987) Proposed mechanisms underlying heat stroke. In: Hales JRS, Richards DAB (eds) Heat stress: physical exertion and environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 85–102
Ketis NV, Lawler J (1990) Effect of thrombopondin antibody on the recovery of endothelial cells from hyperthermia. J Cell Sci 96:263–270
Khogali M (1987) Heat stroke: An overview with particular reference to the Makkah pilgrimage. In: Hales JRS, Richards DAB (eds) Heat stress: physical exertion and environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 21–36
Khogali M, Mustafa K (1984) Physiology of heat stroke. In: Hales JRS (ed) Thermal physiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 503–510
Levasseur JE, Wei EP, Raper AJ, Kontos HA, Patterson JRJr (1975) Detailed description of a cranial window technique for acute and chronic experiments. Stroke 6:308–316
Lin MT, Lin SZ (1992) Cerebral ischemia is the main cause for the onset of heat stroke syndrome in rabbits. Experimentia 48:225–227
Lin PS, Ho KC, Sung SJ, Gladding J (1992) Effect of tumour necrosis factor, heat and radiation on the viability and microfilament organization in cultured endothelial cells. Internat J Hypetherm 8:667–677
Mustafa KY, Omer O, Khogali M, Jamjoom A, Gumaa KA, Abu El Nasr N, Gader MA (1985) Blood coagulation and fibrinolysis in heat stroke. Br J Haematol 61:517–523
Mustafa MKY, Selig WM, Burhop KE, Minnear FL, Malik AB (1986) Hyperthermia induced pulmonary edema. J Appl Physiol 60:1980–1985
Ogura K, Takayasu M, Dacey RGJr (1991) Effects of hypothermia and hyperthermia on the reactivity of rat intracerebral arterioles in vitro. J Neurosurg 75:433–439
Panjwani GO, Mustafa MK, Muhailan A, Aneja IS, Owunwanne A (1991) Effect of hyperthermia on somatosensory evoked potential in the anesthetized rat. Electroencephal Clin Neurophysiol 80:384–391
Robins HI (1984) Role of whole-body hyperthermia in the treatment of neoplastic disease: its current status and future prospects. Cancer Res 44 (Suppl):4878–4883
Rofstad EK, Brustad T (1986) Primary and secondary cell death in human melanoma xenografts following hyperthermic treatment. Cancer Res 46:355–361
Rosenblum WI, El-Sabban F (1977) Platelet aggregation in the cerebral microcirculation: effect of aspirin and other agents. Circ Res 40:320–328
Ryan TP, Hoopes PJ, Taylor JH, Strohbehn JW, Roberts DW, Douple EB, Coughlin CT (1991) Experimental brain hyperthermia: techniques for heat delivery and thermometry. Internat J Radiat Oncol Biol Physics 20:739–750
Sato T (1989) Microvascular injury in hyperthermia of injecting warm water using noradrenaline into tumor feeding artery-induced tumor necrosis of walker-256. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 16:2833–2836
Stewart JR, Gibbs FA (1984) Hyperthermia in the treatment of cancer: perspectives on its promise and problems. Cancer 54:2823–2830
Tanira MOM, El-Sabban F, Fahim MA, Wasfi IA (1994) Aspirin alleviates increased susceptibility to thrombosis in pial microciruclation of dehydrated mice. J Vet Med Sci 56:245–248
Vainshtein GB, Kasadzhaeva GB, Krivcheno AI (1989) Functioning of the cerebral circulatory system in rabbits during hyperthermia. Fiziol Zhumal Sssr Imeni I-M-Sechenova 75:1608–1615
Yamada N (1989) The effects of hyperthermia on cerebral blood flow, metabolism and electroencephalogram. Brain Nerve 41:205–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Professor Khatim Y. Mustafa, who died in a tragic accident while this work was in progress
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sabban, F., Fahim, M.A. Local cerebral hyperthermia induces spontaneous thrombosis and arteriolar constriction in the pia mater of the mouse. Int J Biometeorol 38, 92–97 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01270666
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01270666