Summary
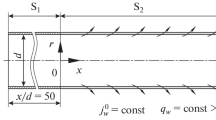
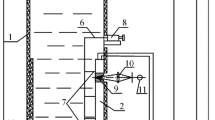
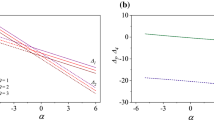
The effect of heat and mass transfer on the steady turbulent compressible boundary-layer flow with adverse pressure gradient are numerically studied. The Reynolds-averaged boundary-layer equations and their boundary conditions are transformed, in a suitable form for numerical solution, by using the compressible version of the Falkner-Skan transformation and the resulting coupled and nonlinear system of partial differential equations is solved using the Keller's-box method and a modified version of it. For the eddy kinematic viscosity the model developed by Cebeci and Smith is employed whereas for the turbulent Prandlt number model a modification of the extended Kays and Crawford's model is used. Numerical calculations are carried out for the case of air, at about free stream temperature of 300°K, and for a linearly retarded flow, known as Howarth's flow when the porous limiting surface is adiabatic, heated or cooled. The porous surface is subjected to a continuous or localized suction/injection velocity and the influence of this velocity as well as of the free-stream Mach number and of the heat-transfer parameter on the turbulent boundary-layer and the separation point is examined. It is hoped that in the absence of detailed investigations into this problem, the obtained results, presented in the figures, are very interesting and give a clearer insight into the mechanism of controlling a turbulent boundary-layer compressible flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlichting, H.: Boundary-layer theory, trans. by Kestin J. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1979, p. 635.
Gad-el-Hak, M., Bushnell, D. M.: Separation control: review. J. Fluid Eng., Transactions of the ASME113, 5–29 (1991).
Bushnell, D. M.: Longitudinal vortex control-techniques and applications. The 32nd Lanchester Lecture, Aeronautical Quartely, pp. 293–312, October 1992.
Gad-el-Hak, M., Bushnell, D. M.: Status and outlook of flow separation control, AIAA Paper 91-0037 (1991).
Kline, S. J., Robinson, S. K.: Turbulent boundary-layer structure: progress, status and challenges, in: Structure of Turbulence and Drag Reduction (Gyr, A., ed.). IUTAM Symposium Zürich, Springer, pp. 3–22, 1990.
Robinson, S. K.: Coherent motions in the turbulent boundary layer. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech.23, 603–639 (1991).
Blackwelder, R. F.: The eddy structures in bounded shear flows. In: Special course on skin friction drag reduction (Cousteix, J., ed.). AGARD Report 786, Paper 6, 1992.
Kim, J. J.: Study of turbulence structure through numerical simulations: the perspective of drag and reduction. In: Special course on skin friction drag reduction (Cousteix, J., ed.). AGARD Report 786, Paper 7, 1992.
Arnal, D.: Control of laminar-turbulent transition for skin friction drag reduction. In: Control of flow instabilities and unsteady flows (Meier, G. and Schnerr, G., eds.) pp. 119–153, CISM Courses and Lectures No. 369, Udine, 1995. Springer: Wien New York, 1996.
Gad-el-Hak, M.: Flow control by suction. In: Structure of turbulence and drag reduction (Gyr, A., ed.) IUTAM Symposium Zürich, Switzerland, Springer, pp. 357–360, 1990.
Sokolov, M., Antonia, R. A.: Response of a turbulent boundary layer to intensive suction through a porous strip. In: Proc. 9th symposium on turbulent shear flows. Kyoto Japan, Paper 5-3, 1993.
Wilkinson, S. P., Anders, J. B., Lazos, B. S., Bushnell, D. M.: Turbulent drag reduction research of NASA Langlay: progress and plans. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow9, 266–277 (1988).
Gad-el-Hak, M., Blackwelder, R. F.: Selective suction of controlling bursting events in a boundary layer. AIAA Journal27 (3), 308–314 (1989).
Myose, R. Y., Blackwelder, R. F.: Control of streamwise vortices using selective suction, AIAA Journal33 (6), 1076–1080 (1995).
Reynolds, W. S., Saric, W. S.: Experiments on the stability of the flat plate boundary layer with suction, AIAA Paper 82-1026, 1982.
Casalis, G., Copie, M. L., Airiau, Ch., Arnal, D.: Nonlinear analysis with PSE approach. In: IUTAM Symposium on nonlinear instability and transition in three-dimensional boundary layers. (Duck, P. W. and Hall, P., eds.), pp. 217–254. IUTAM Symposium, Manchester, UK 17–20 July 1995. Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, 1996.
Hefner, J. N., Bushnell, D. M.: Surface drag reduction via surface mass injection. In: Viscous drag reduction in boundary layers. Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics123, AIAA Washington, D. C., pp. 457–476, 1990.
Cummings, R. M., Schiff, L. B., Duino, J. D.: Experimental investigation of tangential slot blowing on a generic chined forebody. Journal of Aircraft32 (4), 812–824 (1995).
Sumitani, Y., Kasagi, N.: Direct numerical simulation of turbulent transport with uniform wall injection and suction. AIAA Journal33 (7), 1220–1228 (1995).
Spalart, P. R., Moser, R. D., Rogers, M. M.: Spectral methods for the Navier-Stokes equations with one infinite and two periodic directions. J. Comp. Phys.96, 297–324 (1991).
Spalart, P. R., Watmuff, J. H.: Experimental and numerical investigation of a turbulent boundary layer with pressure gradients. J. Fluid Mech.249, 337–371 (1993).
Marusic, I., Perry, A. E.: A wall-wake model for the turbulence structure of boundary layers, Part 2. Further experimental support. J. Fluid Mech.298, 389–407 (1995).
Spalart, P. R., Coleman, G. N.: Numerical study of a separation bubble with heat transfer. Europ. J. Mech.B 16, 169–189 (1997).
Cebeci, T., Bradshaw, P.: Physical and computational aspects of convective heat transfer. 1st ed. New York: Springer, 1984, p. 52.
Cebeci, T., Smith, A. M. O.: Analysis of turbulent boundary layers. New York: Academic Press, 1974.
Minkowycz, W. J., Sparrow, E. M., Schneider, G. E., Pletcher, R. H.: Handbook of numerical heat transfer. 1st ed. New York: Wiley, 1988, p. 120.
Cebeci, T.: A model for eddy conductivity and turbulent Prandtl number. ASME Journal of Heat Transfer95, 227–234 (1973).
Chen, C. J., Chiou, J. S.: Laminar and turbulent heat transfer in the pipe entrance region for liquid metals. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer24, 1179–1189 (1981).
Jischa, M., Rieke, H. B.: About the prediction of turbulent Prandtl and Schmidt number. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer22, 1547–1555 (1979).
Kays, W. M., Crawford, M. E.: Convective Heat and Mass Transfer. 3rd edn. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993.
Weigand, B., Ferguson, J. R., Crawford, M. E.: An extended Kays and Crawford turbulent Prandtl number model. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transfer40, (17) 4191–4196 (1997).
Schreier, S.: Compressible flow. New York: Wiley 1982.
Keller, H. B.: A new difference scheme for parabolic problems. Numerical solutions of partial differential equations, II. (Bramble, J., ed.): New York: Academic Press, 1970.
Rees, D. A. S.: Three-dimensional free convection boundary layers in porous media induced by a heated surface with spanwise temperature variations. Transactions ASME, J. Heat Transfer119, 792–798 (1997).
Rees, D. A. S.: Free convective boundary-layer flow from a heated surface in a layered porous medium. Journal of Porius Media (to appear) (1999).
Ling, J. X., Dybbs, A.: Forced convection over a flat plate submersed in a porous medium: variable viscosity case, Paper 87-WA/HT-23, New York, ASME 1987.
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (67th ed.), CRS Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1986–1987.
Meier, G. E. A., Schnerr, G. H.: Control of flow instabilities and unsteady flows. CISM Courses and Lectures, No. 369, 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kafoussias, N.G., Xenos, M.A. Numerical investigation of two-dimensional turbulent boundary-layer compressible flow with adverse pressure gradient and heat and mass transfer. Acta Mechanica 141, 201–223 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01268678
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01268678