Summary
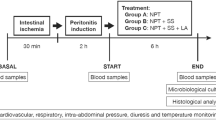
Taurolin (2%) was tested in a peritonitis in the rat. In a control group without treatment the mortality was 63% 80 h after infection. Intraperitoneal application of taurolin did not change this mortality rate but delayed the mortality by 8 h. Intravenous administration of taurolin increased mortality to 87%. In a second experimental protocol the dosis of bacteria was increased and 100% of the animals died within 16 h. Gentamicin-Piperacillin therapy reduced the mortality to 50%. With taurolin this effect of antibiotics could not be improved. In both groups taurolin was not able to reduce toxic lung edema. With these results and the knowledge of the literature taurolin cannot be recommended for clinical use.
Zusammenfassung
An einem Peritonitis-Modell der Ratte wurde 2%iges Taurolin getestet. Bei der 1. Versuchsreihe lag die Letalität einer Kontrollgruppe ohne Therapie nach 80 h bei 63%o. Die intraperitoneale, unmittelbar nach Infizierung der Ratten begonnene - insgesamt 10mal durchgeführte - Instillation von Taurolin verzögerte den Hauptzeitpunkt der Letalität um ein 8 h-Intervall, änderte aber nichts an der Gesamtletalität nach 80 h. Die intravenöse Therapie mit Taurolin verschlechterte die Letalität auf 87%. Bei einer 2. Versuchsreihe starben innerhalb 16 h alle Tiere einer Kontrollgruppe ohne Therapie. Eine Gentamycin-Piperacillin-Therapie senkte die Letalität auf 50%, während in einer weiteren Gruppe die zusätzliche intravenöse Gabe von Taurolin keine Verbesserung der Antibiotica-Wirkung erbrachte. In beiden Versuchsreihen konnte die intravenöse Verabreichung von Taurolin das sich entwickelnde, toxische Lungenödem nicht mildern. Unter Berücksichtigung der vorgestellten Ergebnisse sowie der in der Literatur auftretenden, in dieser Arbeit erwähnten Unklarheiten kann ein klinischer Einsatz von Taurolin nicht uneingeschränkt empfohlen werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Browne MK, Leslie GB, Pfirrmann RW (1976) Taurolin, a new chemotherapeutic agent. J Appl Bacteriol41: 363
Browne MK, Leslie GB, Pfirrmann RW, Brodhage H (1977) The in vitro and in vivo activity of Taurolin against anaerobic pathogenic organism. Surg Gynecol Obstet145:842
Browne MK, Mackenzie M, Doyle PJ (1978) A controlled trial of Taurolin in established bacterial peritonitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet146:721
Browne MK (1981) The treatment of peritonitis by an antiseptic - Taurolin. Pharmatherapeutica2:517
Biihler HU, Milic S, Wicki O (1978) Neuartige chirurgische Spüllösung. Helv Chir Acta45:143
Ellis H (1971) The cause and prevention of postoperative intraperitoneal adhesions. Surg Gynecol Obstet133:497
Erb F, Febvay N, Imbenotte M (1982) Structural investigation of a new organic antiseptic: Taurolidine. Talanta29:953
Geistlich-Pharma, Wolhusen (Schweiz) (1980) Mittel zur Verhinderung oder Verringerung von Adhäsionsbildungen oder zur Beseitigung oder Auflösung vorhandener Adhäsionen bei Körpergeweben. Offenlegungsschrift 3017711 beim Dt. Patentamt (1980)
Geistlich-Pharma, Wolhusen (Schweiz) (1968) Novel Perhydro-1,2,4-Thiadiazine Dioxides(1,1), their preparation and compositions containing them. Patent Specification L124/285; Englisches Patentamt
Hugh TB, Ellis H (1964) Postoperative abdominal adhesions; an experimental study of the value of polyvinylpyrrolidone in prophylaxis. Br J Surg51:381
Knight BJ, Skellern GG, Browne MK, Pfirrmann RW (1981) The chracterisation and quantitation by highperformance liquid chromatography of the metabolites of Taurolin. Br J Clin Pharmacol12:439
Linder MM, Ott W, Wesch G (1980) Die antibakterielle Behandlung der eitrigen Peritonitis: prospektiv randomisierter Vergleich von Antibiotika mit dem neuen Chemotherapeutikum und Antiendotoxin Taurolin. Langenbecks Arch Chir Chirurgisches Forum, S 67
Linder MM, Ott W, Wesch G, Wicki O, Marti MC, Moser G (1981) Die Behandlung der eitrigen Bauchfellentziindung. Langenbecks Arch Chir353:241
Marti MC, Moser G, Bordigoni PH (1978) Empyèmes pleuraux et Tauroflex — Etude d'un nouveau bactéricide. Schweiz Med Wochenschr108:215
Marti MC, Moser G, Wicki O, Linder MM, Del Ponte F (1979) Administration intraveineuse et intrapéritonéale d'un antiseptique: 65 cas de péritonites diffuses traitées par du Taurolin. Helv Chir Acta46:755
Milic S, Wicki O (1976) Bauchtrauma und Sepsis. J43:707
Moser G, Marti MC (1978) A propos de 40 cas de péritonites traitées sans antibiotiques: Application intrapéritonéale et intraveineuse de Tauroflex. Schweiz Rundsch Med (Praxis)67:425
Moser G, Marti MC (1978) Peritonite stercorale. J Chir (Paris)115:175
Myers E, Allwood MC, Gidley MJ, Sanders JKM (1980) The relationship between structure and activity of Taurolin. J Appl Bacteriol48:89
Myers E, Allwood MC (1980) The interaction between taurolin and endotoxin. Microbios Lett13:141
Oettel H, Rothländer H, Schulze W (1954) icht über ein neues Verfahren zur Verhütung von Bauchfellverwachsungen durch Kollidon. Fortschr Med72:177
Pfirrmann RW, Leslie GB (1979) The anti-endotoxin activity of Taurolin in experimental animals. J Appl Bacteriol46:97
Ruegsegger CH, Mosimann R (1978) La Tauroline dans les infections intra-abdominales. Helv Chir Acta45:743
Staub NC (1974) Pulmonary edema. Physiol Rev54:678
Steinbach-Lebbin C Ganz AJ, Chang A, Waser PG (1982) Über die Pharmakokinetik von Taurolin. Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res32:1542
Upplegger H (1956) Die Verhütung von Bauchfelladhäsionen durch Kollidon. Chirurg27:365
Vankemmel M, Scherpereel PH, Pfirrmann RW (1978) Infections bilio-pancréatiques sévères: utilisation isolée, per- et postopératoire d'un antiseptique par voies locale et générale. Nouv Presse Méd46:4229
Wesch G, Petermann CH, Linder MM (1983) Medikamentöse Therapie der Peritonitis. Fortschr Med101:545
Wicki O, Pfirrmann RW (1979) Taurolin bei Peritonitis. In: Burri C, Rüter A (Hrsg) Aktuelle Probleme in Chirurgie und Orthopädie, Bd 12, S 42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hart, H., Seifert, J. & Brendel, W. Wirkung und Nebenwirkung von Taurolin bei einer experimentellen Peritonitis der Ratte. Langenbecks Arch Chiv 368, 149–160 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01261231
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01261231