Summary
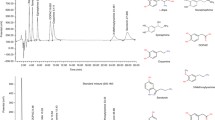
Simultaneous plasma and cerebrospinal free and sulfoconjugated norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine and homovanillic acid determinations in 38 patients with various neurological disorders have shown consistently lower concentrations of dopamine sulfate, norepinephrine sulfate, and epinephrine sulfate in the cerebrospinal fluid than in plasma. An approximately three fold increase of plasma dopamine sulfate concentrations following banana ingestion did not result in increased dopamine sulfate concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid. There were positive correlations between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of free norepinephrine and epinephrine as well as norepinephrine sulfate, dopamine sulfate and free homovanillic acid. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma are apparently separated by the blood-brain barrier impermeable to catecholamine sulfates from the blood. Some other data and the observed positive correlation between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma dopamine and norepinephrine sulfates suggests however that catecholamine sulfates may pass from cerebrospinal fluid to the blood and reflect events in the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buu, N. T., Duhaime, J., Kuchel, O.: The formation and removal of dopamine sulfate in rat brain. In: Proceedings of Sulfate Metabolism and Sulfate Conjugation. Workshop in Noordwijerhout, The Netherlands (Mulder, G. J., Caldwell, J., eds.), pp. 93–98. London: Taylor & Francis.
Chalmers, J. P., Blessing, W. W., West, M. J., Howe, P. R. C., Costa, M., Furness, J. B.: Importance of new catecholamine pathways in control of blood pressure. Clin. Exp. Hyper.3, 393–416 (1981).
Davidson, L., Vandongen, R., Beilin, L. J.: Effect of eating bananas on plasma free and sulfate-conjugated catecholamines. Life Sci.29, 1773–1778 (1981).
Davson, H.: The rates of disappearance of substances injected into the sub-arachnoid space of rabbits. J. Physiol. (London)128, 52–53 (1955).
Dencker, S. J., Haggendal, M., Ilves-Haggendal, M.: Presence of free and conjugated noradrenaline in human cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Physiol. Scand.69, 140–146 (1967).
Eide, I., Kolloch, R., De Quattro, V., Miano, L., Dugger, R., Van der Meulen, J.: Raised cerebrospinal fluid norepinephrine in some patients with primary hypertension. Hypertension1, 255–260 (1979).
Elchisak, M. A., Polinski, T. J., Ebert, M. H., Powers, K. J., Kopin, I. J.: Contribution of plasma homovanillic acid (HVA) to urine and cerebrospinal fluid HVA in the monkey and its pharmacokinetic disposition. Life Sci.23, 2339–2348 (1978).
Elchisak, M. A., Cosgrove, S. E., Ebert, M. H., Burns, R. S.: Distribution of free and conjugated dopamine in monkey brain, peripheral tissues and cerebrospinal fluid determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Brain Res.279, 171–176 (1983).
Jenner, W. N., Rose, F. A.: Studies on the sulphation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-ethylamine (dopamine) and related compounds by rat tissues. Biochem. J.135, 109–114 (1973).
Meek, J. L., Neff, N. H.: Acidic and neutral metabolites of norepinephrine: Their metabolism and transport from brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.181, 457–462 (1972).
Rennick, B., Quebbermann, A.: Site of excretion of catechol and catecholamines: Renal metabolism of catechol. Am. J. Physiol.218, 1307–1312 (1970).
Rivett, A. J., Eddy, B. J., Roth, J. A.: Contribution of sulfate conjugation, deamination and O-methylation to metabolism of dopamine and norepinephrine in human brain. J. Neurochem.39, 1009–1016 (1982).
Sharpless, N. S., Tyce, G. M., Thal, L. J., Waltz, J. M., Tabaddor, K., Wolfson, L. I.: Free and conjugated dopamine in human ventricular fluid. Brain Res.217, 107–118 (1981).
Snider, S. R., Kuchel, O.: Dopamine: An important neurohormone of the sympatho-adrenal system. Significance of increased peripheral dopamine release for the human stress response and hypertension. Endocr. Rev.4, 291–309 (1983).
Sperk, G.: Simultaneous determination of serotonin, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J. Neurochem.38, 840–843 (1982).
Tyce, G., Sharpless, N. S., Kerr, F. W. L., Muenter, M. D.: Dopamine conjugate in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurochem.34, 210–212 (1980).
Wang, P. C., Buu, N. T., Kuchel, O., Genest, J.: Conjugation patterns of endogenous plasma catecholamines in human and rat: A new specific method for analysis of glucuronide conjugated catecholamines. J. Lab. Clin. Med.101, 141–151 (1983).
Ziegler, M. G., Lake, C. R., Wood, J. H., Brooks, B. R., Ebert, M. E.: Relationship between norepinephrine in blood and cerebrospinal fluid in the presence of a blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier for norepinephrine. J. Neurochem.28, 677–679 (1977).
Ziegler, M. G., Lake, C. R., Wood, J. H., Brooks, B. R.: Relationship between cerebrospinal fluid, norepinephrine and blood pressure in neurologic patients. Clin. Exp. Hyper.2, 995–1008 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council of Canada to a multidisciplinary group in hypertension.
We wish to thank for efficient nursing help Mrs.M. Vautour R. N.,F. Salvail R. N.,M. A. Boutin R. N., andC. Doyon R. N., for laboratory work Mrs.Dominique Chevalier andCarmen Savard, for statistical analysis Dr.Michel Bourque and for secretarial help Mrs.Sylvie Ouellet-Collon.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuchel, O., Hausser, C., Buu, N.T. et al. CSF sulfoconjugated catecholamines in man: Their relationship with plasma catecholamines. J. Neural Transmission 62, 91–97 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01260418
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01260418