Abstract
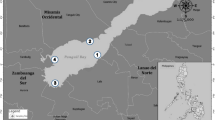
A coordinated program ofin situ and laboratory bioassays supported by water quality analyses was used to evaluate the potential effect of a coal ash storage facility on a yellow perch (Perca flavescens) spawning area. The facility is located in the Zekiah Swamp watershed, a tributary of the Wicomico River, MD.In situ bioassays were conducted in Zekiah Swamp Run and reference locations in 1989 and 1990. Larval mortality was high in non-tidal areas of Zekiah Swamp Run, both at a site upstream and beyond the influence of the facility, and at a site downstream of the facility. Mortality was significantly less at a nearby reference stream and at a station in the tidal area of Zekiah Swamp Run. Analysis of water samples for metals (including inorganic monomeric aluminum), organic contaminants, and pH, as well as measurements of stream flow, did not identify a specific cause for the mortality. The field and laboratory bioassays showed that, although leachate from the ash facility contributed to local contamination of ground water, the facility does not appear to be responsible for the poor survival of larval yellow perch.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Correll, D. L., Miklas, J. J., Hines, A. H., and Schafer, J. J.: 1986,Water, Air, and Soil Poltut. 35, 63.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): 1986a,Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, SW-846. Third Edition. Washington, DC.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): 1986b.Quality Criteria for Water 1986, EPA 440/5-86-001. Washington, DC.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): 1987.Handbook of Methods for Acid Deposition Studies, Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, Las Vegas, NV. EPA 600/4-87/026.
Greening, H. S., Janicki, A. J., Klauda, R. J., Baudler, D. M., Levin, D. M., and Perry, E. S.: 1989,An Evaluation of Stream Liming Effects on Water Quality and Anadromous Fish Spawning in Maryland Coastal Plain Streams: 1988 Results, Report prepared for Living Lakes, Inc. Washington, DC and Maryland Power Plant Research Program, Annapolis, MD.
Hall, L. W., Jr., Pinkney, A. E., Herman, R. L., and Finger, S. E.: 1987,Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 391.
Janicki, A.: 1989,A Survey of Potential Yellow Perch Spawning Streams in the Maryland Portion of the Chesapeake Bay Drainage, Prepared for Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Chesapeake Bay Research and Monitoring Division by Coastal Environmental Services, Linthicum, MD.
Janicki, A. J. and Greening, H. S.: 1988,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 41, 359.
Klauda, R. J.: 1989,Definitions of Critical Environmental Conditions for Selected Chesapeake Bay Fin Fishes Exposed to Acidic Episodes in Spawning and Nursery Areas, Prepared for Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Tidewater Administration by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Shady Side, MD.
Muncy, R. J.: 1959,Evaluation of the Yellow Perch Hatchery Program in Maryland, Maryland Department of Research and Education, Resource Study Rept. 15.
O'Dell, J.: 1987,Status of Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens) in Maryland, 1987, Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Annapolis, MD.
O'Dell, J., Gabor, J., and Dintaman, R.: 1975,Survey of Anadromous Fish Spawning Areas for: Potomac River and Upper Chesapeake Bay Drainages, July 1970–January 1975. Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Annapolis, MD. Completion Rept., Project AFC-8.
Price, R. and Keating, R.: 1991,Assessment of Water Quality Impacts from the Faulkner Fly-ash Facility, Prepared for Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Power Plant and Environmental Review by Environmental Resources Management, Annapolis, MD. PPER-MP-59.
Richkus, W. A. and Stroup, F.: 1987,Source Document: Characterization of the Biology of and Fisheries for Maryland Stocks of Yellow Perch, Prepared for Maryland Department of Natural Resources, Tidewater Administration by Versar, Inc., ESM Operations, Columbia, MD.
SAS Institute, Inc. (SAS): 1985,SAS User's Guide: Statistics, Version 5 Edition, Cary, NC. SAS Institute Inc.
Theis, T. L. and Gardner, K. H.: 1990,CRC Crit. Rev. Environ. Control 20, 21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burton, W.H., Pinkney, A.E. Yellow perch larval survival in the Zekiah Swamp watershed (Wicomico River, Maryland) relative to the potential effects of a coal ash storage facility. Water Air Soil Pollut 72, 235–249 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01257127
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01257127