Abstract
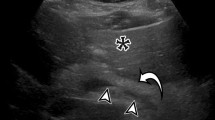
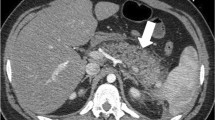
Intravenous morphine sulfate has been used in conjunction with cholescintigraphy. We studied the variations in the degree and duration of the effects of 2 mg morphine on biliary kinetics in patients with gallbladder nonvisualization and undertook a comparison with biliary kinetics in patients not given morphine. Of 24 morphine-augmented cholescintigrams that were obtained without additional injection of technetium-99m diisopropyl-iminodiacetic acid (DISIDA), 19 showed continued gallbladder nonvisualization. Time-activity curves (TACs) of the liver parenchyma and common bile/hepatic duct (CD) of the entire study (before and after morphine) were obtained. In two patients, the CD was not sufficiently visualized to define a region of interest. In 17 patients, the peak CD activity was observed between 14 and 47 min after injection of99mTc-DISIDA. In these 17, the TAC of the CD was declining essentially in parallel with the TAC of the liver parenchyma at the end of the first hour before morphine. After morphine injection, CD activity slowly increased for a variable duration in nine patients, while it continued to decrease in eight. CD activity between 1 h and 2 h showed a continuously decreasing pattern in another group of 20 patients who did not receive morphine despite gallbladder nonvisualization at 1 h. In summary, no significant effect of 2 mg of intravenous morphine on biliary kinetics was detected scintigraphically in a considerable proportion of patients. Also, there was considerable variation in the duration of the effect of morphine, when such an effect was present. This observation may have significant clinical implications for morphine-augmented cholescintigraphy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy P, Solomon J, Roseman DL. Narcotic anesthetic drugs: their effect on biliary dynamics.Arch Surg 1980; 115: 710–711.
Dedrick DF, Tanner WW, Bushkin FL. Common bile duct pressure during enflurance anesthesia: effects of morphine and subsequent naloxone.Arch Surg 1980; 115: 820–821.
Tanaka M, Ikeda S, Nakayama F. Change in bile duct pressure responses after cholecystectomy: loss of gallbladder as a pressure reservoir.Gastroenterology 1984; 87: 1154–1159.
Choy D, Shi EC, McLean RG, Hoscho R, Murray IPC, Ham JM. Cholescintigraphy in acute cholecystitis: use of intravenous morphine.Radiology 1984; 151: 203–207.
Kim EE, Pjura G, Lowery P, Nguyen M, Pollac M. Morphine augmented cholescintigraphy in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis.AJR 1986; 147: 1177–1179.
Vasquez TE, Greenspan G, Evans DG, Halpern SE, Ashburn WL. Clinical efficacy of intravenous morphine administration in hepatobiliary imaging for acute cholecystitis.Clin Nucl Med 1988; 13: 4–6.
Kistler AM, Ziessman HA, Gooch D, Bitterman P. Morphineaugmented cholescintigraphy in acute cholecystitis: a satisfactory alternative to delayed imaging.Clin Nucl Med 1991; 16: 404–406.
Fink-Benett D, Balon H, Robins T, Tsai D. Morphine-augmented cholescintigraphy: its efficacy in detecting acute cholecystitis.J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 1231–1233.
Kim CK, Tse KM, Juweid M, Woda A, Mozley PD, Alavi A. Cholescintigraphy in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis: morphine-augmentation is superior to delayed imaging.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 1866–1870.
Ogawa Y, Tanaka M. Biliary pressure variation in coordination with migrating motor complex of duodenum in patients with cholecystectomy and effects of morphine and cerulein.Dig Dis Sci 1992; 37: 1531–1536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C.K., Lim, J.K. & Machac, J. Variable bile retention on cholescintigraphy after morphine administration. Eur J Nucl Med 23, 1464–1467 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01254469
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01254469