Summary
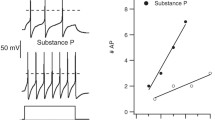
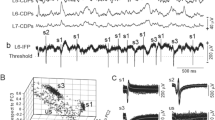
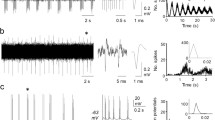
Dorsal root potentials (DRP) and dorsal root reflexes (DRR) have been recorded from the isolated cord of the neonate rat. A single stimulus to the adjacent rostral or adjacent caudal dorsal root or dorsal columns evoked a DRP, the peak amplitude of which was reached in 110–115 msec and which decayed exponentially over most of its time course (time constant 800–850 msec). The same stimuli evoked field potentials in the dorsal horn comprising fast negative, slow negative and slow positive potentials. DRP had a lower threshold than DRR and reached a maximal amplitude at stimulus voltages sub-maximal for DRR. Increasing the intensity of stimulation shortened the latency of DRP and prolonged its time course. DRR and DRP were depressed by a prior conditioning stimulus (CS) and by the addition of Mg++ ions to the bathing solution. A CS was more effective in producing depression of responses evoked more rostrally than more caudally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagust, J., Kerkut, G. A. Some effects of magnesium ions upon conduction and synaptic activity in the isolated spinal cord of the mouse. Brain Res.177, 410–413 (1979).
Barron, D. H., Matthews, B. H. C. The interpretation of potential changes in the spinal cord. J. Physiol. (Lond.)92, 276–321 (1938 a).
Barron, D. H., Matthews, B. H. C.: Dorsal root reflexes. J. Physiol. (Lond.)94, 26 P (1938 b).
Eccles, J. C., Eccles, R. M., Magni, F. Central inhibitory action attributable to presynaptic depolarization produced by muscle afferent volleys. J. Physiol. (Lond.)159, 147–166 (1961 a).
Eccles, J. C., Kostyuk, P. G., Schmidt, R. F. Central pathways responsible for depolarization of primary afferent fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)161, 237–257 (1962 a).
Eccles, J. C., Kostyuk, P. G., Schmidt, R. F. Presynaptic inhibition of the central actions of flexor reflex afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.)161, 258–281 (1962 b).
Eccles, J. C., Kozak, W., Magni, F. Dorsal root reflexes of muscle group I afferent fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)159, 128–146 (1961 b).
Eccles, J. C., Krnjević, K. Potential changes recorded inside primary afferent fibres within the spinal cord. J. Physiol. (Lond.)149, 250–273 (1959).
Eccles, J. C., Magni, F., Willis, W. D. Depolarization of central terminals of group I afferent fibres from muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)160, 62–93 (1962 c).
Eccles, J. C., Malcolm, J. L. Dorsal root potentials of the spinal cord. J. Neurophysiol.9, 139–160 (1946).
Eccles, J. C., Schmidt, R. F., Willis, W. D. The location and the mode of action of the presynaptic inhibitory pathways on to group I afferent fibres from muscle. J. Neurophysiol.26, 506–622 (1963).
Evans, R. H., Francis, A. A., Watkins, J. C.: Ionic dependency of ventral root responses to excitatory amino acids in isolated spinal cord of frog and rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)263, 122 P (1976).
Evans, R. H., Francis, A. A., Watkins, J. C. Selective antagonism by Mg2+ of amino acid-induced depolarization of spinal neurones. Experientia33, 489–491 (1977).
Gasser, H. S., Graham, H. T. Potentials produced in the spinal cord by Stimulation of the dorsal roots. Am. J. Physiol.103, 303–320 (1933).
Gilbert, M., Stelzner, D. J. The development of descending and dorsal root connections in the lumbrosacral spinal cord of the postnatal rat. J. comp. Neurol.184, 821–838 (1979).
Gotch, F., Horsley, V. On the mammalian nervous system, its functions, and their localisation, determined by an electrical method. Phil. Trans. R. Soc.B 182, 267–526 (1891).
Koketsu, K. Intracellular slow potentialof dorsal root fibres. Am. J. Physiol.184, 338–344 (1956).
Lloyd, D. P. C., McIntyre, A. K. On the origins of dorsal root potentials. J. gen. Physiol.32, 409–443 (1949).
May, M. K., Biscoe, T. J. An investigation of the foetal rat spinal cord. II. An ultrastructural study on the development of synapses with the aid of observations on some electrophysiological properties. Cell Tiss. Res.158, 251–268 (1975).
Nicoll, R. A. Dorsal root potentials and changes in extracellular potassium in the spinal cord of the frog. J. Physiol. (Lond.)209, 113–127 (1979).
Qtsuka, M., Konishi, S. Electrophysiology of mammalian spinal cord in vitro. Nature (Lond.)252, 733–734 (1974).
Preston, P. R., Wallis, D. I.: Dorsal root potentials recorded in the isolated spinal cord of the neonate rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)289, 84 P (1979).
Roberts, M. H. T., Wallis, D. I. A method for recording the polarisation of primary afferents and efferents in the spinal cord in vivo using the sucrose gap method. J. Pharmac. Methods2, 295–304 (1979).
Schmidt, R. F. Presynaptic inhibition in the vertebrate central nervous system. Ergebn. Physiol.63, 20–101 (1971).
Takagi, S. F. The slow potential observed in the dorsal column-root preparation. Part I. On the origin of the slow potential in the spinal cord. Jap. J. Physiol.2, 111–124 (1951).
Toennies, J. F. Conditioning of afferent impulses by reflex discharges over the dorsal roots. J. Neurophysiol.3, 515–525 (1939).
Wall, P. D. Repetitive discharge of neurons. J. Neurophysiol.22, 305–320 (1959).
Wall, P. D. Presynaptic control of impulses at the first central synapse in the cutaneous pathway. Progress in brain research, 12, Physiology of spinal neurones (Eccles, J. C., Schadé, J. P., eds.), pp. 92–118. Amsterdam: Elsevier. 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preston, P.R., Wallis, D.I. Characteristics of dorsal root potentials recorded from the isolated spinal cord of the neonate rat. J. Neural Transmission 48, 271–287 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250662
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250662