Abstract
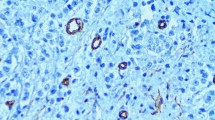
A series of 202 breast cancer biopsy specimens were analysed immunohistochemically for collagen IV to demonstrate basement membrane (BM) structures and blood vessels within tumour tissue. Integrity of the BM was graded into four categories and the number of vascular channels per square millimetre of tumour tissue were counted. Defective BM structures were significantly related to high grade, lack of tubule formation, invasive disease, high S-phase fraction and variability in nuclear size and shape. High vascular channel density was related to poor tumour differentiation and a high proliferation rate of cancer cells as well as to the absence of tubule formation, inconspicuous intraductal growth and low progesterone receptor content. High vascular density and defective BM structures were signs of poor prognosis and short recurrence-free survival in the entire cohort and also in local tumours. In multivariate analysis, the vascular density had independent prognostic value, as did the diameter, axillary lymph node status and mitotic rate. The counting of vascular channels within the tumour provides additional prognostic information in breast cancer, in contrast to analysis of the BM integrity which shows hardly any prognostic information additional to that provided by the special histological features, e.g. tubule formation and intraductal growth pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Eskelinen M, Kosma V-M, Marin S, Alhava E, Syrjänen K (1991a) Hormone receptors as prognostic factors in female breast cancer. Ann Med 23:643–648
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Eskelinen M, Kosma V-M, Marin S, Alhava E, Syrjänen K (1991b) Prognostic scores combining clinical, histological and morphometric variables in assessment of the disease outcome in female breast cancer. Int J Cancer 49:886–892
Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Eskelinen M, Kosma V-M, Marin S, Alhava E, Syrjänen K (1992) Lymphocyte infiltrates as a prognostic variable in female breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 28A:859–864
Barnhill RL, Levy MA (1993) Regression thin cutaneous malignant melanomas (<1.0 mm) are associated with angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 143:99–104
Bosari S, Lee AKC, DeLellis RA, Wiley BD, Heatley GJ, Silverman ML (1992) Microvessel quantitation and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 23:755–761
Daher N, Abourachid H, Bove N, Petit J, Burtin P (1987) Collagen IV staining pattern in bladder carcinomas: relationship to prognosis. Br J Cancer 55:665–671
Daidone MG, Silvestrini R, D'Errico A, Di Fronzo G, Benini E, Manchini AM, Garbisa S, Liotta LA, Grigioni WF (1991) Laminin receptors, collagenase IV and prognosis in node-negative breast cancers. Int J Cancer 48:529–532
Domagala W, Striker G, Szadowska A, Dukowicz A, Weber K, Osborn M (1992) Cathepsin D in invasive ductal NOS breast carcinoma as defined by immunohistochemistry. No correlation with survival at 5 years. Am J Pathol 141:1003–1012
Eskelinen M, Lipponen P, Papinaho S, Aaltomaa S, Kosma V-M, Klemi P, Syrjänen K (1992) DNA flow cytometry, nuclear morphometry, mitotic indices and steroid receptors as independent prognostic factors in female breast cancer. Int J Cancer 51:555–561
Eusebi V, Foschini MP, Betts CM, Gherardi G, Millis RR, Bussolati G, Azzopardi JG (1993) Microglandular adenosis, apocrine adenosis, apocrine adenosis, and tubular carcinoma of the breast. An immunohistochemical comparison. Am J Surg Pathol 17:99–109
Fallowfield ME, Cook MG (1991) The vascularity of primary cutaneous melanoma. J Pathol 164:241–244
Folkman J (1990) What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82:4–6
Folkman J, Klagsbrun M (1987) Angiogenic factors. Science 235:442–447
Lah TT, Kokalj-Kunovar M, Strukelj B, Pungercar J, Barlic-Maganja D, Drobnick-Kosorok M, Kastelic L, Babnik J, Golouh R, Turk V (1992) Stefins and lysosomal cathepsins B, L, and D in human breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer 50:35–44
Lee E, Desu M (1972) A computer program for comparing k samples with right censored data. Computer Program Biomed 2:315–320
Lipponen P (1992) The prognostic value of basement membrane morphology, tumour histology and morphometry in superficial bladder cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 119:295–300
Lipponen P, Aaltomaa S, Eskelinen M, Kosma V-M, Marin S, Syrjänen K (1992) The changing importance of prognostic factors in breast cancer during long-term follow-up. Int J Cancer 51:698–702
Ljubimov AV, Bartek J, Couchman JR, Kapuller LL, Veselov VV, Kovarik J, Perevoshchikov AG, Krutovskikh VA (1992) Distribution of individual components of basement membrane in human colon polyps and adenocarcinomas as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Int J Cancer 50:562–566
Miettinen M (1989) Immunostaining of intermediate filament proteins in paraffin sections. Evaluation of optimal protease treatment to improve the immunoreactivity. Pathol Res Pract 184:431–436
Monschke F, Muller W-U, Winkler U, Streffer C (1991) Cell proliferation and vascularisation in human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer 49:812–815
Raymond WA, Leong A S-Y (1991) Assessment of invasion in breast lesions using antibodies to basement membrane components and myoepithelial cells. Pathology 23:291–297
Srivastava A, Laidler P, Davies RP, Horgan K, Hughes LE (1988) The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76–4.0 mm thick) skin melanoma. A quantitative histologic study. Am J Pathol 133:419–423
Vihko R, Jänne O, Kontula R, Syrjälä P (1980) Female sex steroid receptor status in primary and metastatic breast carcinoma and it's relationship to serum steroid and peptide hormone levels. Int J Cancer 26:13–21
Visscher DW, Sarkar F, LoRusso P, Sakr W, Otosen S, Wykes S, Crissman JD (1993) Immunohistologic evaluation of invasion-associated proteases in breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol 6:302–306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipponen, P., Ji, H., Aaltomaa, S. et al. Tumour vascularity and basement membrane structure in breast cancer as related to tumour histology and prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 120, 645–650 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245375
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01245375