Summary
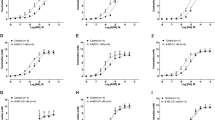
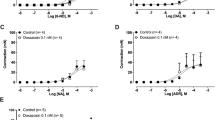
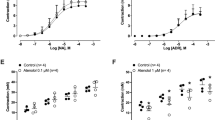
The ergot alkaloid derivatives, lisuride (LIS) and terguride (TDHL), known to interact with central dopamine receptors as agonist and partial agonist, respectively, were studied on the field-stimulated mouse vas deferens, where recently the existence of presynaptic dopamine receptors has been evidenced. LIS was a competitive antagonist at prejunctional α2 and DA1 receptors situated on the sympathetic nerve terminals of the mouse, with a pA2 value of 9.2 and 9.1, respectively. LIS was also able to antagonize the effects of LY 171555, selective DA2 agonist, but the type of interaction cannot be conceptualized in terms of competitive antagonism. Likewise, the type of interaction of TDHL with dopaminergic and adrenergic agonist-activated sites is not suggestive of a competitive antagonism. Based on these results, it seems that central and peripheral pharmacologic profiles of LIS and TDHL cannot be overlapped, LIS being a potent DA1- and α2-antogonist with a high degree of specifity for these receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunlakshana O, Schild HO (1959) Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 14: 48–58
Carlsson M, Carlsson A, Eriksson E (1987) The intrinsic activities of the partial dopamine receptor agonists (−)-3 PPP and TDHL on pituitary dopamine receptors are lower in female than in male rats. Eur J Pharmacol 142: 39–43
Carratú MR, Conte-Camerino D, De Serio A, Ferrari E, Mitolo-Chieppa D (1989) Evidence for the existence of prejunctional receptor sites for dopamine in the mouse vas deferens. J Auton Nerv Syst 27: 221–228
Cote T, Munemura M, Kebabian J (1979) Lisuride hydrogen maleate: an ergoline with β-adrenergic antagonist activity. Eur J Pharmacol 59: 303–306
Goldberg LI, Kohli JD (1983) Peripheral dopamine receptors: a classification based on potency series and specific antagonism. TIPS 4: 64–66
Gräf KJ, Neumann F, Horowski R (1976) Effect of the ergot derivative lisuride hydrogen maleate on serum prolactin concentrations in female rats. Endocrinology 98: 598–605
Horowski R, Wachtel H (1976) Direct dopaminergic action of lisuride hydrogenmaleate, an ergot derivative, in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 36: 373–383
Horowski R (1983) Pharmacological effects of lisuride and their potential role in further research. In: Calne DB, Horowski R, McDonald RJ, Wuttke W (eds) Lisuride and other dopamine agonists. Raven Press, New York, p 127
Hughes J, Kosterlitz MV, Leslie FM (1975) Effect of morphine on adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Assessment of agonist and antagonist potencies of narcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol 53: 371–381
Kashube M, Zetler G (1989) Noradrenergic, purinergic, and cholinergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens: influence of field-stimulation parameters, reserpinization, 6-hydroxydopamine and 4-aminopyridine. J Neural Transm 76: 38–53
Kehr W (1977) Effect of lisuride and other ergot derivatives on monoaminergic mechanisms in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 41: 261–273
Kehr W, Wachtel H, Schneider HH (1983) Dopaminergic and antidopaminergic properties of ergolines structurally related to lisuride. Acta Pharm Suec 2: 98–110
Koller W, Herbster G (1987) Terguride, a mixed dopamine agonist-antagonist, in animal models of Parkinson's disease. Neurology 37: 723–727
Krause W, Dorow R, Nieuweboer B, Hasan SH (1984) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the ergot derivative transdihydrolisuride in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27: 335–339
McDonald RJ, Horowski R (1983) Lisuride in the treatment of Parkinsonism. Eur Neurol 22: 240–255
Ross EM, Gilman AG (1985) Pharmacodynamics: mechanism of drug action and the relationship between drug concentration and effect. In: Goodman Gilman A, Goodman LS, Rall TW, Murad F (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics. MacMillan, New York, p 35
Steal GR, Torrie JH (1960) Principles and procedures of statistics. Mc Graw Hill, New York, p 78
Van Rossum JN (1963) Cumulative dose-response curves. II. Techniques for making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 143: 299–329
Wachtel H, Dorow R (1983) Dual action on central dopamine function of transdihydrolisuride, a 9,10-dihydrogenated analogue of the ergot dopamine agonist lisuride. Life Sci 32: 421–432
Wachtel H (1983) Central dopaminergic and antidopaminergic effects of ergot derivatives structurally related to lisuride. In: Calne DB, Horowski R, McDonald RJ, Wuttke W (eds) Lisuride and other dopamine agonists. Raven Press, New York, p 109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carratù, M.R., DeSerio, A., Mitolo-Chieppa, D. et al. Comparative evaluation of lisuride and terguride, ergot alkaloid derivatives, on the field-stimulated vas deferens of mouse. J. Neural Transmission 84, 221–232 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244972
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244972