Summary
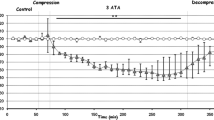
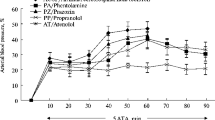
In the present report we have investigated the effects of apomorphine, (−)3-PPP,L-DOPA and haloperidol on the elicitation of convulsions induced in mice by exposure to oxygen at high pressure (HBO) (5 ata O2). It was found that the administration of apomorphine (0.025–0.1 mg · kg−1 s. c.), (−)3-PPP (4 mg · kg−1 i. p.)L-DOPA (200–400 mg · kg−1 i. p.) as well as halo-peridol (0.25–2.0 mg · kg−1 i. p.) produced a significant protection against HBO-induced convulsions. Haloperidol was the only drug to produce a dose-dependent decrease in respiration, and this effect does probably explain the anticonvulsant effects observed. The low doses at which apomorphine was effective, and the effects produced by (−)3-PPP, indicate an effect mediated via DA autoreceptors. Alternatively, and more likely taking the effects ofL-DOPA into account, the DA receptors involved are sensitive enough to disclose postsynaptic agonist properties of apomorphine and (−)3-PPP at the doses employed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén N-E, Butcher SG, Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Ungerstedt U (1970) Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur J Pharmacol 11: 303–314
Andén N-E, Rubenson A, Fuxe K, Hökfelt T (1967) Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J Pharm Pharmacol 19: 627
Carlsson A (1970) Amphetamine and brain catecholamines. In: Costa E, Garattini S (eds) Amphetamines and related compounds. Raven Press, New York, pp 289–300
Cox B (1979) Dopamine. In: Lomax P, Schonbaum E (eds) Body temperature-regulation, drug effects, and therapeutic implications. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 231–255
Criborn C-O (1969) Recording of the respiratory process in mice without strain on the respiratory organs. Life Sci 8 (I): 1351–1358
Criborn C-O, Clemedson C-J, Henriksson Ch (1986) Amphetamine as a protective agent against oxygen induced convulsions in mice. Aviat Space Environ Med 57: 771–781
Ernst AM (1967) Mode of action of apomorphine and dexamphetamine on gnawing compulsion in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 10: 316–323
Hjorth S, Carlsson A, Clark D, Svensson K, Wikström H, Sanchez D, Lindberg P, Hacksell U, Arvidsson L-E, Johansson A, Nilsson JLG (1983) Central dopamine receptor agonist and antagonist actions of the enantiomers of 3-PPP. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 81: 89–99
Jurna I, Regelhy B (1968) The antagonism between reserpine and some antiparkinson drugs in electroseizures. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 259: 442–459
Maynert EW, Marczynski TJ, Browning RA (1975) The role of neurotransmitters in the epilepsies. Adv Neurol 13: 79–147
Pletscher A, Brossi A, Gey KF (1962) Benzoquinolizine derivatives: a new class of monoamine decreasing drugs with psychotropic action. Int Rev Neurobiol 4: 275–306
Radomski MW, Watson WJ, McBurney LJ (1973) Effect of natural antioxidants and radioprotectants on acute oxygen toxicity and brainγ-aminobutyric acid in rats. In: Trapp EG, Banister EW, Davidson AJ, Trapp PA (eds) Proceedings of the 5th international hyperbaric congress 1973. Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, pp 142–149
Riffee WH, Gerlad MC (1976) Effects of amphetamine isomers and CNS catecholaminergic blockers on seizures in mice. Neuropharmacol 15: 677–682
Sovner R, DiMascio A (1978) Extrapyramidal syndromes and other neurological side effects of psychotropic drugs. In: Lipton MA, DiMascio A, Killam KF (eds) Psychopharmacology: a generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 1021–1032
Spencer PSJ, Turner TAR (1969) Blockade of biogenic amine synthesis: its effect on the responses to leptazol and dexamphetamine in rats. Br J Pharmacol 37: 94–103
Strömbom U (1976) Catecholamine receptor agonists. Effects on motor activity and rate of tyrosine hydroxylation in mouse brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 292: 167–176
Stull RE, Jobe PC, Geiger PF, Ferguson GG (1973) Effects of dopamine receptor stimulation and blockade on Ro 4-1284-induced enhancement of electroshock seizure. J Pharm Pharmacol 25: 842–844
Winer BJ (1970) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Criborn, C.O., Henriksson, C., Ahlenius, S. et al. Partial protection against hyperbaric oxygen induced convulsions by dopaminergic agents in mice: Possible involvement of autoreceptors?. J. Neural Transmission 69, 277–285 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244348
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01244348