Abstract
Solid sample introduction into an ICP-MS by laser ablation is an effective method for the total analysis of rare earth elements (REEs) in soils because no digestion is needed. A problem of the method, however, is the difference of the ablated mass for each laser shot. Therefore, internal standard for the compensation of signal instability, sample preparation, and the calibration method have to be carefully chosen.
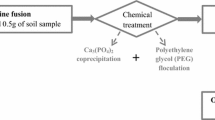
The analyzed sample was a certified standard provided by IAEA (SOIL-7). The sample was mixed with an internal standard solution and polyethylene (PE), dried, homogenized in a ball-mixer/mill, and pressed to a pellet. For the calibration 5 external standards with increasing REEs concentrations (0.4–20 μg/g) as well as a blank were prepared in the same way.
The analysis of the pellets was performed on a VG PlasmaQuad II + with a LaserLab unit. The laser ablation-cell was modified to improve the sample particle transportation characteristics and to allow a quicker sample-exchange. The pellets were ablated from six different spots for 60 s each with a laser-repetition rate of 4 Hz.
The correlation coefficients of the calibration curves based on 5 standards, were better than 0.995. The concentrations cA of the 15 REEs in the soil sample were determined with an average relative confidence interval 100(CI)/cA of 6.95%, as a figure for the precision. This good precision have been obtained with a new laser ablation cell, which will be described in detail.
With 2 exceptions (Ce and La) the measured concentrations were within the confidence intervals (CI) of the certified values. Therefore, with respect to accuracy and precision, the presented method offers a convenient way to analyze homogeneous and powdered soil samples for REE's without digestion. Since a good calibration for the REE determination may be obtained, the laser sampling variance (within the sample) is less significant than the analytical variance. Automation of the method is possible by construction of an autosampler based on the modified laser cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Moenke-Blankenburg,Laser Micro Analysis, Wiley, New York, 1989.
K. E. Jarvis, A. L. Gray, R. S. Houk,Handbook of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, Blackie, Glasgow, 1992.
W. Doherthy,Spectrochim. Acta 1989,44B, 263.
N. Imai,Anal. Chim. Acta 1990,235, 381.
S. F. Durrant,Analyst 1992,117, 1585.
A. A. van Heuzen,Spectrochim. Acta 1991,46B, 1803.
A. A. van Heuzen, J. B. W. Morsink,Spectrochim. Acta 1991,46B, 1819.
W. T. Perkins, R. Fudge, N. J. G. Pearce,J. Analyt. Atom. Spectrom. 1991,6, 445.
L. Moenke-Blankenburg, M. Gäckle, D. Günther, J. Kammel,Spec. Publ. R. Soc. Chem. 1990,85, 1.
B. Magyar, H. Cousin, B. Aeschlimann,Anal. Proc. (London) 1992,29, 282.
B. Magyar, H. Cousin, B. Aeschlimann, X. Y. Zhu,6th Colloquium Atomspektrometrische Spurenanalytik (CAS) (B. Welz, ed.), Konstanz, April 12, 1991.
International Atomic Energy Agency,Certified Reference Material IAEA/SOIL-7, Report No. IAEA/RL/112, May 1984.
R. J. Ackermann, E. G. Rauh, R. J. Thorn,J. Chem. Phys. 1976,65, 1027.
B. Magyar,CRC Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1987,17, 145.
J. C. Miller, J. N. Miller,Statistics for Analytical Chemistry, Ellis Horwood, Chichester, 1986.
N. J. G. Pearce, W. T. Perkins, I. Abell, G. A. T. Duller, R. Fudge,J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 1992,7, 53.
L. A. Haskin, F. A. Frey, R. A. Schmitt, R. H. Smith, in:Physics and Chemistry of the Earth (L. H. Ahrens, F. Press, S. K. Runcorn, H. C. Urey, eds.), Pergamon, Oxford, 1966, pp. 167–321.
N. M. Evensen, P. J. Hamilton, R. K. O'Nions,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978,42, 1199.
H. Baumann,Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1992,342, 907.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cousin, H., Magyar, B. Precision and accuracy of laser ablation-ICP-MS analysis of rare earth elements with external calibration. Mikrochim Acta 113, 313–323 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243621
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243621