Summary
In phase 1 evaluation of potential anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs), insufficient attention has perhaps been directed to the transition from single, and multi-dose studies in normal volunteers to clinical trials of some weeks duration in patients. Acute single dose studies in epileptic patients already receiving AEDs may reduce avoidable errors in early controlled trials.
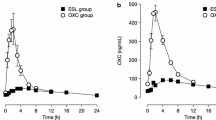
Acute single dose studies provide the opportunity of obtaining some preliminary evidence of efficacy by observing the effects of the drug on quantified epileptiform EEG discharges, both those occurring spontaneously in long term telemetric recordings and those elicited by standardised photic stimulation in susceptible subjects. The pharmacokinetics of the new drug may be profoundly influenced by the comedication (as illustrated by lamotrigine, the half life of which varies by a factor of 10 depending on comedication). Conversely, the new drug may so influence metabolism of the comedication that the results of add-on trials may be virtually uninterpretable, unless steps are taken to maintain blood levels of the other AEDs. A method of addressing this problem is illustrated in the case of an imidazole, R 57720. Adverse experiences may also occur more readily when a new drug is added to comedication than when it is given to normal volunteers and these problems in chronic trials can be anticipated from acute studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartholini G, Bossi L, Lloyd KG, Morselly PL (1985) Epilepsy and GABA receptor agonists. Basic and therapeutic research, vol 3. Raven Press, New York
Binnie CD (1986) The interictal EEG. In: Trimble MR, Reynolds EH (eds) What is epilepsy? Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 116–125
Binnie GD, Aarts JHP, Houtkooper MA, Laxminarayan R, Martins da Silva A, Meinardi H, Nagelkerke N, Overweg J (1984) Temporal characteristics of seizures and epileptiform discharges. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 58: 498–505
Binnie CD, Van Emde Boas W, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité DGA, De Korte RA, Meijer JWA, Meinardi H, Overweg J, Peck AW, Van Wieringen A, Yuen WC (1986a) Acute effects of lamotrigine (BW430C) in persons with epilepsy. Epilepsia 27: 248–254
Binnie CD, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenite DGA, De Korte R (1986b) Photosensitivity as a model for acute antiepileptic drug studies. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 62: 35–41
Coatsworth JJ (1971) Studies of the clinical efficacy of marketed antiepileptic drugs. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, p 36
Fink M, Irwin P, Sannita W, Papakostas Y, Green MA (1979) Aphenytoin: EEG effects and plasma levels in volunteers. Ther Drug Monit 1: 93–103
Gotman J, Marciani MG (1985) Electroencephalographic spiking activity, drug levels, and seizure occurrence in epileptic patients. Ann Neurol 17: 597–603
Gram L, Drachmann Bentsen K, Parnas J, Flachs H (1982) Controlled trials in epilepsy: a review. Epilepsia 23: 491–519
Kellaway P, Frost JD (1983) Biorhythmic modulation of epileptic events. In: Pedley TA, Meldrum BS (eds) Recent advances in epilepsy. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 139–154
Martins da Silva A, Aarts JHP, Binnie CD, Laxminarayan R, Lopes da Silva FH, Meijer JWA, Nagelkerke N (1984) The circadian distribution of interictal epileptiform activity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 58: 1–13
Meinardi H, Binnie DC, Meijer JWA (1985) Assessment of effects of antiepileptic drugs. Long-term monitoring in epilepsy. Elsevier, Amsterdam (EGG Suppl 37, pp 201–214)
Milligan N, Richens A (1982a), Ambulatory monitoring of the EEG in the assessment of antiepileptic drugs. In: Scott FD, Raftery EB, Clement DL, Wright SL (eds) Proc 4th Int Symp Ambulatory Monitoring, Gent, 1981. Academic Press, London, pp 224–233
Milligan N, Dhillon S, Oxley J, Richens A (1982b) Absorption of Diazepam from the rectum and its effect on interictal spikes in the EEG. Epilepsia 23: 323–331
Myslobodsky M, Mintz M, Tomer R, Radwan H, Douglas R (1981) Sodium valproate reduction of photoconvulsive responses; effect or side-effect. Israel J Med Sci 17: 390
Patsalos PN, Shorvon SD, Elyas AA, Smith G (1985) The interaction of denzimol (a new anticonvulsant) with carbamazepine and phenytoin. J Neural Neurosurg Psychiatry 48: 374–377
Richens A (1976) Drug treatment of epilepsy. Henry Kimpton, London, pp 176
Rodin EA, Rim CS, Rennick PM (1974) The effects of carbamazepine on patients with psychomotor epilepsy: results of a double-blind study. Epilepsia 15: 547–561
Stevens JR, Kodama H, Lonsbury B, Mills L (1971) Ultradian characteristics of spontaneous seizure discharges recorded by radio telemetry in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 31: 313–325
Treiman DM, Kupferberg HJ, Ben-Menachem E, Barber K, Chelberg R, Gunawan S (1985) Inhibition of the metabolism of carbamazepine and its metabolites by nafimidone, a new antiepileptic drug. Neurology 35 [Suppl 1]: 285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binnie, C.D. Preliminary evaluation of potential anti-epileptic drugs by single dose electrophysiological and pharmacological studies in patients. J. Neural Transmission 72, 259–266 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243424
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243424