Summary
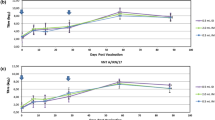
Sendai virus inoculated into the heart of guinea-pigs was demonstrated to produce interferon, which reached a peak at 5 hours. Protection was afforded against foot-and-mouth disease virus from 24 hours before to 24 hours after challenge. No inhibition of interferon or antibody production was demonstrated when Sendai virus was administered at the same time as inactivated foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and no significant effect on the 50% protection dose of vaccine was found. Guinea-pigs given Sendai virus and inactivated vaccines simultaneously were protected from development of foot-and-mouth disease secondary lesions from 5 hours after the time of inoculation, although interferon and antibody were not detected on the second and third days.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, S. G.: The production of antibody in the presence of interferon. Aust. J. exp. Biol. med. Sci.43, 345–350 (1965).
Baron, S., andC. E. Buckler: Circulating interferon in mice after intravenous injection of virus. Science141, 1061–1063 (1963).
Borden, E. C., andF. A. Murphy: The interferon refractory state:in vivo andin vitro studies of its mechanism. J. Immunol.106, 134–142 (1971).
Braun, W., andM. Nakano: Antibody formation: stimulation by polyadenylic and polycytidylic acids. Science157, 819–821 (1967).
De Somer, P., A. Billiau, andE. de Clercq: Inhibition of antibody production in rats and mice by intravenous injection of interferon-inducing amounts of Sindbis virus orE. coli. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.20, 205–214 (1967).
Finter, N. B.: Dye uptake methods of assessing viral cytopathogenicity and their application to interferon assays. J. gen. Virol.5, 419–427 (1969).
Giacometti, G., F. Strozzi etE. E. A. Hahn: Attivitá interferente del virus di Newcastle sull'infezione aftosa sperimentale della cavia. Boll. Ist. sieroter, milan47, 105–114 (1968).
Gizatullin, K. G., andN. K. Gumerov: Interference of viruses against foot-and-mouth disease. Veterinariya (Moscow)46, 23–24 (1969).
Gorhe, D. S.: Inhibition of multiplication of foot-and-mouth disease in adult mice pretreated with Freund's complete adjuvant. Nature (Lond.)216, 1242–1244 (1967).
Mazzur, S. B., andK. Paucker: Studies on the effect of interferon on the formation of antibody in mouse spleen cells. II. The effect of interferon on antibody plaque formation and antibody production by transferred spleen cells. J. Immunol.98, 689–696 (1967).
Medzon, E. L., andS. I. Vas: Studies onin vitro antibody production. II. The effect of Newcastle Disease virus on antibody synthesis. Canad. J. Microbiol.10, 535–541 (1964).
Planterose, D., and L.Smith: Effect of vitamin C status on interferon production in the guinea-pig. Personal communication, December 1968.
Rosenquist, B. D., andR. W. Loan: Production of circulating interferon in the bovine species. Amer. J. vet. Res.30, 1293–1303 (1969).
Sellers, R. F., K. A. J.Herniman, and C. W.Hawkins: The effect of a synthetic anionic polymer (pyran) on the development of foot-and-mouth disease in guinea pigs, cattle and pigs. Ees. vet. Sci., in press.
Sellers, R. F., andG. N. Mowat: Interference between modified and virulent strains of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.23, 20–26 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herniman, K.A.J., Sellers, R.F. Protection of guinea-pigs against foot-and-mouth disease by simultaneous inoculation of sendai virus and inactivated foot-and-mouth disease vaccine. Archiv f Virusforschung 37, 97–103 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01241155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01241155