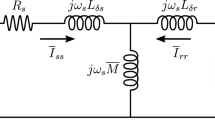
Contents
A new method of equivalent circuit parameters evaluation for induction motor with solid rotor, based on the recorded waveform of decaying of the direct current in the stator winding has been presented. The rotor electric circuit is replaced by a frequency-dependent circuit, represented by a synthetic time constantT e, the resistanceR k and the inductanceL kσ with constant values. This leads to an approximation of the recorded waveform of decaying of the direct current by a function being a sum of decaying components of the type\(\exp (\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{z} ^2 t)erfc(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{z} \sqrt t )\). To assess the correctness of determined parameters the characteristics obtained on the base of equivalent circuit parameters have been compared with the waveforms determined in the experimental way. Close convergence of the results obtained shows that the proposed method is useful for determining the parameters of equivalent circuit of induction motor with solid rotor.
Zusammenfassung
In der Arbeit wurde eine neue Methode der Parameterbestimmung eines Ersatzschaltbildes des Induktionsmotors mit massivem Rotor aufgrund des gemessenen Verlaufs des abklingenden Gleichstroms in der Statorwicklung vorgestellt. Der Rotor wurde mit Hilfe von Parametern dargestellt, die abhängig von der Frequenz, repräsentiert durch eine synthetische ZeitkonstanteT e, durch den WiderstandR k und die InduktivitätL kσ mit konstanten Werten sind. Diese führt zur Approximierung des gemessenen Verlaufs des abklingenden Gleichstroms mit der Summe der abklingenden Komponenten\(\exp (\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{z} ^2 t)erfc(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{z} \sqrt t )\). Zur Beurteilung der Genauigkeit der ermittelten Parameter wurden die erhaltenen Characteristiken mittels Parameter des Ersatzschaltbildes mit den auf dem Meßwege bestimmten Verläufen verglichen. Eine gute Konvergenz der erhaltenen Ergebnisse beweist die Brauchbarkeit der vorgeschlagenen Methode zum Parametrisieren des Ersatzschaltbildes des Induktionsmotors mit massivem Rotor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- f :
-
electric frequency
- I :
-
current
- \(j = \sqrt { - 1} \) :
-
current
- p :
-
Laplace operator
- R, L :
-
resistance, inductance
- \(q = \sqrt p \) :
-
resistance, inductance
- s :
-
slip
- T :
-
time constant
- T e :
-
synthetic time constant
- t :
-
time
- U :
-
voltage
- Z :
-
impedance
- σ:
-
leakage coefficient
- Ψ:
-
flux linkage
- ω:
-
rotor electrical angular speed, ω1(1-s)
- ω1 :
-
electric synchronous angular speed, 2πf 1
- \(\underset{\raise0.3em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle-}$}}{Q} \) :
-
amplitude of complex quantity,Qejϕ
- k:
-
parameters of rotor circuit with constant values
- μ:
-
magnetisation
- σ:
-
leakage
- l:
-
stator
References
Chalmers BJ, Woolley I (1972) General Theory of Solid-Rotor Induction Machines. Proc. IEE, Vol. 119, No. 9: 7–14
Dandeno PL, Poray AT (1981) Development of Detailed Turbogenerator Equivalent Circuits from Standstill Frequency Response Measurements. IEEE Transaction on Power Apparatus and System, Vol. PAS-100, No. 4: 1646–1655
Keyhani A, Moon SI (1992) Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Synchronous Machine Parameters and Study of Noise Effect from DC Flux Decay Data. IEE Proceedings-C, Vol. 139, No. 1: 76–80
Korn GA, Korn TM (1968) Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kręglewski T, Rogowski T, Ruszczyński A, Szymanowski J (1984) Methods Optimization in Fortran Language (in Polish). PWN, Warszawa
Nadolski R, Staszak J (1995) Simplified Method of Determination of Turbogenerator Equivalent Circuit Parameters. Archives of Electrical Engineering (Poland), Vol. XLIV, No. 1: 95–108
Nadolski R, Staszak J (1995) Analysis of the Field Current after Three-Phase Sudden Short-Circuit of Turbogenerators using Equivalent Circuits. Electrical Engineering, Springer-Verlag, Vol. 78, No. 6: 399–406
Paszek W (1979) Beitrag zur analytischen Erfassung der Ausgleichsvorgänge von Turbogeneratoren mit massivem Läufer. Archiv für Elektrotechnik 61: 309–325
Paszek W (1986) Transients states of AC Machines (in Polish). WNT, Warszawa
Press WH, Flannery BP, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT (1986) Numerical Recipes. The Art of Scientific Computing. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Reggio UG, Chinnici R, Denegri GB (1984) Comparison of Frequency Response and D.C. Decay Tests for Identifying Turbogenerator Models. Proceedings of ICEM, Lausanne, Switzerland: 461–464
Ritter C, Stiebler M (1984) Determination of Synchronous Machines Parameters by Means of D.C. Tests at Standstill. Proceedings of ICEM, Lausanne, Switzerland: 465–468
Turner PJ, Reece ABJ (1989) The D.C. Decay Test Determining Synchronous Machines. Measurement and Simulation. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversion, Vol. 4, No. 4: 616–623
Wood AJ (1960) An analysis of solid rotor machines. Part I. Operational impedances and equivalent circuit. AIIIE Transaction on PAS, Vol. 78: 1657–1665
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadolski, R., Staszak, J. Evaluation of parameters of induction motor with solid rotor using the method of direct current decay. Electrical Engineering 81, 177–181 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01236237
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01236237