Abstract
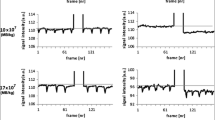
A polysaccharide toxin, GBS toxin, is produced by group BStreptococcus (GBS) isolates from neonates who died of “early-onset disease”. GBS toxin, named CM101 in the clinic, was hypothesized, on the basis of our previous in vivo studies, to induce inflammation in pulmonary neovasculature in neonates by crosslinking of embryonic receptors still expressed after birth and in tumor neovasculature in adults. Immunohistochemical in vitro analysis of human biopsies showed that tumor neovasculature is indeed a binding site for CM101. In vivo studies in mice have demonstrated that CM101 induced inflammatory responses in neoplastic tumor neovasculature causing inhibition of tumor growth and tumor cell necrosis. These experimental observations warranted a phase I clinical trial for CM101 as an anti-neovascularization agent in human cancer therapy. Cancer patients received one cycle of therapy consisting of three treatments during 1 week. CM101 was administered over 15 min by i.v. infusion. Dosages of 7.5 μg/kg (1 U/kg),n=3; 15 μg/kg (2 U/kg),n=6; 24.75 μg/kg (3.3 U/kg),n=3; and 37.5 μg/kg (5 U/kg),n=3 were used. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent sandwich assays (ELISA) of the patients' sera showed a marked elevation of soluble E-selectin with a peak concentration observed at 8–12 h after each CM101. infusion. The average baseline value for soluble E-selectin prior to the first treatment was 97.3±23.4 ng/ml (mean±SEM,n=15) and the average peak level at 8 h was 441.6±62.4 (mean±SEM,n=15;P<0.001). Subsequent treatments gave average maximum soluble E-selectin levels again at 8 h of 466.9±87.6 and 412.0±67.8 ng/ml, for treatment 2 and 3 respectively. Baseline values for treatment 2 and 3 were 192.3±26.4 and 226.4±26.1 ng/ml respectively (p<0.01 versus treatment 1). Out of 15 patients, 5 showed tumor reduction or stabilization and were given additional cycles of therapy. CM101 induced an increase in soluble E-selectin levels, which remained elevated over baseline at the start of the following treatment cycles. The baseline remained elevated for several weeks after the final treatment, i.e.,P<0.01 for levels before treatment 1 compared to those at week 4 after treatment. Elevated soluble E-selectin is considered proof of endothelial engagement in an inflammatory process. Our data support the contention that the inflammatory response observed in these cancer patients is targeting the tumor neovasculature and that measurement of soluble E-selectin levels in patients treated with CM101 can provide important information on the magnitude of CM101-mediated neovascular endothelial activation and tumor cell damage in cancer of endothelial origin, or cancer with a major neo-angiogenic component.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GBS :
-
group BStreptococcus
- CM101 :
-
polysaccharide
- GBS :
-
bacterial exotoxin
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- IL :
-
interleukin
References
Banks RE, Gearing AJH, Hemingway IK, Norfolk DR, Perren TJ, Selby PJ (1993) Circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), E-Selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in human malignancies. Br J Cancer 68:122–124
Bevilacqua MP, Nelson RM (1993) Selectins. J Clin Invest 91:379–387
DeVore R, Johnson DR, Hellerqvist C, Wakefield G, Browning P, Page D, Sundell H, Johnson DH (1995) A phase I study of the anti-neovascularization drug CM101. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol Annu Meet 14:487
Gearing AJH, Newman W (1993) Circulating adhesion molecules in disease. Immunol Today 14:506–512
Hakomori S (1994) Novel endothelial cell activation factor(s) released from activated platelets which induced E-selectin expression and tumor cell adhesion to endothelial cells: a preliminary note. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 203:1605–1613
Hellerqvist CG (1991) Therapeutic agent and method of inhibiting vascularization of tumors. US Patent 5 010 062, 23 April 1991. Patents have been issued in Europe, Canada, Australia and Japan
Hellerqvist CG, Rojas J, Green RS, Sell S, Sundell H, Stahlman MT (1981) Studies on group B β-hemolytic streptococcus. I. Isolation and partial characterization of an extra-cellular toxin. Pediatr Res 15:892–898
Hellerqvist CG, Thurman GB, Page DL, Wang Y-F, Russell BA, Montgomery CA, Sundell HW (1993) Anti-tumor effects of GBS toxin: a polysaccharide exotoxin from group B β-hemolytic streptococcus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 120:63–70
Hellerqvist CG, DeVore RF, Sundell HW, Thurman GB, Wamil BD, Wakefield GB, Johnson DH (1994) Preliminary results of a phase I trial of CM101 in cancer patients. J Leukoc Biol [Supp] 112:35
Hellerqvist C, DeVore R, Thurman G, Wamil B, Zhang M, Wakefield G, Sundell H, Carter C, Yan H, Johnson D (1995a) Cytokine production in cancer patients receiving the antineovascularization drug CM101. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol Annu Meet 14:488
Hellerqvist CG, DeVore RF, Sundell HW, Thurman GB, Wamil BD, Page DL, Wakefield, GB, Johnson DH (1995b) Early results of a phase I trial of CM101 in cancer patients. Proc. Am Assoc Cancer Res Ann Meet 36:224
Hellerqvist CG, Yan H-P, Carter CE, Liu L, Wamil BD, Page DL, Thurman GB, Sundell HW (1996) CM101 induces a complement-activated inflammatory response targeting tumor neovasculature. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res Ann Meet 37:487
Hollander M, Wolfe DA (1973) The dichotomous data problem. In: RA Bradley, JS Hunter, DG Kendall and GS Watson (Eds) Nonparametric statistical Methods. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 15–25
Mackay CR, Imhof BA (1993) Cell adhesion in the immune system. Immunol Today 14:99–102
Meekins JW, McLaughlin PJ, West DC, McFadyen IR, Johnson PM (1994) Endothelial cell activation by tumour necrosis factoralpha (TNF-alpha) and the development of pre-eclampsia. Clin Exp Immunol 98:110–114
Newman W, Beall LD, Carson CW, Hunder GG, Graben N, Randhawa ZI, Gopal TV, Wiener-Kronish J, Matthay MA (1993) Soluble E-selectin is found in supernatant of activated endothelial cells and is elevated in the serum of patients with septic shock. J Immunol 150:644–654
Nguyen M, Watanabe H, Budson AE, Richie JP, Hayes DF, Folkman J (1994) Elevated levels of an angiogenic peptide, basic fibroblast growth factor, in the urine of patients with a wide spectrum of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:356–361
Rojas J, Green RS, Hellerqvist CG, Olegard R, Brigham KL, Stahlman MT (1981) Studies on group B β-hemolytic streptococcus. II. Effects on pulmonary hemodynamics and vascular permeability in unanesthetized sheep. Pediatr Res 15:899–904
Rojas J, Larson LE, Hellerqvist CG, Brigham KL, Gray ME, Stahlman MT (1983) Pulmonary hemodynamic and ultra-structural changes associated with group B streptococcal toxemia in adult sheep and newborn lambs. Pediatr Res 17:1002–1008
Sawada R, Tsuboi S, Fukuda M (1994) Differential E-selectin-dependent adhesion efficiency in sublines of a human colon cancer exhibiting distinct metastatic potentials. J Biol Chem 269:1425–1431
Sciacca FL, Stürzl M, Bussolino F, Sironi M Brandstetter H, Zietz C, Zhou D, Matteucci C, Peri G, Sozzani S, Benelli R, Arese M, Albini A, Colotta F, Mantovani A (1994) Expression of adhesion molecules, platelet-activating factor, and chemokines by Kaposi's sarcoma cells. J Immunol 153:4816
Sundell HW, Fish WG, Sandberg KL, Edberg KE, Pappas RS, Hellerqvist CG (1990) Lung injury by streptococcal toxins. In: Brigham L, Stahlman MT (eds) Respiratory distress syndromes. Vanderbilt University Press, Nashville, Tenn, pp 58–70
Sundell HW, Yan H-P, Wu K, Wamil BD, Gaddipati R, Carter CE, Stahlman MT, Hellerqvist CG (1996) Isolation and identification of group B β-hemolytic streptococcal (GBS) toxin from septic newborn infants. Pediatr Res 39:302A
Thurman GB, Russell BA, York GE, Wang Y-F, Page DL, Sundell HW, Hellerqvist CG (1994a) Effect of GBS toxin on long-term survival of mice bearing transplanted Madison lung Tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 120:479–484
Thurman GB, Wamil BD, Yan H, Zhang M, Johnson DH, DeVore RF, Wakefield GB, Hellerqvist CG (1994b) Cytokine production in cancer patients in response to CM101, a polysaccharide exotoxin from group B streptococcus (GBS). J Leukoc Biol [Suppl] 113:36
Thurman GB, Page DL, Wamil BD, Wikinson LE, Kasami M, Hellerqvist CG (1996) Acute inflammatory changes in subcutaneous microtumors in the ears of mice induced by intravenous CM101 (GBS toxin). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 122:549–553
Wamil BD, Price JO, Minton PA, Sundell HW, Thurman GB, Yan H-P, Carter CE, Hellerqvist CG (1996) Leukocyte activation in response to CM101 treatment of cancer patients. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res Annu Meet 37:487
Warren JS (1993) Cellular processes such as leukocyte activation, chemotaxis, intercellular adhesion and secretion of proinflammatory soluble mediators are regulated by a complex set of cell surface, matrix-associated and soluble mediators. Drug News Perspect 6:450–459
Whitley MZ, Thanos D, Read MA, Maniatis T, Collins T (1994) A striking similarity in the organization of the E-selectin and beta interferon gene promoters. Mol Cell Biol 14:6464–6475
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by Carbo Med. Inc., 5115 Maryland Way, Brentwood, Tennessee 37027, USA, and National Institute of Health, General Clinical Research Center grant M01 RR00095
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wamil, B.D., Thurman, G.B., Sundell, H.W. et al. Soluble E-selectin in cancer patients as a marker of the therapeutic efficacy of CM101, a tumor-inhibiting anti-neovascularization agent, evaluated in phase I clinical trial. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 123, 173–179 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01214670
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01214670