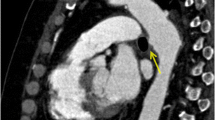
Abstract
We present a case of aortocaval fistula (ACF) secondary to spontaneous rupture of an atherosclerotic infrarenal aortic aneurysm into the inferior vena cava that was initially diagnosed with computed tomography (CT). This is believed to be the first report of this condition with CT demonstration of the exact site of fistula and CT—pathologic correlation. We retrospectively reviewed the CT findings of another two cases of ACF and the previous literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker WH, Sharzer LA, Ehrenhaft JL. Aortocaval fistula as a complication of abdominal aortic aneurysms.Surgery 1972;72:933–935
Syme J. Care of spontaneous varicose aneurysm.Edinburgh Med Rev 1831;36:104–107
Lupetin AR, Dash N, Contractor FM. MRI diagnosis of aortocaval fistula secondary to ruptured infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1987;10:24–27
Cook AM, Dyet JF, Mann SL. Case report: ultrasonic and comparative angiographic appearances of a spontaneous aorto-caval fistula.Clin Radiol 1990;41:286–288
Clements R, Fitzgerald E, Thorpe A. Diagnosis of spontaneous aorto-caval fistula by computed tomography.Br J Radiol 1986;59:403–404
Brewster DC, Cambria RP, Moncure AC, Darling RC, La-Muraglia GM, Geller SC. Aortocaval and iliac arteriovenous fistulas: recognition and treatment.J Vasc Surg 1991;13:253–264
Marx M, Geller S, Bettmann M. Traumatic aortocaval fistula presenting as atypical chest pain.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1986;9:17–18
Khargi K, Bemelman WA, Voorwinde A, Keeman JN. Aortocaval fistulas.Neth J Surg 1991;43:1–5
Koslin DB, Kenney PJ, Stanley RJ, Van Dyke JA. Aortocaval fistula: CT appearance with angiographic correlation.J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987;11:348–350
Middleton WD, Smith DF, Foley WD. CT detection of aortocaval fistula.J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987;11:344–347
Sheward SE, Spencer RR, Hinton TR, Hightower CW, Patel PV, Suckarieh JG. Computed tomography of primary aortocaval fistula.Comput Med Imaging Graph 1992;16:121–124
Thomas PR. Caval thrombectomy in a ruptured aortic aneurysm associated with aorto-caval fistula.Eur J Vasc Surg 1990;4:645–646
Cohen LJ, Sukov RJ, Boswell WD, Ashor G. Spontaneous aortocaval fistula: report of 2 cases.Radiology 1981;138:357–359
Young SW, Noon MA, Marincek B. Dynamic computed tomography time-density study of normal human tissue after intravenous contrast administration.Invest Radiol 1981;16:36–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quiroga, S., Alvarez-Castells, A., Hidalgo, A. et al. Spontaneous aortocaval fistula: CT findings with pathologic correlation. Abdom Imaging 20, 466–469 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213274
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213274