Summary
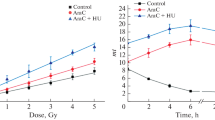
The effect of beta-arabinofuranosyladenine (araA) on the repair of radiation induced DNA damage, as measured by the DNA unwinding technique, was studied in exponentially growing and plateau-phase CHO-cells after exposure to x-rays. Induction of DNA damage by radiation was found to be similar in exponentially growing and plateau-phase cells. In the absence of araA, repair of radiation induced DNA damage proceeded with similar kinetics in exponentially growing and plateau-phase cells. AraA at concentrations between 0–1500 µM inhibited DNA repair both in exponentially growing and in plateau-phase cells. However, the degree of inhibition was significantly higher (by a factor of 3) in plateau-phase cells. A similar degree of repair inhibition by araA was observed in plateau phase cells treated in their conditioned medium, as well as in plateau phase cells that were transfered in fresh growth medium just before treatment initiation. These results indicate the importance of biochemical parameters associated with alterations in the growth state of the cells for the inhibitory effect of araA and may help in the elucidation of the molecular mechanism(s) underlying repair inhibition by inhibitors of DNA replication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahnstroem G, Edvardsson KA (1974) Radiation induced single-strand breaks in DNA determined by rate of alkaline strand separation and hydroxylapatite chromatography as alternative to velocity sedimentation. Int J Radiat Biol 26:493–501
Bryant PE (1983) 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine increases the frequency of x-ray induced chromosome abnormalities in mammalian cells. Int J Radiat Biol 43:459–464
Bryant PE, Bloecher D (1982) The effects of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine on the repair of DNA strand breaks in x-irradiated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Int J Radiat Biol 42:385–394
Bryant PE, Bloecher D (1980) Measurement of the kinetics of DNA double strand break repair in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells using the unwinding method. Int J Radiat Biol 38:335–347
Dicioccio RA, Srivastava BIS (1977) Kinetics of inhibition of deoxynucleotide-arabinofuranosyladenine-5-triphosphate and 1-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine-5-triphosphate. Eur J Biochem 79:411–418
Fleming I, Simone J, Jackson R, Johnson W, Walters T, Mason C (1974) Splenectomy and chemotherapy in acute myelocytic leukemia of childhood. Cancer 3:427–434
Gee TS, Yu KP, Clarkson BD (1969) Treatment of adult acute leukemia with arabinosylcytosine and thioguanine. Cancer 23:1019–1032
Graubman S, Dikomey E (1983) Induction and repair of DNA strand breaks in CHO-cells irradiated in various phases of the cycle. Int J Radiat Biol 48:475–483
Hanawalt PCC, Cooper PK, Ganesan AK, Smith CA (1979) DNA repair in bacteria and mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem 48:783–836
Iliakis G (1981) Characterization and properties of repair of potentially lethal damage as measured with the help of beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine in plateau-phase Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Radiat Res 85:77–90
Iliakis G (1980) Effects of beta-arabinofuranosyladenine on the growth and repair of potentially lethal damage in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Radiat Res 83:537–552
Iliakis G, Bryant PE (1983) Effects of nucleoside analogues alpha-araA, beta-araA and beta-araC on cell growth and repair of both potentially lethal damage and DNA double strand breaks in mammalian cells in culture. Anticancer Res 3:143–150
Iliakis G, Bryant PE, Ngo FQH (1985) Independent forms of potentially lethal damage fixed in plateau-phase Chinese hamster cells by post-irradiation treatment in hypertonic salt solution or araA. Radiat Res 104:329–345
Iliakis G, Ngo FQH (1985) Effects of adenosine deaminase inhibitor 2′-deoxycoformycin on repair and expression of potentially lethal damage sensitve to beta-araA. Radiat Environ Biophys 24:81–88
Iliakis G, Pantelias G, Seaner R (1988) Effect of arabinofuranosyladenine on radiation induced chromosome damage in plateau phase CHO cells measured by premature chromosome condensation: Implications for repair and fixation of alpha PLD. Radiat Res (in press)
Mueller WEG, Rohde HJ, Beyer R, et al. (1975) Mode of action of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine on the synthesis of DNA, RNA and protein in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res 35:2160–2168
Okura A, Yoshida S (1978) Differential inhibition of DNA polymerases of calf thymus by 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine-5-triphosphate. J Biochem 84:727–732
Phillips RA, Tolmach LJ (1966) Repair of potentially lethal damage in x-irradiated HeLa cells Radiat. Res 29:413–432
Preston RJ (1980) The effect of cytosine arabinoside on the frequency of x-ray induced chromosome aberrations in normal human leucocytes. Mutation Res 69:71–79
Rydberg B (1975) The rate of strand separation in alkali of DNA of irradiated mammalian cells. Radiat Res 61:274–287
Sakai K, Okada S (1984) Radiation induced DNA damage and cellular lethality in cultured mammalian cells. Radiat Res 98:479–490
Sinclair WK (1968) Combined effect of hydroxyurea and x-rays on Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Cancer Res 28:198–206
Ward JF (1986) Mechanisms of DNA repair and their potential modification for radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 12:1027–1032
Weiss GB, Tolmach LJ (1967) Modification of X-ray induced killing of HeLa S3 cells by inhibitors of DNA synthesis. Biophys J 7:774–775
Weissbach A (1979) The functional roles of mammalian DNA polymerases. Arch Biochem Biophys 198:386–396
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iliakis, G., Seaner, R. Differences in inhibition by beta-arabinofuranosyladenine (araA) of radiation induced DNA damage repair in exponentially growing and plateau-phase CHO-cells. Radiat Environ Biophys 27, 295–305 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209758
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209758