Abstract
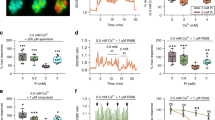
Chromogranin A is an acidic protein that is costored and cosecreted with parathyroid hormone (PTH) from parathyroid cells. Pancreastatin (PST), is derived from chromogranin A, and inhibits secretion from several endocrine/neuroendocrine tissues. Effects of different pancreastatin peptides were investigated on dispersed cells from bovine and human parathyroid glands. Bovine PST(1–47) and bovine PST(32–47) inhibited PTH release from bovine cells in a dose-dependent manner. The former peptide was more potent and suppressed the secretion at 1–100 nM. This inhibition was evident in 0.5 and 1.25 mM, but not in 3.0 mM external Ca2+. Both peptides failed to alter the concentration of cytoplasmic Ca2+([Ca2+]i) of bovine cells. Human PST(1–52) and PST(34–52) did not affect PTH release or [Ca2+]i of parathyroid cells from patients with hyperparathyroidism, nor [Ca2+]i of normal human parathyroid cells. Furthermore, bovine PST(1–47) and bovine PST(32–47) failed to alter the secretion of abnormal human parathyroid cells. The study indicates that PST exerts secretory inhibition on bovine but not human parathyroid cells, and that this action does not involve alterations of [Ca2+]i.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohn, D. V., Zangerle, R., Fischer-Colbie, R., Chu, L. H. H., Elting, J. J., Hamilton, J. W. and Winkler, H. (1982) Similarity of secretory protein-I from parathyroid gland to chromogranin A from adrenal medulla.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:6056–6059.
Ravazzola, M., Orci, L., Habener, J. F. and Potts Jr, J. T. (1978) Parathyroid secretory protein: immunocytochemical localization within cells that contain parathyroid hormone.Lancet 2:371–372.
Cohn, D. V., Elting, J. J., Frick, M. and Eide, R. (1984) Selective localization of parathyroid secretory protein-I/adrenal medulla chromogranin A protein family in a wide variety of endocrine cells of the rat.Endocrinology 114:1963–1974.
Hogue Angeletti, R. (1986) Chromogranins and neuroendocrine secretion.Lab. Invest. 55:387–390.
Morrissey, J. J. and Cohn, D. V. (1978) The effects of calcium and magnesium on the secretion of parathormone and parathyroid secretory protein by isolated porcine parathyroid cells.Endocrinology 103:2081–2090.
Iacangelo, A. L., Affolter, H.-U., Eiden, L. E., Herbert, E. and Grimes, M. (1986) Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues.Nature 323:82–86.
Iacangelo, A. L., Fischer-Colbrie, R., Koller, K. J., Brownstein, M. J. and Eiden, L. E. (1988) The sequence of porcine chromogranin A messenger RNA demonstrates chromogranin A can serve as the precursor for the biologically active hormone, pancreastatin.Endocrinology 122:2339–2341.
Iacangelo, A. L., Okayama, H. and Eiden, L. E. (1988) Primary structure of rat chromogranin A and distribution of its mRNA.FEBS Lett. 227:115–121.
Konecki, D. S., Benedum, U. M., Gerdes, H.-H. and Huttner, W. R. (1987) The primary structure of human chromogranin A and pancreastatin.J. Biol. Chem. 262:17026–17030.
Helman, L. J., Ahn, T. G., Levine, M. A., Allison, A., Cohen, P. S., Cooper, M. J., Cohn, D. V. and Israel, M. A. (1988) Molecular cloning and primary structure of human chromogranin A (secretory protein I) cDNA.J. Biol. Chem. 263:11559–11563.
Nakano, I., Funakoshi, A., Miyasaka, K., Ishida, K., Makk, G., Angwin, P., Chang, D. and Tatemoto, K. (1989) Isolation and characterization of bovine pancreastatin.Regul. Pept. 25:207–213.
Kitayama, N., Tateishi, K., Funakoshi, A., Miyasaka, K., Shimazoe, T., Kono, A., Iwamoto, N. and Matsuoka, Y. (1994) Pancreastatin molecular forms in normal human plasma.Life Sci. 54:1571–1578.
Eiden, L. E. (1987) Is chromogranin a prohormone?Nature 325:301.
Iacangelo, A. L., Grimes, M. and Eiden, L. E. (1991) The bovine chromogranin A gene: structural basis for hormone regulation and generation of biologically active peptides.Mol. Endocrinol. 5:1651–1660.
Tatemoto, K., Efendic, S., Mutt, V., Makk, G., Feistner, G. and Barchas, J. D. (1986) Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion.Nature 324:476–478.
Lewis, J. J., Zdon, M. J., Adrian, T. E. and Modlin, I. M. (1988) Pancreastatin: a novel peptide inhibitor of parietal cell secretion.Surgery 104:1031–1036.
Doi, R., Inoue, K., Hosotani, R., Higashide, S., Takaori, K., Funakoshi, S., Yajima, H., Rayford, P. L. and Tobe, T. (1991) Effects of synthetic human pancreastatin on pancreatic secretion and blood flow in rats and dogs.Peptides 12:499–502.
Funakoshi, A., Miyasaka, K., Nakamura, R., Kitani, K., Funakoshi, S., Tamamura, H., Fujii, N. and Yajima, H. (1988) Bioactivity of synthetic human pancreastatin on exocrine pancreas.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 156:1237–1242.
Fasciotto, B. H., Gorr, S. U., De Franco, D. J., Levine, M. A. and Cohn, D. V. (1989) Pancreastatin, a presumed product of chromogranin-A (secretory protein-I) processing, inhibits secretion from porcine parathyroid cells in culture.Endocrinology 125:1617–1622.
Drees, B. M. and Hamilton, J. W. (1992) Pancreastatin and bovine parathyroid cell secretion.Bone Miner. 17:335–346.
Grimelius, L., Åkerström, G., Johansson, H., Juhlin, C. and Rastad, J. (1991) The parathyroid glands. In: Functional endocrine pathology, Vol 1. Kovacs, K. and Asa, L., (eds) Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Boston, pp. 375–395.
Ridefelt, P., Hellman, P., Wallfelt, C., Åkerström, G., Rastad, J. and Gylfe, E. (1992) Neomycin interacts with Ca2+ sensing of normal and adenomatous parathyroid cells.Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 83:211–218.
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M. and Tsien, R. Y. (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties.J. Biol. Chem. 260:3440–3450.
Jüppner, H., Rosenblatt, M., Segre, G. V. and Hesch, R. D. (1983) Discrimination between intact and mid-C-regional PTH using selective radioimmunoassay systems.Acta Endocrinol. 102:543–548.
Brown, E. M. (1994) Homeostatic mechanisms regulating extracellular and intracellular calcium metabolism. In: The Parathyroids, Bilizikian, J. P., Levine, M. A. and Marcus, R., (eds) Raven Press, New York, pp. 15–54.
Miyasaka, K., Funakoshi, A., Kitani, K., Tamamura, H., Fujii, N. and Funakoshi, S. (1990) The importance of the C-terminal amide structure of rat pancreastatin to inhibit pancreatic exocrine secretion.FEBS Lett. 263:279–280.
Lindskog, S., Skoglund, G. and Ahrén, B. (1992) Pancreastatin inhibits insulin secretion from isolated rat islets: studies on its mechanism of action.Diabet. Res. 19:119–123.
Sánchez-Margalet, V., Lucas, M. and Goberna, R. (1992) Pancreastatin increases cytosolic Ca2+ in insulin secreting RINm5F cells.Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 88:129–133.
Lewis, J. J., Goldenring, J. R., Asher, V. A. and Modlin, I. M. (1989) Pancreastatin: a novel peptide inhibitor of parietal cell signal transduction.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163:667–673.
Brown, E. M., Gamba, G., Riccardi, D., Lombardi, M., Butters, R., Kifor, O., Sun, A., Hediger, M. A., Lytton, J. and Hebert, S. C. (1993) Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid.Nature 366:575–580.
Åkerström, G., Rastad, J., Ljunghall, S., Ridefelt, P., Juhlin, C. and Gylfe, E. (1991) Cellular physiology and pathophysiology of the parathyroid glands.World J. Surg. 15:672–680.
Brown, E. M. (1991) Extracellular Ca2+ sensing, regulation of parathyroid cell function, and role of Ca2+ and other ions as extracellular (first) messengers.Physiol. Rev. 71:371–411.
Fasciotto, B. H., Gorr, S.-U. and Cohn, D. V. (1992) Autocrine inhibition of parathyroid cell secretion requires proteolytic processing of chromogranin A.Bone Miner. 17:323–333.
Fasciotto, B. H., Gorr, S.-U., Bourdeau, A. M. and Cohn, D. V. (1990) Autocrine regulation of parathyroid secretion: inhibition of secretion by chromogranin-A (secretory protein-I) and pottentiation of secretion by chromogranin-A and pancreastatin antibodies.Endocrinology 127:1329–1335.
Wand, G. S., Takiyyudin, M., O'Connor, D. T. and Levine, M. A. (1991) A proposed role for chromogranin A as a glucocorticoid-responsive autocrine inhibitor of proopiomelanocortin secretion.Endocrinology 128:1345–1351.
Levine, M. A., Dempsey, M. A., Helman, L. J. and Ahn, T. G. (1990) Expression of chromogranin-A messenger ribonucleic acid in parathyroid tissue from patients with primary hyperparathyrodism.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metal. 70:1668–1673.
Drees, B. M., Rouse, J., Johnson, J. and Hamilton, J. W. (1991) Bovine parathyroid glands secrete a 26-kDa N-terminal fragment of chromogranin-A which inhibits parathyroid cell secretion.Endocrinology 129:3381–3387.
Fasciotto, B. H., Trauss, C. A., Greely, G. H. and Cohn, D. V. (1993) Parastatin (porcine chromogranin A347-419), a novel chromogranin A-derived peptide, inhibits parathyroid cell secretion.Endocrinology 133:461–466.
Galindo, E., Rill, A., Bader, M.-F. and Aunis, D. (1991) Chromostatis, a 20-amino acid peptide derived from chromogranin A, inhibits chromaffin cell secretion.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:1426–1430.
Deftos, L., Hogue-Angeletti, R., Chalberg, C. and Tu, S. (1990) A chromogranin A-derived peptide differentially regulates the secretion of calcitonin gene products.J. Bone Miner. Res. 9:989–991.
Aardal, S. and Helle, K. B. (1992) The vasoinhibitory activity of bovine chromogranin A fragment (vasostatin) and its dependence of extracellular calcium in isolated segments of human blood vessels.Regul. Pept. 41:9–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ridefelt, P., Hellman, P., Stridsberg, M. et al. Different secretory actions of pancreastatin in bovine and human parathyroid cells. Biosci Rep 14, 221–229 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209727
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209727