Summary
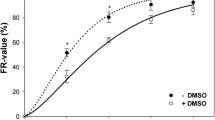
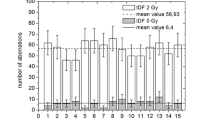
Caffeine and hypertonicity affect the survival ofγ-irradiated Chinese Hamster V79 cells in different ways: while caffeine reduces the shoulder of the dose effect curve, hypertonic treatment mainly affects its final slope suggesting that different types of damage and (or) repair mechanisms are involved. Rejoining of DNA double strand breaks (dsb), as measured by neutral filter elution technique, exhibits a fast and a slow component, indicating that dsb rejoining consists of two different processes. Hypertonicity causes a temporary inhibition of the fast rejoining step but has no effect on the overall rejoining efficiency. Thus, it appears that its sensitizing effect on survival is not correlated with impaired dsb rejoining. Caffeine was found to inhibit the rejoining of dsb even after 6 h but the length of G2 phase was normal. By contrast, hypertonically treated cells are blocked in G2 but rejoining of dsb was normal. From these results we conclude that successful rejoining of part of the dsb involves arresting the cells reversibly in G2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baisch H, Göhde W, Linden WA (1975) Analysis of PCP-data to determine the fraction of cells in the various phases of cell cycle. Radiat Environ Biophys 12:31–39
Bases R, Mendez F, Liebeskind D, Elequin F, Neubort S (1980) DNA of Hela cells during caffeine-promoted recovery from X-ray induced G2 arrest. Int J Radiat Biol 37:437–445
Benjamin RC, Gill DM (1980a) ADP-ribosylation in mammalian cell ghosts. J Biol Chem 255:10493–10501
Benjamin RC, Gill DM (1980b) Poly(ADP-ribose) synthesisin vitro programmed by damaged DNA. J Biol Chem 255:10502–10508
Bradley MO, Kohn KW (1979) X-ray induced DNA double strand break production and repair in mammalian cells as measured by neutral filter elution. Nucl Acids Res 7:793–804
Goth R, Cleaver JE (1976) Metabolism of caffeine to nucleic acid precursors in mammalian cells. Mutat Res 36:105–114
Hieber L, Lücke-Huhle C (1983) PCC technique reveals severe chromatin lesions and repair in G2-arrested cells after alpha irradiation. Exp Cell Res 144:57–62
Iliakis G, Nüsse M (1983) Effects of caffeine on X-irradiated synchronous, asynchronous and plateau phase mouse ascites cells: the importance of progression through the cell cycle for caffeine enhancement of killing. Int J Radiat Biol 36:649–658
Jeggo PA, Kemp LM (1983) X-ray sensitive mutants of chinese hamster ovary cell line: Isolation and cross-sensitivity to other DNA-damaging agents. Mutat Res 112:313–327
Kemp LM, Sedgwick SG, Jeggo PA (1984) X-ray sensitive mutants of chinese hamster ovary cells defective in double-strand break rejoining. Mutat Res. 132:189–196
Kihlman BA (1974) Effects of caffeine on the genetic material. Mutat Res 26:53–71
Kihlman BA (1977) Caffeine and chromosomes. Elsevier, Amsterdam New York Oxford
Lücke-Huhle C (1982) Alpha-irradiation-induced G2 delay: a period of cell recovery. Radiat Res 89:298–308
Martin-Bertram H (1981) S1 sensitive sites in DNA afterγ-irradiation. Biochim Biophys Acta 652:261–265
Schroy CB, Todd P (1979) The effects of caffeine on the expression of potentially lethal and sublethal damage inγ-irradiated cultured mammalian cells. Radiat Res 78:312–316
Schroy CB, Furcinitti PS, Todd P, Kukulinsky NE (1980) Potentiation by caffeine of potentially lethal fast-neutron damage in cultured human cells. Radiat Res 84:353–358
Szostak JW, Orr-Weaver TL, Rothstein RJ (1983) The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell 33:25–35
Utsumi H, Elkind MM (1979) Potentially lethal damage versus sublethal damage: independent repair processes in actively growing chinese hamster cells. Radiat Res 77:346–360
Waldren CA, Rasko I (1978) Caffeine enhancement of X-ray killing in cultured human and rodent cells. Radiat Res 73:95–110
Weibezahn KF, Coquerelle T (1981) Radiation induced DNA double strand breaks are rejoined by ligation and recombination processes. Nucl Acids Res 9:3139–3150
Weibezahn KF, Lohrer H, Herrlich P (1985) Double-strand break repair and G2 block in chinese hamster ovary cells and their radiosensitive mutants. Mutat Res 145:177–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. G. Hotz on his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weibezahn, K.F., Coquerelle, T.M. Relationship between double strand break rejoining and G2 block formation in V79 cells. Radiat Environ Biophys 25, 13–21 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209680
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01209680