Abstract
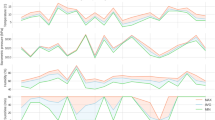
The relationships between the results of Beijing International Marathon Races and the corresponding weather conditions are analysed quantitatively. There are obvious interrelationships between the marathon results and weather factors such as air temperature, wet bulb temperature and human biometeorological indices. For example, the correlation coefficient between the average times of the top ten finishers and temperature isr=0.8910. The meteorological conditions are classified into three categories, suitable, moderate and unsuitable for running a marathon race, and the optimum meteorological index is given. Also the concept of a meteorological result, i.e. the part of the actual performances fluctuating with the changes in weather conditions, is presented. This plays an important role in some kinds of sports such as marathon racing. Finally, the results of physiological tests are given, which illustrate the physiological reactions of long- and middle-distance runners to the surrounding temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrand PO, Saltin B (1964) Plasma and red cell volume after prolonged severe exercise. J Appl Physiol 19:829
Baibakova EM, Iljičeva EM, Nevraev GA, Švareva JN (1964) Metodika izučenija i schema opisanija klimate kurortov. Moskva
Bunyatyan A, Erez V (1972) Effect of physical exertion on transcortin binding of corticosteroids in plasma. Probl Endocrinol 18:13
Hentschel G (1961) Die thermischen Empfindungen des Menschen unter natürlichen klimatischen Bedingungen. Abhdlg Meteorol Hydrol Dienstes DDR 8:40
Hentschel G (1986) A human biometeorology classification of climate for large and local scales. World Clinate Programme Applications No. 1, World Meteorological Organization, pp 120–138
Humphreys J, Holman R (1983) Focus on the Marathon. (Translation edition). China International Cultural Press, pp 88–89, 157
Korenskaya E (1967) Fatigue in physical exercise and the adrenal cortex function. Probl Endocrinol 13:65
Lehmann H (1936) Microclimatic investigations of cooling in a forest region. Veröff Geophys Inst Leipzig 2, Serie Bd VII (4)
Missenard A (1937) L'Homme et le climat. Paris
Pugh LG, Corbett JI, Johnson RH (1967) Rectal temperature, weight losses and sweating rates in marathon running. J Appl Physiol 23:347
Shanghai First Medical College (1981) Environmental hygiene
Siple PA, Passel CF (1945) Measurements of dry atmospheric cooling in subfreezing temperature. Proc Am Phil Soc 89:177–199
Trapasso LM, Cooper JD (1989) Record performances at the Marathon: Biometeorological factors. Int J Biometeorol 33:233–237
Thom EC (1957) Air Condit Heat Ventil, June
Tromp SM (1980) Biometeorology. Heyden, London, p 54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suping, Z., Guanglin, M., Yanwen, W. et al. Study of the relationships between weather conditions and the marathon race, and of meteorotropic effects on distance runners. Int J Biometeorol 36, 63–68 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01208915
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01208915