Summary
In isolated transverse hippocampal slices GABA (gamma-amino-butyric acid) was applied iontophoretically to various parts of the dendritic tree of CA1 pyramidal cells. Indices of GABA effects were reduced amplitude of orthodromically driven CA1 population spikes and inhibition of single CA1 units driven by orthodromic stimulation or by application of L-glutamate.
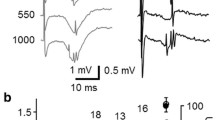
Weak iontophoretic currents of GABA (3–6 nA, backing current -3 nA) effectively reduced the amplitude of the population spike and arrested unit activity when applied in a position close to the soma. The effect was halved when GABA was applied 25–30 μm away at right angles to the main dendritic axis. In the direction of the main dendritic axis, GABA was effective as far as 250 and 150 μm from the soma in the apical and basal dendritic directions, respectively, corresponding to about 50% of the total dendritic length. The best effect was usually found at a depth corresponding to that of the recording electrode, probably because the main dendritic axis was parallel to the slice surface.
The sharp localization of GABA sensitivity when applied in the pyramidal layer supports earlier evidence that GABA mediates the basket cell inhibition on the soma of the pyramidal hippocampal cells. In the dendritic tree, GABA may also have an inhibitory function with an effectiveness matching that of the soma application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P, Blackstad TW, Lømo T (1966) Location and identification of excitatory synapses on hippocampal pyramidal cells. Exp Brain Res 1: 236–248
Andersen P, Bliss TVP, Skrede KK (1971) Lamellar organization of hippocampal excitatory pathways. Exp Brain Res 13: 222–238
Andersen P, Dingledine R, Gjerstad L, Langmoen IA, Mosfeldt Laursen A (1980a) Two different responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to application of gamma-amino butyric acid. J Physiol 305: 279–296
Andersen P, Eccles JS, Løyning Y (1964) Location of postsynaptic inhibitory synapses of hippocampal pyramids. J Neurophysiol 27: 592–607
Andersen P, Silfvenius H, Sundberg SH, Sveen O (1980b) A comparison of distal and proximal dendritic synapses on CA1 pyramids in hippocampal slicesin vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 307: 273–299
Biscoe TS, Straughan DW (1966) Micro-electrophoretic studies of neurones in the cat hippocampus. J Physiol (Lond) 183: 341–359
Blackstad TW, Brink K, Hem J, Jeune B (1970) Distribution of hippocampal mossy fibres in the rat. An experimental study with silver impregnation methods. J Comp Neurol 138: 433–450
Curtis DR, Felix D, McLennan H (1970) GABA and hippocampal inhibition. Br J Pharmacol 40: 881–883
Curtis DR, Johnston GAR (1974) Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol 69: 98–188
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A (1971) Uptake of (3H)noradrenaline and γ-(3H)ammobutyric acid in isolated tissues of rat: An autoradiographic and fluorescence microscopic study. In: Eränkö O (ed) Histochemistry of nervous transmission. Elsevier, Amsterdam (Progress in Brain Research, vol 34, pp 87–102)
Iversen LL, Bloom FE (1972) Studies on the uptake of (3H)GABA and (3H)glycine in slices and homogenates of rat brain and spinal cord by electron microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res 41: 131–143
Lorente de Nó R (1934) Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. II. Continuation of the study of the Ammonic system. J Psychol Neurol (Lpz) 46: 113–177
Okada Y, Shimada C (1976) Intrahippocampal distribution of GABA and GAD activity in the guinea pig: Microassay method for determination of GAD activity. In: Roberts E, Chase TN, Tower DB (eds) GABA in nervous system function. Raven Press, New York, pp 223–228
Pohle W, Matthies H (1970) Die Topohistochemie von Transmitter-Systemen in Cortex und Hippocampus des Kaninchens. Acta Biol Med Germ 25: 447–454
Ramon y Cajal S (1893) Über die feinere Struktur des Ammonshornes. Z Wiss Zool 56: 615–663
Ribak CE, Vaughn JE, Saito K (1978) Immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in neuronal somata following colchicine inhibition of axonal transport. Brain Res 140: 315–332
Skrede KK, Westgaard RH (1971) The transverse hippocampal slice: a well-defined cortical structure maintainedin vitro. Brain Res 35: 589–593
Stefanis C (1964) Hippocampal neurons: Their responsiveness to microelectrophoretically administered endogenous amines. Pharmacologist 6: 171
Storm-Mathisen J, Fonnum F (1971) Quantitative histochemistry of glutamate decarboxylase in the rat hippocampal region. J Neurochem 18: 1105–1111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, P., Bie, B. & Ganes, T. Distribution of GABA sensitive areas on hippocampal pyramidal cells. Exp Brain Res 45, 357–363 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01208595
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01208595