Abstract
The paper considers the problem of optimal truss topology design with respect to stress and local stability (i.e. buckling) constraints. In a context of topology optimization, the exact. management of buckling constraints is highly complex: member forces must satisfy functions which discontinuously depend on the design variables.
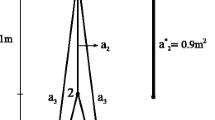
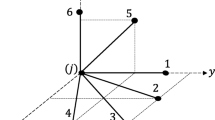
New terminologies and an exact problem formulation are provided. It turns out that the classical constraints (equilibrium, stress) together with topological local buckling constraints do not necessarily guarantee the existence of a solution structure. We discuss a simple but typical example demonstrating this effect inherently contained in the problem. It is proved that the inclusion of slenderness constraints guarantees a solution. These additional constraints are motivated by practice and preserve the topology nature of the problem. Finally, an alternative formulation is developed serving as a basis for computational approaches. The numerical treatment is the topic of Part II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archtziger, W. 1994: An SLP-approach for computing optimum truss topology designs covering full local buckling.Mat-Report 1994–55, Dept. of Math., Techn. Univ. of Denmark (DTU)
Achtziger, W. 1999: Local stability of trusses in the context of topology optimization, Part II: A numerical approach.Struct. Optim. (to appear)
Barta, J. 1957: On the minimum weight of certain redundant structures.Acta Techn. Aca. Sci. Hung. 18, 67–76
Bendsøe, M.P. 1995:Methods for optimization of structural topology, shape and material. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer
Birker, T. 1995:Methods for optimization of structural topology, shape and material. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer
Birker, T. 1996:New developments in structural optimization using optimility criteria. Series 18, No. 199, Düsseldorf: VDI
Cheng, G.D.; Guo, X. 1997: ε-relaxed approach in structural topology optimization.Struct. Optim. 13, 258–266
da Silva Smith, O. 1996: Topology optimization of trusses with element linking in buckling. In: da Silva Smith, O.Optimal truss topology design: generation of ground structures and local stability constraints, pp. 65–101. Ph.D. Thesis, Dept. of Math., Techn. Univ. of Denmark (DTU), Lyngby, Denmark
da Silva Smith, O. 1997: Topology optimization of trusses with local stability constraints and multiple loading conditions-a heuristic approach.Struct. Optim. 13, 155–166
Dorn, W.; Gomory, R.; Greenberg, M. 1964: Automatic design of optimal structures.J. de Mécanique 3, 25–52
Gerdes, D. 1995:Strukturoptimierung unter Anwendung der Optimalitätskriterien auf diskretisierte Tragwerke bei besonderer Berücksichtigung der Stabilität (in German). Series 18, No. 171, Düsseldorf: VDI
Haftka, R.T.; Gürdal, Z. 1992:Elements of structural optimization. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Haug, E.J.; Arora, J.S. 1979:Applied optimal design. New York: J. Wiley & Sons
Hörnlein, H.R.E.M. 1979:Ein Algorithmus zur Strukturoptimierung von Fachwerkskonstruktionen Diploma Thesis (in German), Ludwigs-Maximilian-Universität, Munich, Germany
Kirsch, U. 1989a: Optimal topologies of structures.Appl. Mech. Rev. 42, 223–239
Kirsch, U. 1989b: Optimal topologies of truss structures.Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 72, 15–28
Oberndorfer, J.; Achtziger, W.; Hörnlein, H.R.E.M. 1996: Two approaches for truss topology optimization: A comparison for practical use.Struct. Optim. 11, 137–144
Pedersen, P. 1970: On the minimum mass layout of trusses. Symp. on Structural Optimization, Istanbul 1969, Conf. Proc. No. 36, Advisory Group for Aerospace Research and Development,AGARD-CP-36-70
Pedersen, P. 1993: Topology optimization of three dimensional trusses. In: Bendsøe, M.P.; Mota Soares, C.A. (eds.)Topology optimization of structures, pp. 19–30. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Rozvany, G.I.N. 1996: Difficulties in truss topology optimization with stress, local buckling and system stability constraints,Struct. Optim. 11, 213–217
Rozvany, G.I.N. 1998: Topology optimization of multi-purpose structures.Math. Meth. Oper. Res. 47, 265–288
Rozvany T.I.N.; Bendsøe, M.P.; Kirsch, U. 1995: Layout optimization of structures.Appl. Mech. Rev. 48, 41–119
Topping, B.H.V. 1993: Topology design of discrete structures. In: Bendsøe, M.P.; Mota Soares, C.A. (eds.)Topology optimization of structures, pp. 517–534. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Zhou, M. 1996: Difficulties in truss topology optimization with stress and local buckling constraints.Struct. Optim. 11, 134–136
Zhou, M.; Rozvany, G.I.N. 1992/1993: DCOC: An optimality criteria method for large systems. Part I: Theory. Part II: Algorithm.Struct. Optim. 5, 12–25;6, 250–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achtziger, W. Local stability of trusses in the context of topology optimization Part I: Exact modelling. Structural Optimization 17, 235–246 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206999
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206999