Abstract
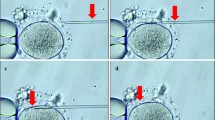
This work was undertaken in order to evaluate the effect of partial zona digestion on fertilization in vitro of mouse oocytes and assess zona surface changes induced by the procedure. Three hundred forty-six oocytes allocated for treatment were exposed to Ham's F-10 medium supplemented with 0.5% Pronase for either 3 min (188 oocytes) or 5 min (158 oocytes); 324 oocytes served as controls. Oocyte losses incurred as a result of the procedure were small (15 oocytes; 4.3%). Control and Pronase-treated oocytes were each divided into four subgroups and inseminated with 5 ×10 5,5 ×10 4,5 ×10 3,or 5 ×10 2 sperm cells/ml. Fertilization was assessed 8 hr following insemination by the appearance of two pronuclei and development to the two- to four-cell stage the following day. The morphology of the zona pellucida following Pronase treatment was assessed by phase-contrast and scanning electron (SEM) microscopies performed immediately after treatment. Fertilization rate of control oocytes was 80% at a sperm concentration of 500,000/ml and gradually declined to ~30% at 500 cells/ml. In contrast, treated oocytes inseminated with 500 sperm cells/ml demonstrated a normal rate of fertilization. At this low sperm concentration the longer Pronase treatment was significantly (P < 0.05) more efficient in enhancing fertilization (69 and 88% for 3 and 5 min of Pronase treatment, respectively). Polyspermic fertilization was not observed in any of the subgroups. Phase-contrast microscopic examination of oocytes at the time of Pronase treatment showed an initial swelling of the zona pellucida for 30–60 sec with a time-dependent increase in its transparency. SEM demonstrated that the fine meshlike structure of the outer surface of zona pellucida digested away, leaving a smoother surface. These morphologic changes were not associated with a diminution in sperm binding or penetration. This work demonstrates that partial zona digestion, which causes uniform dissolution of the zona pellucida and reduction of its thickness, is simple and safe. The procedure significantly increased fertilization efficiency at very low sperm concentrations and could, by itself or in conjunction with other methodologies, improve the reproductive capacity of men producing sperm with a reduced penetrating ability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yovich JL, Stanger JD: The limitation of in vitro fertilization from male with sever oligospermia and abnormal sperm morphology. Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1988;1:172
Acosta AA, Oehinger S, Morshedi M, Swanson RJ, Scott R, Irianni F: Assisted reproduction in the diagnosis and treatment of the male factor. Obstet Gynecol Surv 1989;44:1
Mann JR: Full term development of mouse eggs fertilized by a spermatozoon microinjected under the zona pellucida. Biol Reprod 1988;38:1077
Lassale B, Courtot AM, Testart J: In vitro fertilization of hamster and human oocytes by microinjection of human sperm. Gamete Res 1987;16:69
Laws-King A, Trounson A, Sathananthan AH, Kola I: Fertilization of human oocytes by microinjection of a single spermatozoon under the zona pellucida. Fertil Steril 1987;48:637
Ng SC, Bongso A, Chang SI, Sathananthan H, Ratnam S: Transfer of human sperm into the perivitelline space of human oocytes after zona-drilling or zona puncture. Fertil Steril 1989;52:73
Gordon JW, Talansky BE: Assisted fertilization by zona drilling; A mouse model for correction of oligospermia. J Exp Zool 1986;239:347
Gordon JW, Grunfeld L, Garrisi GJ, Talansky BE, Richards C, Laufer N: Fertilization of human oocytes by sperm of infertile males after zona-pellucida drilling. Fertil Steril 1988;50:68
Malter HE, Cohen J: Partial zona dissection of human oocytes a nontraumatic method using micromanipulation to assist zona pellucida penetration. Fertil Steril 1989;51:139
Kiessling AA, Loutradis D, McShane PM, Jackson KV: Fertilization in trypsin treated oocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1988;541:614
Nogues C, Ponsa M, Vidal F, Boada M, Egozcue J: Effect of aging on the zona pellucida surface of oocytes. J Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1988;5:225
Wassarman PM: The biology and chemistry of fertilization. Science 1987;221:553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mordel, N., Ohad, S., Zentner, B. et al. Enhancing in vitro fertilization of mouse oocytes by partial zona pellucida digestion. J Assist Reprod Genet 9, 128–132 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01203752
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01203752