Summary
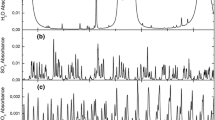
A method based on flash-combustion of the sample in a flow of temporarely oxygen-enriched helium, catalytic oxidation and reduction of the combustion gases within the same reactor, gas-chrom- matographic separation and thermal-conductivity detection of the end-products, has been developed in order to determine C-H-N-S simultaneously in organic and inorganic substances, with a 0.1–2 mg sample. To develop this method, optimization of analytical parameters was necessary because of the chemical and physical behaviour of oxides of sulphur in the analyser. Therefore flashcombustion in a tin container, use of a tungstic oxide oxidative layer close to a copper reductive layer, setting the copper temperature at 850° C and selective halogen adsorption are the main features. The temperature of 850° C for the copper gives a quantitative yield of SO2 in spite of the reaction between sulphur oxides and cupric oxide, and also gives quantitative reduction of the nitrogen oxides. The individual components of the combustion mixture are separated by means of a Porapak QS column and detected in the sequence Na, CO2, H2O and SO2, the signals being automatically integrated and printed. Detector response for SO2 is linear from someμg up to 10 mg.
Zusammenfassung
Zur gleichzeitigen Bestimmung von C, H, N und S in 0,1 bis 2 mg anorganischer oder organischer Substanz wurde ein Verfahren entwickelt, wobei die Substanz in zeitweilig sauerstoff-angereichertem Helium verbrannt, die Verbrennungsprodukte im selben Reaktionsrohr zunächst katalytisch oxydiert, dann reduziert werden. Anschließend werden die Endprodukte gas-chromatographisch getrennt und mittels Wärmeleitfähigkeitsmessung bestimmt. Zur Entwicklung dieses Verfahrens mußten die analytischen Parameter wegen des chemischen und physikalischen Verhaltens der Schwefeloxide optimiert werden. Daher werden Flammenverbrennung in einem Zinngefäß, Verwendung von Wolframoxid als oxydierende Schicht unmittelbar neben Kupfer als reduzierender Schicht, die auf 850° C gehalten wird, sowie selektive Adsorption der Halogene als wichtigste Schritte betrachtet. Die Temperatur von 850° C gewährleistet quantitative Ausbeute an SO2 im Gegensatz zur Reaktion zwischen Schwefeloxiden und Kupferoxid und führt auch zur quantitativen Reduktion der Stickstoffoxide. Die einzelnen Teile des Verbrennungsgemisches werden mit einer Säule aus Porapak QS getrennt und in der Reihenfolge N2, CO2, H2O und SO2 nachgewiesen, wobei die Signale automatisch integriert und gedruckt werden. Der Detektorausschlag für SO2 ist von einigen Mikrogramm bis 10 mg linear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Juránek and A. Ambrová, Coll. Czechoslov. Chemic. Commun.25, 2814 (1960).
D. R. Beuerman and C. E. Meloan, Analyt. Chemistry34, 319 (1962);34, 1671 (1962).
W. K. Stuckey and J. M. Walker, Analyt. Chemistry35, 2015 (1963).
S. Pennington and C. E. Meloan, Analyt. Chemistry39, 119 (1967).
D. R. Beuerman and C. E. Meloan, Analyt. Lett.1, 195 (1967).
P. W. H. Schlüssler, J. Chromatog. Sci.7, 763 (1969).
G. Dugan and V. A. Aluise, Analyt. Chemistry41, 495 (1969).
M. N. Chumachenko and N. N. Alekseeva, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Khim.964 (1969).
E. P. Chicherina, M. F. Prokopyeva, and V. K. Bukina, Dokl. Akad. Nauk Uzb. SSR28, 39 (1971).
R. F. Culmo, Microchem. J.17, 499 (1972).
E. Pella and B. Colombo, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1973, 697.
E. Pella, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1961, 472.
H. J. Francis, Jr., Paper presented at the 3rd FACSS Meeting, Philadelphia, Nov. 1976.
G. Giovannini, G. Poggio, and P. Séqui, Commun. Soil Sciences and Plant Analysis,6, 39 (1975).
M. E. Coller and R. K. Leininger, Analyt. Chemistry27, 949 (1955).
E. Kissa, Microchem. J.1, 203 (1957).
E. Kissa and M. Seepere-Yllo, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1967, 287.
M. Večeřa and D. Šnobl, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1958, 28.
R. Belcher, J. E. Fildes, and A. J. Nutten, Analyt. Chim. Acta13, 431 (1955).
Y. A. Gawargious and A. M. G. Macdonald, Analyt. Chim. Acta27, 119 (1962).
H. Pieters and W. J. Buis, Microchem. J.8, 383 (1964).
M. A. Carey, B. A. Roby, and C. V. Banks, Analyt. Chemistry36, 1166 (1964).
E. Pell, L. Macherndl, and H. Malissa, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1963, 615.
E. Debal and R. Lévy, Bull. soc. chim. France1968, 426.
A. Cedergren, Talanta20, 621 (1973).
G. Dugan and J. F. Carre, Hercules Research Center Report N. 27201 (1972).
T. Mitsui, K. Yoshikawa, and C. Furuki, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1962, 385.
W. J. Kirsten, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1964, 486.
E. Pella, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1969, 490.
G. Kainz and K. Zidek, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1967, 725.
R. M. Bethea and M. C. Meador, J. Chromatog. Sci.7, 655 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. H. Lieb for his 90th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pella, E., Colombo, B. Simultaneous C-H-N and S microdetermination by combustion and gas chromatography. Mikrochim Acta 69, 271–286 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201732
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201732