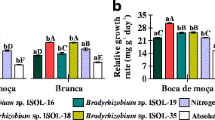
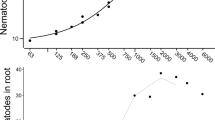
Abstract
Soybean nodulation was induced indigenously by three strains ofBradyrhizobium japonicum inoculated in each of the two previous seasons. The same strains were applied, as a peat-based inoculum in similar cell density as the indigenous ones, to a rhizobia-free soll from the same field. Inoculation was tested under soll application of 10 or 20 ppm Mn and/or 2 or 4 ppm Mo. Inoculation with the peat-based inoculum significantly increased nodule numbers and weight, dry weight, N content and mg N/g of the 50-day-old plants, number of pods and seeds per plant, seed yield, seed N content and percentage, and mg N/g of the empty pods. Increasing the application of Mn and Mo fed to further increases. There was a complex response of nodulation, vegetative growth and yield to the applications of Mn and Mo.
Résumé
La nodulation chez le soja a été induite de manière indigène par trois souches deBradyrhizobium japonicum, inoculées pendant chacune des deux saisons précédentes. Les mêmes souches ont été appliquées dans un inoculum à base de tourbe de densité similaire aux inocula indigènes, à un sol exempt de rhizobia dans le même champ. L'inoculation a été testée sous des applications au sol de 10 ou 20 ppm de Mn et/ou de 2 ou 4 ppm de Mo. L'inoculation avec l'inoculum à base de tourbe a augmenté de manière significative le nombre et le poids des nodules, leur contenu en azote et en mg d'N par g de plants âgés de 50 jours, le nombre de cosses et de grains par plant, le rendement en graines, leur contenu en azote ainsi que le pourcentage et le rapport mg d'N par g de cosses vides. L'augmentation de l'application de Mn et du Mo a conduit à un nouvel accroissment. La réponse de la nodulation, de la croissance végétative et du rendement aux applications de Mn et Mo s'est révèlée complexe.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hafez, A.G. &Yanni, Y.G. (1988) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation in soybean and possible improvement under saline stress.Journal of Agricultural Research (Tanta University) 14, 628–638.
Allen, O.M. 1959Experiments in Soil Microbiology, Minnesota, MN: Burgess.
Alley, M.M. 1975. Manganese deficiency in Virginia soils and correction of manganese deficiency in soybeans (Glycine max L.).Dissertation Abstracts International (Virginia Polytechnical Institute and State University, Blacksburg, USA)36, 523.
Balasundaram, V.R. &Rao, N.S.S. 1974 Researches on the establishment of soybean in India through indigenous inoculants.Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy 40, 636–640.
Black, A., Evans, D.D., Ensminger, F.E., White, J.I., Clark, F.E. &Dinaver, R.C. 1965Methods of Soil Analysis—II. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, No. 9 in the Series of Agronomy. Madison, WI: American Society for Agronomy.
Boonkerd, N. Weber, D.F. &Bezdicek, D.F.: 1978 Influence ofRhizobium japonicum strains and inoculation methods on soybeans grown in rhizobia-populated soil.Agronomy Journal 70, 547–549.
Karaguishieva, D. &Alibekova, SH. 1978 Effect of trace elements on symbiotic fixation of nitrogen by soybeans.Vestnik Sel' skokhozyaistvennui Nauki (Alma-Ata, Kazakh SSR) 2, 28–31.
Kroetz, M.C., Schmidt, W.R., Beverlein, J.E. &Ryder, G.L. 1977 Prevent manganese deficiency in soybeans.Better Crops with Plant Food, Vol. 61, pp. 26–28. Wooster, OH: Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center.
Lee, S.K., Ryu, J.C. &Tyu, I.S. 1977 Effects of inoculation withRhizobium japonicum and conditions on symbiotic acetylene reducing activities and yield of soybean growth in newly reclaimed upland soil. Research Reports of the Office of Rural Development (Soil Science, Fertilizer, Plant Protection and Micrology), Institute of Agricultural Science, Suweon, South Korea, Vol. 19, pp. 133–138.
Ohki, K., Wilson, D.O., Boswell, F.C., Parker, M.B. &Shuman, L.M. 1977 Mn concentration in soybean leaf related to bean yields.Agronomy Journal 69, 597–600.
Parker, M.B. &Harris, H.B. 1977 Yield and leaf nitrogen of nodulating and nonnodulating soybeans as affected by nitrogen and molybdenum.Agronomy Journal 69, 551–554.
Rubes, L. 1974 The effect of nitrogen and molybdenum on the nutrition of soya (Glycine max (L.) Merrill).Rostlinna Vyroba 20, 1123–1132.
Schmidt, E.L. 1979 Legume symbiosis A. Ecology of the legume root nodule bacteria. InInteractions Between Non-pathogenic Soil Microorganisms and Plants, ed Dommergues, Y. R. & Krupa, S. V., pp. 269–303. Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific.
Shivashankar, K. 1977 Effect of straw and molybdenum on the growth and yield of soybeans.Mysore Journal of Agricultural Science 11, 33–35.
Somasegaran, P & Hoben, H.J. 1985Methods in Legume-Rhizobium Technology. NIFTAL Project and MIRCEN, Department of Agronomy and Soil Science, University of Hawaii. United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
Yanni, Y.G., Abdel-Hafez, A.G. &Elmofty, M. Kh. 1982 Effect of inoculation, N-fertilization and foliar application of trace elements on nodulation, N2-fixation and seed yield of soybean plant, var. Clark.Journal of Agricultural Research, (Tanta University, Egypt)8, 148–157.
Yanni, Y.G., El-Beheiry, M.M. &Hoda, F.M. 1987 Nodulation, vegetative growth, infestation with the spider miteTetranychus cucurbitacearum (Sayed) and seed yield of N-fertilized soybean plants in the Nile Delta.MIRCEN Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 3, 297–306.
Yanni, Y.G. &Mohamed, Y.A.H. 1985 Enhancement of nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen-fixation byRhizobium japonicum in soybean plant as contribution of the asymbiotic nitrogen-fixerAzotobacter chroococcum.Beitrage zür Biologie der Pflanzen 60, 207–221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanni, Y.G. Response of symbiotic interrelationship between soybean and the indigenous or inoculated microsymbiont,Bradyrhizobium japonicum, to soil application of manganese and molybdenum. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 6, 289–294 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201299
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01201299