Abstract
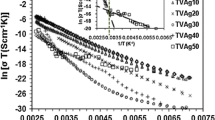
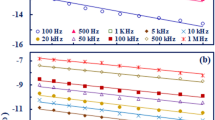
The a.c. conductivity for the TeO2-P2O5 glassy system was measured in the temperature range 300–573 K and in the frequency range 100 Hz to 10 kHz. The a.c. conductivity Σ(Ω) increased with frequency according to the relation Σ(Ω)αΩs. The frequency exponent s was found to decrease with increasing temperature. The composition dependence of the conductivity was also investigated. The density of states was also calculated using the Elliott model. The a.c. conductivity increased over the studied temperature range. The obtained experimental data have been analysed with reference to various theoretical models. The analysis shows that the correlated barrier hopping (CBH) model is the most appropriate mechanism for conduction in the TeO2-P2O5 glass system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Surinach M. D. Baro M. T. Clavagueramora andN. Clavaguera Fluid Phase Equilibria 20 (1985) 341.
N. V. Ovcharenko, “The physicochemical properties of Phosphate-Tellurite glasses”, Discussion Themes for All-Union Conference Phosphates-84 in Russian. Part 1, Alma-Ata (1984) pp. 189.
A. Abdel-Kader A. A. Higazy andM. M. Elkholy J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elec. 2 (1991) 157.
A. Abdel-Kader A. A. Higazy andM. M. Elkholy J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elec. 2 (1991) 204.
N. U. Ovcharenko, andV. U. Volkova, Translated fromFizika i Khimiya Stekla 15 (2) (1989) 190.
A. Mansingh R. P. Tandom andJ. K. Valid Phys. Rev. B21 (1980) 4829.
A. Mansingh J. K. Valid andR. P. Tandom J. Appl. Phys. C8 (1975) 1023.
L. Murawski Phil. Mag. B50 (1984) L69.
A. Ghosh andB. K. Chaundhuri J. Mater. Sci. 22 (1987) 2376.
U. Khzhukharov M. Marinov andG. Grigorova J. Non-Cryst. Solids 28 (1978) 429.
A. Abdel-Kader A. A. Higazy M. M. Elkholy andR. M. El-Bahnasawy J. Mater. Sci. 26 (1991) 4298.
G. E. Pike Phys. Rev. B6 (1972) 1572.
S. R. Elliott Phil. Mag. 36 (1977) 1291.
S. R. Elliott Adv. Phys. 36 (1987) 135.
M. Pollak andT. H. Geballe Phys. Rev. B122 (1961) 1742.
I. Austin andN. F. Mott J. Adv. Phys. 18 (1969) 41.
K. Shimakawa Phil. Mag. B46 (1982) 123.
A. R. Long Adv. Phys. 31 (1982) 553.
M. Polak Phys. Rev. 138 (1965) 1822.
R. M. Hill andA. K. Jonscher J. Non-Cryst. Solids 32 (1979) 53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elkholy, M.M. A.c. conductivity for amorphous TeO2-P2O5 glass system. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 5, 157–162 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01198947
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01198947