Summary
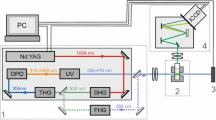
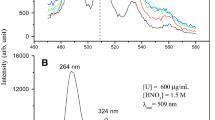
A versatile, direct method for the determination of trace amounts of uranium in solution has been developed utilizing pulsed-laser fluorometry and a pyrophosphate fluorescence enhancing reagent. Measurements with a 2–3% relative standard deviation and accurate to better than 1% have been obtained in the 0.01 to 4μg U/g range. The detection limit is 0.005 ng uranium. Time required per determination is 6 min. A special feature of the method is the use of a standard addition technique to eliminate sample matrix effects. The effects of temperature, acidity, reagent impurity and anionic impurities have been studied.
Zusammenfassung
Eine Direktmethode zur Bestimmung von Uranspuren in Lösungen mit Hilfe der Laser-Fluorometrie und eines fluoreszenz-anregenden Pyrophosphates wurde entwickelt. Die Messungen erfolgen mit einer rel. Standardabweichung von 2–3% und einer Genauigkeit besser als 1% bei Mengen von 0,01–4μg U/g. Die Nachweisgrenze beträgt 0,005 ng U. Eine Bestimmung dauert 6 min. Um Matrix-Effekte zu vermeiden, verwendet man die Standard-Zusatz-Technik. Der Einfluß der Temperatur, der Acidität und etwaiger Verunreinigungen wurde untersucht.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. L. Booman and J. E. Rein, in I. M. Kolthoff and P. J. Elving (eds.), Treatise on Analytical Chemistry, Part II, Analytical Chemistry of the Elements, New York: Wiley. 1959. Vol. 9, p. 102.
Ref. 1, p. 111.
Ref. 1, p. 102.
G. R. Price, R. J. Ferretti, and S. Schwartz, Analyt. Chemistry25, 322 (1953).
F. A. Centanni, A. M. Ross, and M. A. DeSesa, Analyt. Chemistry28, 1651 (1956).
J. E. Strain, U. S. Dept. of Energy Rep., ORNL/TM-6431 (July 1978).
Savannah River Plant, Analytical Procedure (unpublished), 2 SP 40. 3 a (January 1978).
R. J. McElhaney, J. D. Caylor, S. H. Cole, T. L. Futrell, and V. M. Giles, U. S. Dept. of Energy Rep., Y-2111 (March 1978).
C. J. Rodden (ed.), U. S. At. Energy Comm. Rep., TID-7029 (2nd Ed.), 1972, p. 232.
J. C. Robbins, Field Technique for the Measurement of Uranium in Natural Waters, CIM Bulletin 793 (May 1978) 61–67.
W. Campen and K. Bachmann, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1979 II, 159.
L. E. White, U. S. Dept. of Energy Rep., Y-2205 (May 1980).
A. C. Zook and L. H. Collins, American Nuclear Society Topical Meeting, Nov. 26–30, 1979, published in NBS Special Publication 582, June 1980, p. 147.
Scintrex Instruction Manual, UA-3 Uranium Analyzer, Scintrex, Concord, Ontario, Canada, August 1978.
J. C. Robbins and J. D. Kinrade, Canadian Patent 10564726 (1979).
Ref. 1, p. 62.
Ref. 1, p. 61.
R. G. Milkey, Analyt. Chemistry26, 1800 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zook, A.C., Collins, L.H. & Pietri, C.E. Determination of nanogram quantities of uranium by pulsed-laser fluorometry. Mikrochim Acta 76, 457–468 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01196964
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01196964