Summary
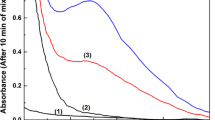
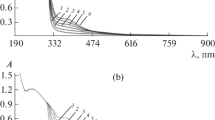
A procedure is described for the determination of cobalt at the ppb level in samples of water from the Detroit River, Lakes Erie and St. Clair and wells in the Essex County, Ontario region using 2-pyridyl-2-thienyl-β-ketoxime as the spectrophotometric reagent after preconcentration with 2-nitroso-1-naphthol. The effects due to diverse ions, humic acid, acid backwashing, pretreatment of the samples and acid decomposition in the presence of organic matter are discussed. The outlined procedure indicates that cobalt may be determined in water samples over the range 0.2 to 1.0 ppb.
Zusammenfassung
Ein Verfahren zur Bestimmung von ppb-Mengen Kobalt in Wasserproben aus dem Detroit-River, dem Erie-See, dem St. Clair-See sowie in Quellwässern aus dem Gebiet von Essex, Ontario, wurde beschrieben, wobei nach Anreicherung mit 2-Nitroso-1-naphthol als spektrometrisches Reagens 2-Pyridyl-2-thienyl-β-ketoxim verwendet wurde. Die Wirkung verschiedener Ionen, der Huminsäure, der sauren Rückextraktion, der Vorbehandlung der Proben und der sauren Veraschung in Gegenwart organischer Substanzen wurde besprochen. Das angegebene Verfahren ermöglicht die Bestimmung von 0,2–1,0 ppb Kobalt in Wasser.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. R. Notenboom, W. J. Holland, and R. G. Billinghurst, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien]1973, 467.
P. Beaupré and W. Holland, Mikrochim. Acta [Wien], to be published.
E. S. Underwood, Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 2nd ed. New York: Academic Press. 1962. Chapter 6.
D. C. Burrell, At. Absorption Newsletter4, 309 (1965).
R. F. Gould, Advances in Chemistry Series, Trace Inorganics in Water, American Chemical Society Publications, U. S. A., Vol. 73, p. 230.
M. Schnitzer, et al., Can. J. Chem.49, 1053 (1971).
M. Schnitzer, Soil Science109, 333 (1970).
Windsor Utilities Commission, Water Division, Windsor, Ontario, Canada, private communication, 1974.
Report to the Joint Commission on the Pollution of Lakes Erie and Ontario and the International Section of the St. Lawrence River, Volume 2, Lake Erie, 1968.
E. B. Sandell, Colorimetric Determination of Traces of Metals. 3rd ed., New York: Interscience. 1952. p. 434.
Tran-Van Danh, Analyt. Chim. Acta36, 204 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaupré, P., Holland, W.J. Pyridine ketoximes as analytical reagents. XV. Mikrochim Acta 70, 95–104 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01196472
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01196472