Summary
-
1.
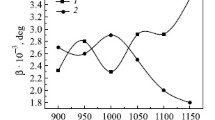
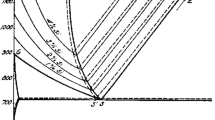
Nonuniform saturation of austenite by carbon from graphite during sintering is the main cause of the anomalous structure of iron-graphite cermet alloys. The relatively high contents of ash and other impurities in the available graphite have an adverse effect on the structure of sintered alloys and impair their mechanical properties.
-
2.
The low rate of diffusion during sintering is another cause of the anomalous structure of the iron-graphite alloys. It is desirable to search for an apply such activating admixtures that would speed up the diffusion of carbon and smooth out the microstructure.
-
3.
The circumstance that the nonuniform concentration of carbon iron-graphite cermet products causes the pearlitic conversion to proceed by a mechanism differing from that in molten steels is also responsible for the anomalous structure.
-
4.
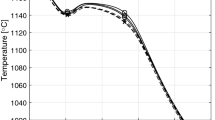
Observations on iron-copper-graphite alloys during heating from room temperature up to the melting point have shown that a liquid copper phase does not form in mixtures with a copper content within the solubility range in austenite. Consequently, sintering of these mixtures takes place in the solid phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. I. Likhtman and I. N. Smirnova, Physicochemical Regularities in the Formation of Iron-Graphite Cermets [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1954).
A. K. Natanzon, Handbook: Metallography and Thermal Treatment [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1956), p. 982.
P. I. Bebnev, Collection: Powder Metallurgy [in Russian], Yaroslavl' (1956), p. 90.
M. Yu. Bal'shin, Collection: Principles of Metallurgy, Vol. 1, Part II [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1961), p. 373.
V. N. Goncharova, Collection: Powder Metallurgy [in Russian], Yaroslavl' (1956), p. 61.
G. I. Aksenov and V. K. Sorokin, Collection: Powder Metallurgy [in Russian], Yaroslavl' (1956), p. 78.
N. Z. Pozdnyak and E. K. Ponomarenko, Metallovedenie i termicheskaya obrabotka, No. 12 (1960).
N. Z. Pozdnyak and E. K. Ponomarenko, Poroshkovaya metallurgiya, No. 1, 56 (1961).
I. E. Kantorovich, Thermal Treatment of Steel and Crude Iron [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1950), p. 111.
V. K. Sorokin, Izvestiya vysshikh uchebnykh zavedenii, Chernaya metallurgiya, No. 8 (1959), p. 101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pozdnyak, N.Z. Study of structure formation during sintering of iron-graphite alloys. Powder Metall Met Ceram 2, 403–407 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194679
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01194679