Abstract
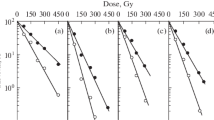
Diploid yeast,Saccharomyces cerevisiae, was exposed to single microsecond pulses of 12-MeV-electrons at dose rates up to 3×1010 rad s−1 under oxygenated and hypoxic conditions. No difference in surviving fractions was found with total doses up to about 150 krad as compared to exposures at conventional dose rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry, R. J., Hall, E. J., Forster, D. W., Storr, T. H., Goodman, M. H.: Survival of mammalian cells exposed to X-rays at ultra-high dose rates. Brit. J. Radiol.42, 102 (1969).
Boag, J. W.: Oxygen diffusion and oxygen depletion problems in radiobiology. In: Ebert, M., Howard, A., Eds., Current topics in radiation research, Vol. V, p. 141. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publ. Co. 1969.
Dewey, D. L., Boag, J. W.: Inaktivierung von Bakterien mittels einzelner Elektronenimpulse. Z. Naturforsch.15b, 372 (1960).
Epp, E. B., Weiss, H., Santomasso, A.: The oxygen effect in bacterial cells irradiated with high intensity pulsed electrons. Radiat. Res.34, 320 (1968).
Hersch, P.: Galvanic determination of traces of oxygen. Nature (Lond.)169, 792 (1960).
Kiefer, J., Ebert, M.: Some theoretical considerations concerning ultra-high dose-rate survival experiments. 2nd Symp. Microdosimetry, Stresa 1969. Proceedings in the press.
Nias, A. H. W., Swallow, A. J., Keene, J. P., Hodgson, B. W.: Effects of pulses of radiation on the survival of mammalian cells. Brit. J. Radiol.42, 231 (1969).
Oliver, R.: The effect of irradiation at extremely high dose-rates. Brit. J. Radiol.42, 231 (1969).
Phillips, T. L., Worsnop, B. R.: Ultra-high dose-rate effects in radiosensitive bacteria. Int. J. Radiat. Biol.14, 573 (1969).
Sanner, T., Pihl, A.: Significance and mechanisms of the indirect effect in bacterial cells. The relative protective effect of added compounds inE. coli B, irradiated in liquid and frozen suspension. Radiat. Res.37, 216 (1969).
Thomas, J. K., Hart, E. J.: The radiolysis of aqueous solutions at high intensities. Radiat. Res.17, 408 (1962).
Town, C. D.: Effects of high dose rates on survival of mammalian cells. Nature (Lond.)215, 847 (1967).
Wickerham, L. J.: Taxonomy of yeasts. Tech. Bull. US Deptmt. Agrio. 1029 C (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave from Strahlenzentrum der Universität Gießen. Present address: Institut für Biophysik, Strahlenzentrum, 63 Gießen, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiefer, J., Ebert, M. The effect of ultra-high dose-rateβ-ray irradiation in aerobic and hypoxic conditions on the survival of diploid yeast. Biophysik 6, 271–274 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189087
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01189087